What is TSI engine? How is it arranged, and what is his strengths and weaknesses? What is a TSI engine.
Each abbreviation in automotive production, meaning. So, the concepts of FSI and TFSI are also important. Only this is what the difference between almost the same abbreviations. We will analyze what is laid in the names and, what a difference in them.
Characteristic
The FSI power unit is a german-made motor from the Volkswagen concern. This engine won popularity due to its high technical characteristics, as well as the simplicity of design, repair and maintenance.
The FSI abbreviation is decrypted as Fuel Stratified Injection, which means - a layered fuel injection. Unlike widespread TSI, FSI does not have turbocharging. If we speak by the human language, this is an ordinary atmospheric engine, which often used Skoda.

Engine FSI
The TFSI abbreviation is deciphered as Turbo Fuel Stratified Injection, which means the turbocharged fuel injection. Unlike widespread FSI, TFSI has turbocharging. If we speak by the human language, this is an ordinary atmospheric engine with a turbine, which often used Audi on A4, A6 models, Q5.

Engine TFSI
Like FSI, TFSI has an enhanced environmental norm and efficiency. Due to the Fuel Stratified Injection system, and thanks to the features of the intake manifold, fuel injection and the "tamed" turbulence, the engine can operate both on the ultra-walled and a homogeneous mixture.
Pros and cons of use
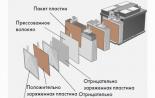
The positive side of the Fuel Stratified Injection motor is the presence of fuel dual-circuit injection. From one contour, fuel under low pressure, and from the second - under high. Consider the principle of operation of each contour of the fuel supply.
Low pressure circuit in the list of composite elements has:
- fuel tank;
- gasoline pump;
- filter fuel;
- bypass valve;
- fuel pressure control;
The high-pressure circuit device suggests:
- high pressure fuel pump;
- high pressure lines;
- distribution pipelines;
- high pressure sensor;
- fuse valve;
- injector nozzles;
A distinctive feature is the presence of an absorber and purge valve.

Motor FSI Audi A8
Unlike conventional gasoline power units, where the fuel, before entering the combustion chamber, falls into the intake manifold, on FSI - fuel directly into cylinders. The nozzles themselves have 6 holes, which provides an improved injection system and increased efficiency.
Since the air enters the cylinders separately, through the flap, the optimal ratio of the air-fuel mixture is formed, which allows gasoline to burn evenly, without exposing the pistons to excess wear.
Another positive quality of the use of such an atmospheric is the economy of a fuel and high environmental norm. The Fuel Stratified Injection injection system will allow the driver to save up to 2.5 liters of fuel per 100 km run.

Table Applicability TFSI, FSI and TSI
But, where many positive sides, there is a significant number of flaws. The first minus one can assume that the atmospheric is very sensitive to the quality of fuel. On this engine will not save, because on bad gasoline, he simply refuses to work normally and will fail.
Another lack of drawback can be considered that in the frost, the power unit is simply not to start. If you take into account the common problems and FSI engines, problems in this ruler may occur with the cold start. The culprit is considered to be all the same layering injection and the desire of engineers to reduce the toxicity of the exhaust during warming up.
Oil consumption - is one of the shortcomings. According to most owners of this power unit, an increase in lubrication consumption is often noticeable. To make it not happened, it recommends to hold the tolerances VW 504 00/507 00. In other words, changing engine oil 2 times a year - during periods of transition to summer and winter mode of operation.
Output
The difference in titles, and more precisely the presence of the letter "T" means that the motor has turbocharging. Otherwise, there is no difference. FSI and TFSI engines have a significant number of positive and negative sides.
As can be seen, the use of the atmospheric is good in terms of savings and ecology. Motor is too sensitive to low temperatures and poor fuel. It is for the disadvantages that it stopped and switched to the TSI and MPI systems.
If you are well versed in engines, it is definitely, you know what TSI is. If not, we recommend reading this article.
TSI engine - this is a gasoline power unit, whose distinctive feature is double turbocharging. In this case, the TSI abbreviation (Turbo Stratified Injection) is translated as an engine with a turbocharging system and layered fuel injection.
The design of the TSI engine is noteworthy in that the developers have separated a mechanical compression system and turbocharger on different parts of the engine. Due to the use of exhaust energy, the standard turbocharged engine is supplied with an additional power. Exhaust gases are spinning the turbine wheel, and with the help of the drive system create increased injection and compression of air. This system is more efficient compared to the traditional gasoline engine.
Advantages of TSI Engine
The usual turbocharged engine has one large drawback - on small and complete revs its effectiveness is small. In turn, the TSI engine is equipped with a mechanical compressor (working on small revolutions) and a turbocharger that provides a significant increase in power at high revs. That is, practically throughout the range revolutions occurs additional injection and air compression in the engine system.
Thanks to this fact, power grows multiple times on the background reducing the consumption of fuel.
Such a decrease provides a layer-in-law system, dosage injection and a double injection system. All these factors suggest that the engine with the TSI system has been developed by Volkswagen, has an impressive power.
To compare, take the classic turbocharged engine of the same manufacturer. Having a nominal volume of 1.2 liters, the TSI-motor demonstrates the results on average for 12 horsepower better (102 horsepower at the TSI-motor against 90 horsepower at a standard turbocharged engine). In addition, due to the double compression system eliminated failure failure and improves thrustboth on small and large revolutions.
Naturally, the complexity of the layout of the TSI-motor affected its price. However, a small rise in price with interest pays off in high power and a decrease in fuel consumption.
TSI engine ( Turbo Stratified Injection, literally turbocharging and layered injection) combines the latest achievements of design thought - direct fuel injection and turbocharging.
The Volkswagen Concern has developed and offers on its cars a line of TSI engines, differing in design, engine volume, power indicators. In the design of the TSI engines, the manufacturer implemented two approaches: double reducing and just turbocharging.
Abbreviation TSI is a patented trademark of the Volkswagen concern.
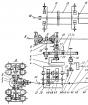
Double supervision is carried out depending on the need of the engine with two devices: a mechanical supercharger and turbocharger. The combined application of these devices allows you to realize the rated torque in a wide range of engine speed.
In the engine design, the mechanical supercharger type ROOTS is used. It is two rotors of a certain shape placed in the housing. Rotors rotate in opposite parties than the absorption of air on one side is achieved, compression and discharge - on the other. The mechanical supercharger has a belt drive from the crankshaft. The drive is activated using a magnetic coupling. To adjust the pressure charged parallel to the compressor, an adjusting valve is installed.
The standard turbocharger is installed on the TSI engine with double superimposor. Advance air cooling is carried out by an intercooler of air type.
The effective operation of the double supervision provides the engine control system, which in addition to the electronic unit combines the input sensors (pressure in the intake pipeline, pressure pressure, pressure in the intake manifold, potentiometer of the adjusting damper) and actuators (magnetic coupling, carrier servomotor, adjustment valve Valve recycling turbocharger).
Sensors track downward pressure in various places of the system: after a mechanical supercharger, after a turbocharger and after an intercooler. Each of the pressure sensors is combined with air temperature sensors.
Magnetic coupling Included by the signals of the engine control unit, in which voltage is supplied to the magnetic coil. The magnetic field attracts the friction disc and closes it with the pulley. Mechanical compressor starts to rotate. The compressor operation is performed until voltage is supplied to the magnetic coil.
Servomotor Turns the adjusting damper. With the valve closed, the entire suction air passes through the compressor. Adjusting the pressure of the mechanical compressor is performed by opening the flap. In this case, part of the compressed air is supplied again into the compressor, and the pressure of the superior is reduced. With a non-working compressor, the flap is fully open.
Advance pressure limit valve It works when the energy of exhaust gases creates an overpressure pressure. The valve provides the operation of the vacuum drive, which in turn opens the bypass valve. Part of the exhaust gases goes past the turbine.
Valve recycling turbochargers Provides the operation of the system on the forced idling (when the throttle is closed). It prevents the creation of overpressure in the interval between the turbocharger and the throttle valve closed.
Principle of operation of double superchard engine TSI
Depending on the rotational speed of the crankshaft (load), the following modes of operation of the double supercharge system are distinguished:
- hopeless mode (up to 1000 rpm);
- the operation of the mechanical supercharger (1000-2400 rpm);
- joint work of the supercharger and turbocharger (2400-3500 rpm);
- the operation of the turbocharger (over 3500 rpm).
At idle, the engine works in undead mode. The mechanical supercharger is turned off, the adjusting valve is open. The energy of the exhaust gases is small, the turbocharger does not create pressure presses.
With an increase in the number of revolutions, a mechanical supercharger turns on and an adjusting valve is closed. Pressure pressure, mainly creates a mechanical supercharger (0.17 MPa). The turbocharger provides a small addition of air compression.
At the speed of the engine crankshaft in the limit 2400-3500 rpm, the pressure of the superior creates a turbocharger. The mechanical supercharger is connected if necessary, for example, with a sharp acceleration (with a sharp opening of the throttle). Advance pressure can reach 0.25 MPa.
Next, the operation of the system is carried out only at the expense of the turbocharger. Mechanical supercharger is turned off. The adjusting valve is open. To prevent detonation with increasing speed, the pressure drops somewhat falls. At the speed of 5500 rpm, it is about 0.18 MPa.
TSI engine turbocharging
In these engines, the supervision is carried out exclusively by the turbocharger. The design of the turbocharger ensures the achievement of the nominal torque already at low engine speeds and maintain it in a wide limit (from 1500 to 4000 rpm). The outstanding characteristics of the turbocharger obtained due to the maximum reduction in the inertia of rotating parts: reduced the outer diameter of the turbine and compressor impeller.
Adjustment of the superior in the system is traditionally carried out using the bypass valve. The valve may have a pneumatic or electrical drive. The operation of the pneumatic drive provides an electromagnetic valve of pressure limitation. The electrical drive is represented by an electric guide device consisting of an electric motor, a gear transmission, lever mechanism and a device position sensor.
In the turbocharged engine, unlike double supervision, a liquid boost air cooling system is used. It has an independent contour engine cooling system and forms a two-circuit cooling system with it. The cooler air cooling system includes: an upper air cooler, pump, radiator and pipeline system. The indoor air cooler is located in the intake manifold. The cooler consists of aluminum plates through which the cooling system pipes pass.
The charge air cooling is performed along the motor control unit in turning the pump. The flow of heated air passes through the plates, gives them heat, and those, in turn, give it fluids. The coolant moves along the contour using the pump, cooled in the radiator and then in a circle.
TSI engines (Turbo Stratified Injection, from English turbocharging and layered injection) - power units with direct (straight) fuel injection and. These motors are produced by the German concern WAG and are installed on various models of cars Audi, Volkswagen, Seat, Skoda, etc.
TSI engines (full TFSI name, usually the name is used for Audi models) are built based on FSI atmospheric motors with direct injection (from English Fuel Stratified Injection, which means layer-by-layer fuel injection).
Read in this article
Engine Features TSI: Pros and Cons

Motor development and the first TSI engines appeared at the very end of the 90s, although the beginning of the mass promotion can be considered 2005-2006. TSI is the brainchild of Audi, and the abbreviation itself belongs to the Volkswagen concern. A distinctive feature of TSI motors line (TFSI) is that with such an abbreviation may have:
- double supervised, implemented by simultaneous installation and;
- single supervision, which means the presence of only one turbine;
TSI aggregates with a capacity of up to 140 hp There are only one turbine, while the power plants from 150 "horses" are already obtained by a turbine and compressor. In other words, TSI is a whole line of Turbomotors of the WAG concern. TSI engines have different power and working volume. The TSI line contains 1.2 (105 hp), 1.4 (122 hp), 1.8 (140 hp), 2.0 (180 hp) and 3.0 (200 hp) -ltric units. It is also worth noting that the power on separate working volumes can be even higher, since further forced and deformed modifications are existed.
The TSI motor is the perfect combination of direct fuel and turbocharging injection. Thanks to this solution, the engines of this line provide high power, have an outstanding torque characteristic, differ in fuel economy and meet the rigid environmental standards.
With relatively small working volumes, the TSI engine issues as much or even more power relatively with more abstract gasoline engines. For example, a 1.2-liter TSI with one turbine has a power index at 105 hp, which is quite comparable to a 1.6-liter atmospheric analogue. At the same time, the maximum torque is available on low revs, which provides better accelerating dynamics. It is also worth noting a widely wide regiment of torque. The largest popularity in the entire line of motors deservedly has 1.4 TSI. This engine has many awards and was recognized as the best engine of the year for 7 years in a row.
A distinctive feature of all TSI engines is the optimal ratio of power and fuel economy. The internal combustion engine of this line provides an outstanding dynamics and excellent traction in all revolutions. Installing the compressor parallel to the turbine provided this motor elasticity and allowed to get rid of a number of problems inherent in turboctors.
CO2 emission level allows TSI to remain in the list of leaders in terms of environmental friendliness. The direct injection of TSI allows you to realize the most effective mixing and fuel supply to cylinders. Also, the motors of this row are quite reliable and have a large resource.
There are no noticeable disadvantages of TSI engines compared to other turbocharged units. Subject to normal operation on good fuel and oil, maintenance on professional service and timely replacement of consumables, these motors can walk from 300 thousand and more. The only node that requires increased attention is a turbocharger. The turbine is extremely desirable to cool after driving and slow down before each next trip. As for the compressor (if available), this unit is quite reliable.
Low fuel and oil quality can reduce the TSI engine's planning resource by 2-3 times. The service life of the TSI motor on dirty low-quality gasoline with an inappropriate octane number can be only 100-150,000 km. This is especially true of low-pass modifications. We add that TSI repair requires serious financial spending. The failure of the turbine can occur already at 100,000 km. Run, regardless of the specific model of the TSI engine.
TSI with compressor and turbine

As mentioned above, the motors of this line can have both a turbine and a bunch of turbines and a compressor. Engines with a working volume of 1.4 liters have a turbocharger and a mechanical supercharger. On the example of such a TSI with a capacity of 150 hp You can superficially consider the principle of collaboration of two superchargers. If the motor operates in the mode of small loads, then the crankshaft turns are low or medium, then the turbine and compressor work in parallel.
Raising turns up to 2500 rpm and above allows the intensive flow of exhaust gases to interact with the turbine to the most effectively. The mechanical supercharger is turned off. The control system uses the compressor only during sharp accelerations. Thus, the inertia of the turbine is compensated and the turboyami effect is minimized.
In other words, the compressor works when the turbine is not enough exhaust gases for confident pickup. This scheme allows you to get rid of failures that are peculiar to turbine turbine, in the entire range of revolutions. In parallel, it is worth noting high efficiency and TSI motors.
That in the end
To begin with, we note that the productive and reliable TSI motors are fairly popular not only among ordinary consumers, but also among the tuners. Forcing and TSI allows without significant alterations to increase the power of such an engine. After you can count on an additional 7-15 hp With a deep tuning, which involves the replacement of the turbine, compressor, nozzles and other elements to more productive, it is possible to add from 100 and more horsepower.
Finally, add that a popular TSI with a volume of 1.2 liters is installed on the WAG model of various classes. At the same time, many skeptics have concerns about his motresurs. As practice shows, in the CIS, the service life of such an engine is about 100-120 thousand km, the turbine can fail even earlier.
The fact is that although 1.2 TSI is characterized by a good "on nizakh", this motor has a high degree of forsing, only three cylinders and relatively small power. For this reason, the owners often exploit such in high speed to maintain an active rate of driving. It is also necessary to take into account the poor quality of fuels in the CIS. It is also important that the owners often do not comply with a number of requirements during operation. For this reason, the combination of negative factors can quickly "kill" such an engine. Always remember, it is necessary to acquire used cars with low-aligned TSI high-mounted engines and any others in the secondary market.
Read also
Engine FSI family: differences, features, pros and cons of the power unit of this type. Common problems of FSI engines, motor maintenance.


The innovative breakthrough in the field of automotive industry was the development of a new line of engines, a distinctive feature of which is high power with a small fuel consumption.
It was possible to achieve this, using a combination of direct fuel injection and double supervision. Internal combustion gasoline engines have TSI marking, are installed on well-known German brands, such as Volkswagen, Audi, Seat, Skoda, etc.
TSI motor history
There is a certain confusion between two practically the same power units that are marked differently on some cars. This is connected with the step of transition from atmospheric engines to the turbocharged.
In 2004, a 2.0-liter atmospheric motor with a direct injection system, referred to as FSI, and, accordingly, added to its name T - TFSI letter (Turbochaged Fuel Stratified Injection). The abbreviation was decrypted as "Tubaardv, layered fuel injection." The Volkswagen concern reduced the full name to "Turbocharged Stratified Injection" and patented a new abbreviation - TSI.
In 2006, a 1,4-liter engine was developed with a more reliable and simple injection system having two supercharger (turbine and mechanical compressor). The abbreviation began to decrypt somewhat differently: "Twincharged Stratified Injection" (double supervision, layered injection).
Since then, Volzvagen has developed and improved the TSI engines series, characterized by the volume and quantity of compressors used. On Audi cars, such aggregates are still referred to - TFSI.
The principle of operation of TSI engines and their main differences
TSI motors are largely different from their predecessors (atmospheric and turbocharged units) in the following indicators:
- the presence of two compressors;
- improved cooling system;
- changed fuel injection;
- the engine block is facilitated;
- increased power.
On low revs, the turbocharger and the mechanical supercharger work together. When climbing turns over 1,700 rpm, the mechanical supercharger is connected only at the moments of sharp accelerations, and further development occurs with a turbocharger alone. The combined application of two devices provides excellent pickup and nominal torque in a wide range of revolutions, debugged and stable operation of the unit.
Video - the principle of operation of the TSI engine from Volkswagen:
Unlike ordinary "turbo" options, the concept of "cooling liquid" appeared in TSI engines. Cooling system nozzles pass through the intercooler, due to which the main air is injected in the cylinders. The pressure indicator becomes higher, resulting in uniform filling of the combustion chamber of the combustible mixture and increase the speaker.
The fuel in the TSI engine cylinders is served "directly" (bypassing the fuel rail), where it is subjected to layer-by-layer mixing with air. The combustion is taking place with high efficiency. Such an injection system made it possible to increase power and.
The new engine is facilitated by almost 14 kg. This was achieved using a new design of the block placement and head. Distributional shafts and some other details weigh less than their predecessors.
An order of magnitude higher and the performance of motors of this series. For example, the capacity of the unit with a volume of 1.2 liters is 102 hp, while the ordinary turbocharged motor of the identical volume, this figure is only 90 hp.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of German engines are considered:
- high performance;
- economy;
- lack of "turbists" in any rolver range and at acceleration;
- ecology. The indicator of 2 TSI motors is at times less than atmospheric;
- the smaller cost of customs;
- wide tuning opportunities. Forcing engines simple enough.
The disadvantage of TSI is their high sensitivity and increased maintenance requirements. Motors need precipitant care, frequent replacement of consumables (oils, filters, etc.), the use of high quality fuel. It is not suiced to the repair of such force aggregates.
TSI engines problems
The main headache of motors of this series is the drive of the timing. Premature tensile and wear of the chain can lead to its slipping through the stars teeth, as a result of which damage to valves and pistons will occur. It does not inspire confidence and tension regulator, the failure of which leads to the same problems.
New motors of 1.2 liters and 1.4 liters of EA211 series have lost problems associated with the timing drive. The chains of these motors are replaced by gear straps.
Another TSI problem is a high oil consumption. Plant Manufacturer for different versions Consumption from 0.5 to 1 l per 1000 km. Often, the result of such consumption of lubricants becomes clogging of candles.
Video - among the problems, car owners often mark the unusual sound of the TSI engine and increased oil consumption:
Celebrations reviewers
During its existence, cars with TSI engines wound hundreds of thousands of kilometers on our roads, and in the meantime, there were certain opinions about the reliability and convenience of operation.
On the contrary, short distances were not too favorable (especially in a cold time), since the aggregates require a long and full of warm-up cycle, which is possible only when driving. Most motorists are not recommended to acquire a German novelty for operation in the northern regions.
Almost-industrial consent reached car owners about the need to use exclusively high-quality consumables and fuel. Moreover, many advise as often as possible - every 5-7 thousand km, and if there are extraneous noise and cod in the engine, they recommend contacting the service without delay.
If you do not detect and not eliminate the malfunction, then when it is aggravated, further repairs may be unprofitable. The sad outcome of such cases is the complete replacement of the engine, which is quite expensive.
From Germany, it should be carefully examined by its service history. If the oil change was carried out with a large interval (40-50 thousand km), it is better not to acquire such a car.