Responsible for cooling the engine. Computer cooling systems: their types, species and varieties
The cooling system is a set of devices that carry out forced adjustable removal and heat from the engine parts in environment.
The cooling system is designed to maintain the optimal temperature modeproviding maximum power, high efficiency and long-term engine life.
When combustion of the working mixture, the temperature in the engine cylinders rises to 2500 ° C and on average when the engine is running 800 ... 900 ° C. Therefore, the parts of the engine are very hot, and if they are not cooling, the engine power will be reduced, its economy, increase the wear of parts and can occur versions of the engine.
With excessive cooling, the engine also loses power, its economy deteriorates and wear out.
For forced and adjustable removal of heat in the engines of cars, two types of cooling systems () are used. The cooling system type is determined by the coolant (working substance) used to cool the engine.
Picture 1 - Types of cooling systems
Application in engines of various cooling systems depends on the type and purpose of the engine, its power and class of the car.
Liquid cooling system
IN liquid cooling system Special cooling fluids are used - antifreeze different markshaving a thickening temperature - 40 ° C and below. Antifreeze contain anti-corrosion and anti-speaking additives, excluding scale formation. They are very poisonous and demand cautious. Compared to water, antifreeze has a smaller heat capacity and therefore remove heat from the walls of the engine cylinders is less intensively.
So, when cooling with antifreeze, the temperature of the walls of cylinders by 15 ... 20 ° C is higher than when cooling with water. It accelerates the engine heating and reduces the wear of the cylinders, but in the summer it can lead to engine overheating.
The optimal temperature mode of the engine with a liquid cooling system is considered to be such at which the temperature of the coolant in the engine is 80 ... 100 ° C on all modes of engine operation.
This is possible, provided that the coolant is carried out into the environment 25 ... 35% of the heat released during the combustion of the fuel in the engine cylinders. At the same time B. gasoline engines The value of the heat removed is greater than in diesels.
Engine cooling system consists From the cooling shirt head and block of cylinders, radiator, pump, thermostat, fan, expansion tank, connecting pipelines and drain crants. In addition, the cooling system includes a car body salon.
System work

Figure 3. - Engine cooling system
1, 2, 3, 5, 15, 18 - hoses; 4 - nozzle; 6 - tank; 7, 9 - plugs; 8 - cooling shirt; 10 - radiator; 11 - casing; 12 - fan; 13, 14 - pulleys; 16 - belt; 17 - pump; 19 - Thermostat
For impact engine The main valve of the thermostat 19 () is closed, and the coolant does not pass through the radiator 10. In this case, the liquid is injected with a pump 17 in the cooling shirt 8 and the engine cylinder head. From the head of the cylinder block through the hose 3, the liquid enters the additional thermostat valve and gets again to the pump. Due to the circulation of this part of the fluid, the engine is quickly heated. At the same time, a smaller part of the fluid comes from the head of the cylinder block into the heater (shirt) of the engine inlet pipeline, and with an open crane - to the heater of the car body salon.
For heated engine An additional thermostat valve is closed, and the main valve is open. In this case, most of the liquid from the cylinder head falls into the radiator, cooled in it and through the open main valve of the thermostat enters the pump. A smaller part of the fluid, as well as an impenetrable engine, circulates through the engine inlet pipe and the heater of the body's cabin. In some temperature range, the main and additional thermostat valves are open at the same time, and the coolant circulates in this case by two directions ( circles circulation).
The number of circulating fluid in each circle depends on the degree of opening the thermostat valves, which automatically maintains the optimal temperature mode of the engine. The expansion tank 6 filled with coolant is reported to the atmosphere through the rubber valve installed in the 7 tank stopper. The tank is connected by a hose with a bulk neck of the radiator, which has a plug 9 with valves. The tank compensates for changes in the coolant volume, and the system maintains a constant volume of circulating fluid.
To drain the coolant from the cooling system, there are two drain holes with threaded plugs, one of which is located in the low tank of the radiator, and the other in the engine cylinder block. The fluid temperature in the system is controlled by a pointer, the sensor of which is installed in the engine of the engine cylinder block.
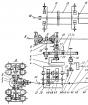
The liquid pump provides forced fluid circulation in the engine cooling system. On the engines of cars apply paddle pumps of centrifugal type ().

Figure 4. - Liquid pump (a) and fan (b) engine
1 - impeller; 2 - body; 3 - window; 4 - lid; 5 - Bearing; 6 - shaft; 7 - hub; 8 - screw; 9 - sealing device; 10 - nozzle; 11, 13,14 - pulleys; 12 - belt; 15 - fan; 16 - lining; 17 - Bolt.
The pump shaft 6 is mounted in an aluminum alloy with a lid 4 in a double-row unintellular bearing 5. The bearing is placed and fixed in the cover of the locking screw 8. At one end of the shaft, the cast iron impeller 1, and on the other end - the hub 7 and pullee 11 fan 15 is press. When the pump shaft rotates, the coolant through the nozzle 10 goes to the center of the impeller, is captured by its blades, discarded to the pump body 2 under the action of centrifugal force and through the window 3 in the housing is sent to the engine cylinder cooling shirt. The sealing device 9, consisting of a self-sufficient cuff and a graphota componence ring, mounted on the pump shaft, eliminates the injection of the fluid into the shaft bearing.
Drive and fan drive is carried out wedge belt 12 from pulley 13, which is installed at the front end crankshaft Engine. Using this belt also rotates 14 generator pulley. Normal pump and fan operation provides proper tension belt.
The belt tension is adjusted by moving the generator away from the engine (shown on the arrow). The pump is housing 2, cast from the aluminum alloy, is attached to the flange of the cylinder block in the front of the engine.
Liquid pump drive from a toothed belt
Consider the pump device whose drive is carried out with a gear strap ().

Figure 5. - Liquid engine pump
1 - pulley; 2 - screw; 3 - Bearing; 4 - shaft; 5 - case; 6 - sealing device; 7 - hole; 8 - impeller
The pump shaft 4 is installed in the housing 5 of the aluminum alloy in an unintended double-row ball bearing 3. The bearing will stop in the housing of the screw 2 and is compacted by a special device 6, which includes a graphota component ring and cuff. At the front end of the shaft, the gear pulley 1 from the sintered material is pressed, and at the rear end - the impeller 8. Two were made in the impeller through holes 7, which connects the coolant cavities among themselves, located on both sides of the impeller. Thanks to these holes, the cooling fluid pressure on the impeller on both sides is aligned, which eliminates the axial loads on the pump shaft during its operation.
The pump shaft is driven by rotation through the pulley 1 with a gearbelt of the camshaft drive from the crankshaft. When the shaft rotates, the fluid enters the center of the impeller and under the action of centrifugal force is sent to the engine cooling shirt. The pump is attached to the housing to the engine cylinder block through the sealing gasket.
It helps to accelerate the engine warming up and adjusts under certain limits the amount of coolant passing through the radiator. The thermostat is an automatic valve. In engine engines, unsubscribed two-flaped thermostats with solid filler are used.

Figure 6.
1, 6, 11 - nozzles; 2, 8 - valves; 3, 7 - springs; 4 - cylinder; 5 - diaphragm; 9 - rod; 10 - filler
) It has two inlet nozzles 1 and 11, the outlet nozzle 6, two valves (main 8, optional 2) and a sensitive element. The thermostat is mounted before entering the coolant pump and is connected to it through the nozzle 6. Through the nozzle 1, the thermostat is connected to the head of the engine cylinder block, and through the nozzle 11 with the lower tank of the radiator.The sensitive element of the thermostat consists of a cylinder 4, rubber diaphragm of 5 and stock 9. Inside the cylinder between its wall and rubber diaphragm there is a solid filler 10 (fine-crystalline wax) with a high volume extension coefficient.
The main valve 8 of the thermostat with spring 7 begins to open at a coolant temperature of more than 80 ° C. At a temperature of less than 80 ° C, the main valve closes the yield of the fluid from the radiator, and it comes from the engine to the pump, passing through the opening additional valve 2 of the thermostat with spring 3.
As an increase in the temperature of the coolant more than 80 ° C in the sensitive element, a solid filler melts, and its volume increases. As a result, the rod 9 comes out of the cylinder 4, and the balloon moves up. An additional valve 2 begins to close and at a temperature of more than 94 ° C overlaps the coolant pass from the engine to the pump. The main valve 8 in this case opens completely, and the coolant circulates through the radiator.
Expansion tank
Expansion tank It serves to compensate for changes in the volume of coolant during fluctuations of its temperature and to control the amount of fluid in the cooling system. It also contains some coolant reserve on its natural loss and possible losses.
Translucent plastic tanks with a filling neck closed with plastic plug are used on cars. Through the neck, the system is filled with the coolant, and through the valves placed in the plug, the internal cavity of the tank and the cooling system with the atmosphere. In the plug of expansion tanks, there is often one rubber valve, triggered at a pressure close to the atmospheric. When draining the coolant from the system, the plug is removed from the expansion tank. The expansion tank is placed in open space Engine separation, where attached to the car body.
Car radiators
Radiator Provides the heat of the cooling fluid heat into the environment. On the passenger cars Tubular plate radiators are used.

Figure 7. - Inspection radiator (a) and casing (b) engine fan
1 - cork; 2 - neck; 3, 4 - tanks; 5 - core; 6 - nozzle; 7, 8 - valves; 9 - casing; 10 - Seal
On some engines () an electric fan is applied. It consists of an electric motor 6 and a fan 5. The fan is four-bladed, attached to the motor shaft. The blades on the hub of the fan are located unevenly and at an angle to the plane of its rotation. This increases the flow of the fan and reduces the noise of its operation. For more efficient operation, the electric fan is placed in a casing 7, which is attached to the radiator. Electristant attached to the casing on three rubber bushings. The electric fan is turned on and off automatically sensor 3, depending on the coolant temperature.
Most of the car serious malfunctions is associated with engine overheating. The temperature of gases in the cylinder reaches 2000 grams. When combustion of fuel in the cylinder, a large amount of heat is formed, which must be left and thereby prevent overheating of engine parts.
Principles for constructing cooling systems
Reducing the efficiency of the cooling system leads to an increase in the temperature of the pistons, a decrease in the gaps between the piston and the cylinder. Thermal gaps are reduced to zero. The piston hurts behind the walls of the cylinder, the jackets are formed, superheated oil loses lubricating properties and the oil film is broken. Such a mode of operation can lead to engine jamming. The overheating is accompanied by an uneven expansion of the block head, fastening bolts, engine block, etc. In the future, the engine destruction is inevitable: cracks in the head head, the deformation of the head of the head and the block itself, the cracks of the valves were formed, and the like. - even listed even listed, all this, so it's better not to bring it!
The engine cooling system and oil is designed to prevent such developments of events, but in order for the system to cope with the tasks assigned to the tasks, it is necessary to use high-quality cooling fluid (coolant). Low-changing coarse call antifreeze - From the English word "antifreeze". Previously, the coolant was prepared on the basis of aqueous solutions of monohydric alcohols, glycols, glycerol and inorganic salts. Currently, preference is given to monoethylene glycol - a colorless syrup-shaped liquid with a density of approximately 1.112 g \\ cm2 and a boiling point of 198 grams. The task of the coolant is not only cooling the engine, but not boil throughout the temperature of the engine and its components in the entire range of temperature, have a high heat capacity and thermal conductivity, not to foam, do not adversely affect the nozzles and seals, have lubricating and anti-corrosion properties.
In the 70s, antifreeze was produced based on aqueous solution of monoethylene glycol with a temperature of the beginning of crystallization - 40 grams. It did not require dilution with water when the cooling system is added. This drug was named Tosol - by the name of the laboratory "Technology of Organic Synthesis". Because The name is not patented, then to the tool is called the product ready for use, and the antifreeze is a concentrated solution (although Tosol is also antifreeze).
Ready antifreeze are painted for safety and choose catchy colors: blue, green, red. During operation, antifreeze loses beneficial features - reduced anti-corrosion properties, increasing the tendency to foaming. The service life of domestic coolant from 2 to 5 years, imported 5-7 years.
The figure below shows the car cooling system circuit. There is nothing special or complex in the cooling system and nevertheless ...
Fig. 1 - Engine, 2 - radiator, 3 - heater, 4 - thermostat, 5 - expansion tank, 6 - Radiator tube, 7 - upper nozzle, 8 - bottom nozzle, 9 - radiator fan, 10 - Fan power sensor, 11 - Sensor Temperatures, 12 - pump.
When the engine starts, the pump (water pump) begins to rotate. The pump drive can have its own pulleys, driven by the auxiliary equipment belt or drive the timing belt. In the cooling system there is an impeller, which is rotating, leads to a coolant coolant. For quick warm warming The engine system is "shortened", i.e. The thermostat is closed and does not let the fluid in the cooling radiator. As the coolant temperature rises, the thermostat opens, translating the system to another state when the coolant passes along the long path - through the cooling system radiator (a short path is blocked by a thermostat). Thermostats have different discovery characteristics. Usually, the opening temperature is applied on the edge. Probably should not explain the radiator device. At the bottom of the radiator, the fan power sensor is installed. If the coolant temperature reaches a certain value - the sensor will be closed, and because Electrically, it is connected to the rupture of the power supply chain of the electric fan, then when closed - the cooling system fan must turn on. As the coolant cooling is cooled - the fan turns off, and the thermostat overlaps the long path to the short one. Everything is simple, but not very ...
Such a scheme is the basis, but life does not stand still and various manufacturers will improve the cooling systems. On some cars you will not find the cooling system fan sensor, because The fan turns on from the ECU engine depending on the readings of the coolant temperature sensor. It is worth paying attention to the situation at which when the ignition is inserted, the cooling system fan immediately turns on. Or a temperature sensor is faulty, or its chain is damaged, or the ECU itself is defective - it does not see the engine temperature and just in case includes a fan immediately.
On some a \\ m on the way to the heater, special electroclapa are installed, allowing or overlapping coolant (BMW, Mercedes). Such valves sometimes "help" the cooling system fail.
Troubleshooting in the cooling system
Specialists from AB-Engineering under the leadership of Chruleva A.E. Developed a table of causes and consequences of engine overheating. Self engine overheating - This is the temperature mode of its work characterized by boiling the coolant. But not only overheating is a malfunction. Engine operation at a constantly reduced temperature, we also consider a malfunction, because At the same time, the engine works with the temperature-mounted temperature mode. Failure of the thermostat, electric fan or viscous coupling, thermal switches, etc., will lead to emergency work of the cooling system. If the driver detects signs of violation of the thermal mode of operation of the engine and does not allow irreversible processes, then the repair of the cooling system will not be expensive and long. Therefore, we strongly recommend paying your (and your customers) attention to the temperature modes of the engine.
BUT. First of all, it is necessary to check the circuit connections of the cooling system nozzles if the car is not new or repaired after repair on another service.
Someone this offer will seem funny, but life has shown the opposite, examples:
- the car collected after the overhaul had a connection of the crankcase ventilation system with an expansion tank of the cooling system;
- mounted abnormal fan with blades guide the air flow not to the other side;
- the blades of the electric fan are freely rotated on the shaft of the engine of the engine;
- electrical fan connectors are dispersed or trimmed, etc.
Inspect the radiator for external clogging. Inspect the zones and ways of natural engine cooling. A negative example is the powerful protection of the lower part of the engine, which blocks the path of the airflow, the cooling engine from the bottom. Sometimes the bumper breakdown, the lower part of which has airflow guides to the engine, leads to overheating (VW "Passat" B3).
B. After inspection, it is necessary to check the coolant level in the system, the presence and health of the valves of the radiator covers and the expansion tank, the integrity of the nozzles and hoses. Clarify which antifreeze or simply water is flooded in the system, because The boiling point of each liquid is its own.
If the first two points (a or b) revealed some malfunctions, they need to be eliminated or taken to note when the "sentence" is issued. When adding a coolant, it is necessary to remember that not all cars are designed according to the principle of "just add water". For example, on bMW car (M20, E34) When adding a coolant, it is necessary to turn on the ignition and install the stove temperature controllers into the "Maximum heat" mode, so that the stove valves turn on and opened to move the coolant on the system, besides, it is necessary to raise the radiator up, because. The expansion tank, built into the radiator "wonder-designers" of Germany, is located below the level of the salon stove and it is often delivered.
If there is a suspicion that the engine is delivered (the system contains air, which prevents the fluid movement), it is necessary to unscrew the special plugs of the cooling system for the release of air. They are usually located at the top of the engine cooling system. Run the engine, turn on the salon heaters, will turn on the fan. Watch the engine warming, nodes and aggregates. If the system has an expansion tank, then check the circulation of fluid, i.e. Her movement on the system. When the engine turns is added to 2,500 - 3,000, a powerful coolant jet should flow into the tank. From the outdated (not completely!) The plugs can flow air for some time and as soon as the liquid is polished - the plugs must be spinning. As the engine is heated from the salon heater, heated air should go. If the engine is warming up, and the air from the heater is cold, then this is the first sign of "delighting" the cooling system. It is necessary to drown out the engine and take steps to search and eliminate this fault.
With a good thermostat (the opening temperature can be different from 80 to 95 degrees) after heating the lower nozzle of the radiator should have about the same temperature as the top. If this is not the case, it means there is bad coolant pumping through the radiator.
With a good thermostat, after a while after its discovery, the cooling system fan must turn on. If the system is not installed in the system, then it is necessary to check the electromagnetic coupling circuit switching sensor or the operation of the viscous coupling. If the viscous clutch is malfunction, the cooling system fan on a preheated engine can be stopped and retaining with hand (when stopped abide by caution - stop the soft object to not damage the impeller of the fan or hand). It is necessary to check the air pressure and its temperature - hot air should be directed to the engine.
The pressure in the cooling system should slowly increase as the engine warms and slowly drop after the engine is turned off. If the upper nozzle going to the radiator is swept when the engine is raised, it is necessary to check whether part of the exhaust gases do not fall into the cooling system. It is usually noticeable by oil film in expansion tank or bubble of coolant. In this case, from the muffler usually intensively goes white smoke From the heated and evaporating coolant falling into the engine cylinders. In this case, it is necessary to check the oil-culberry neck of the engine and sat on it a white emulsion, then the coolant is not only in the engine cylinders, but also in the lubrication system (it is necessary to stop moving). We give a few examples from the practice of various services that "say" that the engine diagnosis is inseparable from the diagnosis of all car systems, including the cooling system.
A \\ m Mazda 626 - the owner complains of the uneven engine revolutions or increased revs idle move. Checking the control system (and self-diagnostics) did not reveal faults. Drew attention to high voltage on temperature sensor Coolant.
The control system adds the amount of fuel, because Reacts to high voltage on the sensor (cold engine). It turned out that there is little liquid in the cooling system, the "bare" sensor. Just added to a normal cooling fluid level and revolutions are normalized.
A \\ m Ford - the coolant fell into the oil by unconventional way - through the cooling system of the oil, located around the oil filter.
A \\ m Ford - after warming up the engine, one cylinder stopped working. Replacing the candle and other works led to a positive result (to definition of a malfunction, it was not a relationship, just during the work of the engine cooled) - the cylinder started to work and the client was leaving. The next day he is again with us. It turned out to be a crack in the head of the block in the exhaust valve area of \u200b\u200bthe non-working cylinder. So far, the engine is cold - everything is normal. When heating - the crack increased and began to pass the cooling fluid into the cylinder. The mixture was impoverished and the interruptions began in work, and then the cylinder was completely disconnected.
Such examples can be given a lot, they are in the practice of each auto repair. The main conclusion should make everyone who is seriously engaged in the auto repair - to notice and analyze everything significant and insignificant, because These positions can change in places sharply.
Briefly on how the car engine cooling system works.
Answer the question which part of the car is more important:, or the engine cooling system? If you chose one or two of the proposed positions in the list, you answered incorrectly. In fact, all the above positions are vital for any machine. A failure in each of them will lead to serious consequences to correct which will not be easy.

Take, for example, the engine cooling system. If it is faulty or engine mode exceeds the work indicators laid when it is design, there is a possibility that you can see a rare phenomenon, which will later come to you in nightmarish dreams, from under the hood will begin to pour thick hot steam from under the hood, and the engine temperature sensor arrow will strengthen Red zone marking the critical overheating of the motor. The engine after such a steam bath and limit temperatures is quite possible to go to the car service on overhaul or straight on the landfill. This is the result of the improper operation of the cooling system.
And so, the first helpful information for newbies. The purpose of the cooling system is to create the perfect thermal working conditions for the engine that will exclude its overheating. Exothermic reactions occur in the engine (i.e. it produces a large amount of heat) and if the cooling system is unable to pick up excessive heat from the cylinder block, the engine will begin to deform (maybe the head of the cylinder block), the oil will not be able to provide sufficient protection (His worsen protective properties), the engine will begin to wear quickly and ultimately swap it.
The most important part of the engine cooling system is definitely a water pump. It causes a cooling fluid based on ethylene glycol to circulate along the hottest parts of the engine, as well as through the thermostat case, radiator, heater radiator, and other tubes and hoses included in the cooling system.
All engines internal combustion cooled by convective heat exchange (heat transfer in unevenly heated liquid, gaseous and other fluids, read more detail here: yandex.ru) and almost in all modern cars A liquid based on ethylene glycol is used as liquid antifreeze. She has a number of advantages compared to other technical liquids, such as high heat capacity, very heat Boiling and low freezing temperature. It is her that pumps it through the water pump engine driven by the drive belt drive of the auxiliary aggregates drive.

How does the thermostat work?
Thermostat uses wax. The wax flooded into a brass or aluminum capsule when heated pushes a small piston from the thermostat body, squeezing the spring. The thermostat opens. After cooling the spring system, the thermostat in the closed position is returned (the thermostat operation is shown at 5.37 minutes of video. By the way! This version can be used as an inspection of the thermostat from your car if you doubt it properly functioning)
On a cold engine, the coolant goes along the so-called small circle through the cylinder block, the head of the cylinder block, called the "head" and (for this reason you immediately get warm air in the cabin after starting the engine).
Once the motor reaches about 95 degrees, the wax in the thermostat is expanding and opens the valve directing the cooling fluid from the engine to the cooling radiator.
How is the cooling radiator?

The heated coolant passes through the radiator tubes, giving heat from the coolant (liquid) tubes, then transmitting it to the ribs of the radiator (the ribs are made of corrugated metal). The ribs, with their large surface area, contribute to high heat transfer met with a cooled air flux (to increase the cooling effect or in cases where the car is in a stationary state, a large fan is installed in front of the radiator, which additionally drives the air through the cooling edges). Thus, the coolant fluid is cooled through the radiator grille and falls into the opposite tank on the radiator. The cycle is repeated, the cooled fluid returns to the water pump and cools the engine, the circle closed.

The radiator slice shows us two rows of tubes through which the cooling fluid passes, which carries the heat from the engine to the ribs of the radiator grid.
For normal operation of the engine, a temperature of 80 - 90 degrees is required. And the temperature in the cylinder in working condition can grow to 2000 degrees, which destructively affects the details. The cooling system in the car allows the motor not overheat in the heat and not to freeze in the frost. Temperature violation fraught fast wear details increased flow Fuel and oils, a drop of engine power.
Thus, the cooling system monitors the temperature limits for the perfect work of the car.
Purpose of air cooling
The direct purpose of the cooling system is to maintain the optimum temperature for the engine. The cooling system is responsible for heating air in the cabin, for cooling motor oil and working fluid The automatic box, sometimes the receiving collector and the throttle node are cooled. As a result of the combustion of fuel, 35% of heat dissipates.
Did you know? The first cooling system appeared in 1950.
The principle of operation of the cooling air system

The name speaks for itself - the air flow is the main in the air cooling system. Air is removed from the cylinders, the head of the block and the oil radiator. The entire system consists of a fan (drives from the pulley of the crankshaft with a belt), cooling edges of cylinders and heads, removable casing, deflectors and control devices. On the fan there is a protective grid to exclude foreign objects.
The air flow enables the engine with the help of aluminum fan blades. Air moves between the edges of the cooling, and then it is evenly distributed using deflectors to all parts of the motor.
The fan consists of a directing diffuser (around the circle in it there are fixed radially located blades of alternating cross section to direct the air flow) and the rotor with 8 radially located blades. The blades of the diffuser change the direction of the air flow, and it moves to the opposite direction from rotation. This increases the air pressure and is better cooled by the engine.
Interesting to know! In 1997, the engine was installed air cooling with two turbines in 400 horse power. It is considered the most powerful.
 To increase the surface area for contact with air, additional edges are installed on the block and head of the cylinder block. In a minute, the fan can submit 30 cubes of air, which allows the engine to operate at temperatures from -40 ° to + 40 °. Thermostats and dampers allow the engine cooling intensity.
To increase the surface area for contact with air, additional edges are installed on the block and head of the cylinder block. In a minute, the fan can submit 30 cubes of air, which allows the engine to operate at temperatures from -40 ° to + 40 °. Thermostats and dampers allow the engine cooling intensity.
Natural air cooling
Most. simple way Engine cooling is natural air cooling. On the outer surface of the cylinders, the ribs are through which heat is given. Such a cooling system is on motorcycles, mopeds, piston engines and etc.
Forced air cooling
In the system of forced air cooling there is a fan and cooling edges. The casing covers the fan and ribs. This contributes to the direction of the air flow and prevents the penetration of heat from the outside.
Advantages and disadvantages
Benefits Air-cooled engines:
1. Easy design. Easy to repair.
2. Minor weight.
3. Reliability.
4. Inexpensive.
5. Good indicators Cold launch of the motor.
Disadvantages:
1. Creates noise.
2. Motor size increases.
3. Uneven blowing and local overheating.
4. Sensitivity to the quality of fuel, oil and spare parts.
Attention! Even a thin layer of dirt on the motor housing reduces cooling productivity. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the purity of the engine housing.
Common breakdowns
 The sensor shows an increase in oil temperature in - the cooling system gives a failure in operation. Immediately muffle the motor and find out the reason. On the dashboard A lamp lights up, which signals about malfunctions. The reason may be in the fan belt break. The problems in the operation of the thermostat happen very rarely.
The sensor shows an increase in oil temperature in - the cooling system gives a failure in operation. Immediately muffle the motor and find out the reason. On the dashboard A lamp lights up, which signals about malfunctions. The reason may be in the fan belt break. The problems in the operation of the thermostat happen very rarely.
Where the engines are used by the cooling system
Engines with air cooling system are less and less (they are displaced by liquid cooling) in mechanical engineering (compact small bars, diesel DVS, trucks, agricultural machinery).