Accumulators car device work. The main thing about the main thing - the car battery
Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to the battery of your car and its (car) of the electrical system. In fact, if the engine is the heart of our car, then it is his central nervous system (and maybe even the soul) - it stores and produces electricity, and also controls the power of the current power supply. The last thing you would like is to stay on a deserted track with a dead battery. The more you know about the battery and the electrical system as a whole, the less likely to get into this situation.
How does a car battery work?
The car battery provides all the electrical power supply of the machine with the necessary amount of electricity to power all electrical components in your car. And the speech here is about rather huge responsibility. Without battery, the car, as you, probably, have already understood, will not go anywhere. Let's take a look at how this powerful little box works!
Chemical reaction is the main principle of battery operation: it simply converts chemical energy into the electrical needed to power your car, providing the starter voltage and many other electrical components of the machine, as well as electrical - back to chemical. Another important battery function - it ensures the constancy of the current - it also stabilizes the voltage in order for the engine to work.
In a simple principle of the battery, it is possible to characterize this: the chemical processes in it lead in the appearance of an electric current to which the car is powered - this current is especially useful, and most of all it is consumed when you start the engine with a starter; When the car is headed, the engine twists the generator - and here we see the process of transformation of mechanical energy (the generator grinding) into electric - in turn, the generator transmits the battery current produced by them, and the electricity has already turned into a chemical - accumulates it, saves it again "feed" her starter or any other electrical systems The car, when the generator does not work or when electricity produced by the generator is not enough to provide all car systems.
The car battery has two poles: one positive and second is negative, and you probably already know it if at least once you have seen or disconnected / fixed the battery terminals. These poles are connected to the car and are responsible for the nutrition of the row very important mechanisms car, including:
- Engine starting
- Reproduction of audio system
- All light mechanisms (headlights, rear lights, different types of backlight, etc.)
- Windscreen wipers
- Much more.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the battery consists of six cells. Two electrodes are placed in each cell, which are made of eight overlapping metal plates. These eight overlapping metal plates form what is known as the "galvanic element". Thus, in total, each cell includes 2 electrodes and 16 plates. It is through these plates that the car electricity is powered. But how does it work?
In fact, everything is quite simple - let's summarize the above described:
- The battery consists of six cells
- Each cell consists of two sets of plates
- Each set of plates includes eight overlapping metal plates
And now a little chemistry ...
The first set of plates in the cell is positive, and the second is negative. A positive grid is covered with lead oxide and brings electrons into a cell. The negative set is covered directly by lead, and it, on the contrary, frees the electrons. Metal plates - Remember, eight of them in each grid, 16 in each cell - are in a mixture of water and sulfuric acid (in fact, only about 35 percent of sulfuric acid in this concentration, but this is more than enough to, for example, burn clothes And heavily burn the skin. This mixture acts as an electrolyte - a substance that does well conduct electricity.
When the battery is charged (from the generator or other methods), then a chemical lead oxidation reaction occurs on a positive charge, as a result of which the electrolyte is saturated with sulfuric acid and the proportion of electrolyte increases. When the battery, on the contrary, is discharged, feeding any car electrical system (we remember that the main consumer is a starter), then due to the recovery of lead on the other - a negative set of plates, as a result of which more water is formed, and, therefore, the specific Electrolyte weight decreases. At the same time, the chemical process in each of the plates is so negligible that very little energy is distinguished, but at the outlet of the battery a passenger carWhen all these reactions pass through all 6 cells, we already get the already intimate 12 volts.
Possible battery malfunctions
The battery over time comes into disrepair - this is its natural wear and, in addition, a different kind of harmful processes in it and the impact on it can significantly shorten the life of his life. And the first symptoms that there are problems in the battery, are the inability to make a car (especially in frosty weather).
So, what could be the problem with the battery?
- Low fluid level in the battery: Car batteries usually have a small part of the case in the form of a translucent strip - so that you can always follow the liquid level of your battery. If the fluid level is below lead plates (electricity conductor) inside the battery, then it is time to either add it or replace the battery.
- The "eatery" of the battery is when the housing of your battery looks as if he ate a lot and swept. This may indicate an urgent replacement of the battery. You can accuse the excess amount of heat as the cause of the blink of the battery and, as a result, reducing the battery life.
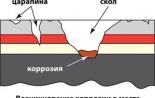
- The smell of rotten eggs from the battery: you can notice the sharp smell of a rotten egg (in fact, this is the smell of sulfur) around its battery. Cause: battery leakage. This leakage, except smell, also causes corrosion around the terminals.
The battery (AKB) of the car is a particularly significant element of the machine device. It is a source of current having the ability to store the energy required for the operation of the electrical elements of the vehicle.
Its functions are responsible for:
- Run - the power supply to the starter that is responsible for rotating the engine at startup.
- Current development for the operation of electronic systems in the event of insufficient generator power.
- Nutrition devices with a non-veiled car.
Characteristic of a non-servant battery
Battery marking
Today's level technical Development Gave the opportunity to firms to automakers to use the most advanced and high-quality batteries - non-maintained rechargeable batteries.
The device is maintained by the car battery has characteristics, giving a pleasant opportunity to consumers to pay a minimum of attention to this battery.
It is worth identifying that unqualified battery - This is a modern source of energy, which does not imply in its device and does not have special holes for topping the water or electrolyte, the battery data housing is completely sealed.
Since the development of the car battery, more than 150 years have passed and its base device remains unchanged for any type of battery to present. The main elements of the battery are: Acid and lead plates.
Rechargeable battery design
Modern Akb consists of the following main elements:
- Plates (galvanic elements)
- Separators - layers
- Pole conclusions
- Sealed housing (monoblock)
- case cover

Battery elements
Battery plates
IN technical device Rechargeable batteries included galvanic elements (plates) - chemical sources of electricity. Their amount is 6 pieces, they are connected to each other sequentially, with jumpers. One negatively charged block output is attached to the positive conclusion of the other.
Galvanic elements are located in a separate case, while they are separated by partitions. In its combination, the batteries form a battery.
The galvanic element of the car battery refers to reversible sources. chemical current - This means that the "charge-discharge" cycle can be repeated several times. It consists of two electrodes (semi-blocks) of different polarity - lead lattice plates. Electrodes are located in a solution of sulfuric acid (38%) and distilled water. The mixture is an electrolyte - a substance capable of conducting a current.

Separators - layers
 There is a separator between the electrodes, to avoid short circuit, is a dielectric layer. The separator performs the function of the insulator, and does not allow contact of the electrodes of different polarity, but does not disturb the electrolytic conductivity of the battery.
There is a separator between the electrodes, to avoid short circuit, is a dielectric layer. The separator performs the function of the insulator, and does not allow contact of the electrodes of different polarity, but does not disturb the electrolytic conductivity of the battery.
The separator is made of plastic microporous structure, in the form of an envelope, on galvanic elements of a positive charge. This technique helps the active mass with positively charged plates not to settle at the bottom of the monoblock and not touch with the plates of the negative charge.
The development of a separator device in the form of an envelope allowed the firms to manufacturers of batteries to come to low-service and non-servant batteries.
Pole conclusions
Pole conclusions of the battery are made of lead. Their size varies depending on the polarity of the output, so positive is greater in relation to negative. This feature It is not random and serves as protection from the wrong connection of the battery elements, which in turn eliminates the loss of active masses and helps to avoid reducing the performance of the AKB.
Hermetic case of AKB
The housing of the battery (monoblock) passed its evolution from the wooden, coated from the inside with leaf lead, then - an ebony.
In the 40s The XX century appeared the first hulls from synthetic materials. Modern battery consists of synthetic polypropylene. The materials of the monoblocks are made by large requirements for its durability and security. The housing is calculated withstanding the constant contact of the chemical components, vibration and temperature change.
case cover
Purpose of the cover of the case - the dense closure of inter-element connections of the AKB. In the former batteries, the cells were threaded plugs intended for topping the electrolyte and gas removal during the operation of the battery. In the design of the mainstream, the plugs are not installed at all or tightly closed. Gas output is provided with the central ventilation system.

It consists of two parts and is equipped with a labyrinth. With the help of a labyrinth, water vapors formed when charging the batteries condenses and flow back into the battery. The central gas feed and gas protection system is integrated into the lid. Inflammation protection is made at the exit of the gas supply from the battery in the form of a small round disk, it received the name - Fritt. The principle of the Fritty is concluded in the free passage of gas into the atmosphere, but when gas is ignited, preventing fire breakage inside to prevent the battery explosion.

Types of Account
All car batteries as mentioned were previously the same in design and filled with electrolyte, only slightly different from each other. Each modification is designed to achieve a certain goal to the detriment of other characteristics.
Akb with liquid electrolyte
Represent open systems, i.e. Gas released during charging can stand out into the atmosphere. He has excellent performance features, Large shelf life up to 15 months, but there is no protection against electrolyte leakage.
Akb Economy
This type of battery is optimal in terms of cost and service life, there are fewer leads in it. He has a reduced power of the cold start of the engine and slightly reduced the service life (4 years or 80,000 km). At the same time, a more favorable price, a smaller mass and a low self-discharge current, which does not increase as the battery aging. Can be used in vehicles with start-stop system.
Advanced AKB
They have abbreviation EFB. Enhanced flooded battery) - reinforced battery with liquid electrolyte. Constructively distinguished by a thicker grille of a negative electrode, which provides high corrosion resistance when the load is loaded, as well as the addition of carbon into the active mass of the negative electrode, which leads to an improved adhesive ability.
It has protection against deep discharge and excellent performance characteristics, but there is no protection against electrolyte leakage.
In its design, a passive mixing element is applied, it reduces the bundle of electrolyte, i.e. The formation of a layer with different concentrations of sulfuric acid, which is concentrated in the lower part of the galvanic elements, which leads to insufficient electrolyte density at the top. This happens with frequent charging and discharge processes.
AGM AKB
ABSORBENT Glass Mat. - Fiberglass, which has a very high absorbent ability. They are also called recombination, apply on vehicles with start-stop system and energy recovery function. In such batteries, the electrolyte is adsorbed by a fiberglass rug. They represent a closed system, i.e. All galvanic elements are isolated from the atmosphere by valves.
It has protection against leakage, even if the battery case is damaged, the probability is insignificant and amounts to no more than a few milliliters. They have a long service life, excellent performance and high reliability. But, on the other hand, it has a high cost and higher sensitivity to elevated temperature.
Gel AKB
Also there are batteries with gel electrolyte, it is formed by adding silicic acid to it. Represent ordinary lead batteries. They have a very low probability of electrolyte loss, high cyclic resistance and reduced gas formation. Their mass distribution limits a number of serious disadvantages, such as: impaired starting properties at low temperatures, high price, intolerance of elevated temperatures and the associated non-impurity of the installation in the subcontrol space.
Disconnection devices AKB
In the security battery circuit, sinopathrots or a disconnection relay can be used, especially if it is located in the cabin or in the trunk. The task of these elements is disconnected from the battery the starter wire and the generator at the time of the accident, because The closure of these wires can cause fire. But the power supply of the on-board network is saved to provide security features ( alarm, lighting, etc.)

Charge and discharge processes
The charge process of the battery means the accumulation of electrical energy battery. In the outcome of this process, the electrical energy is undergoing conversion to chemical.
The battery is powered by a generator with a car engineered. Voltage that produces a standard charged battery during operation, equal to 12.65 V.
The process of charge can be described as a transition of lead sulfate and water formed by discharge of the battery in lead, lead dioxide and sulfuric acid. In this case, the amount of sulfuric acid becomes greater, the density of the electrolyte substance increases.
As a result, chemical energy is accumulated and restored, which is necessary in the future to generate electricity.

The process of discharge of the ACB is characterized by the return to consumers of the battery of electrical energy. There is a reverse chemical process - chemical energy passes the transformation into electrical.
The battery is subjected to a discharge procedure in the presence of an electrical current consumer connected to it. In this case, sulfuric acid disintegrates, respectively, its content in the electrolyte substance drops.
Legging chemical reactions contribute to water formation (H2O). For increased level Water decreases the density of electrolyte.
The discharge of the battery leads to the appearance of lead sulfate. Such an effect is the same for positive and negative electrodes.

The main characteristics of AKB

Energy conversion coefficient
Energy flowing to the battery during the battery charge is greater than the discharge. The excess of the energy of the "charge" to the energy of the "discharge" is based on the need to cover costs in the flow of electrical and chemical processes.
For a complete charge, 105-110% of energy from the amount spent earlier is needed. Thus, the conversion factor will have a value from 1.05 to 1.10.
Capacity
The capacity of the battery is proportional to the number of electrical current issued by it. Unit of measurement capacity-ampere-clock (A-H).
The capacity of the container is influenced by the discharge current and temperature. It has a property to decline with increasing the discharge current and the temperature drop, in particular with values \u200b\u200bless than 0 degrees.
Rated voltage
The standard voltage of each element of the battery corresponds to 2 V, and the voltage of the entire battery circuit is equal to the number of galvanic elements. The battery of the machine consists of 6 batteries, which corresponds to a nominal container in 12 V.
Cold scrolling current
This indicator serves as a characteristic of the battery start-up capabilities during its operation in low temperatures. This parameter is measured at -18 ° C. The voltage of the fully charged battery does not fall below the time specified for a certain amount. The current level affects the launch of the car engine, as the higher the value of the current in the cold scrolling, the easier it will be started in winter time of the year.
Voltage
Voltage, the value of which is measured between the two pole terminals of the battery - voltage on terminals.
Suggestion voltage - The parameter, when the battery is exceeded in the housing, water is formed. It occurs when the voltage is exceeded by the entire battery, the maximum allowable value of 14.4 V.
The decomposition of water leads to the formation of hydrogen and oxygen, which in the compound form gas. Attention is explosive!
Owner or voltage idle move - The state when the loads on the outputs are not. Charge and discharge cycles change idling stress. When the amount of sulfuric acid is restored between the electroplating elements, the idling stress comes to the final value - the stance voltage.
AUTOLEEK.Question43: Rechargeable batteries (AKB). Appointment, working conditions. Basic requirements for AKB. Types (types) AKB. Marking. Accommodation on transport machines.
The battery is a chemical current source in which the chemical reaction energy is repeatedly converted into an electrical and vice versa. Thus, the battery, having the opportunity to convert chemical energy into electrical, is able to store it and store for a long time. Chargeing, the battery accumulates electrical energy, discharged, gives it to the consumer. A standard modern 12-volt car battery is made of six sequentially interconnected blocks of variemlessly charged plates, each of which is simple battery with output voltage about 2 volts. A positively charged plate (electrode) is a lead grid with an active mass of lead dioxide (PBO 2), and the electrode with a minus sign is a grid with an active mass of spongy lead (Pb). Semi-blocks of differently charged plates are inserted into each other. In order to avoid the occurrence of a short circuit between the plates, they are separated by porous separators from the insulating material. The collected blocks are placed in the housing and are poured with an electrolyte (sulfuric acid solution with a density of 1.27-1.29 g / cm 3). The poles (Bartka) of the extreme elements are connected to the contact terminals - bulls located outside the housing. If you connect the load to the battery, then lead plates with an active mass, the electrolyte and load form a closed circuit. Inside the battery, a chemical reaction begins, as a result of which the active mass of both electrodes will begin to change the initial composition, converting from spongy lead and its dioxide into a sulfate lead (lead sulfate PBSO 4), and the electrolyte density begins to fall. As a result, the directional movement of ions is formed in the chain, and electric current flows. This process is the discharge of the battery. When connecting to the battery of an external current source begins the reverse process - the charge. When charging, the active mass of the plates restores its original composition, the electrolyte density grows. These chemical processes can be described by the following equations: - on a positive plate: PBO 2 + H 2 SO 4 \u003d PBSO 4 + H 2 O + 2E; - on a negative plate: PB + H 2 SO 4 \u003d PBSO 4 + H 2 - 2e. Of all the above, it follows that the number of energy reserves by the battery (container) is determined by the volume of active mass and electrolyte. Since the automotive 12-volt battery consists of six batteries connected in the battery sequentially, then in fact the device, in a daily use of simply called "battery", is actually a battery from multiple batteries. For the first time, battery batteries began to install on Cadillac cars in 1912. On the first cars, batteries were removed, because Due to the lack of an on-board generator, after the discharge, they had to recharge them from an external current source. In the car, the battery performs three functions: first, it starts the engine, secondly, it feeds onboard electrical devices at a time when the engine does not work, and finally, when the engine is running, the generator helps the generator when he does not cope with the load in the onboard electrical network.
Rechargeable battery design
The modern rechargeable battery consists of the following main parts:
plates;
separators;
connecting conclusions.
monoblock (body), serving a tank for electrolyte;
Main types of batteries designs
Depending on the design features, rechargeable batteries can be divided into three types:
served;
low-service;
fully non-servant.
Serviced battery batteries
The serviced batteries require constant monitoring of the electrolyte level and its density. This is due to the fact that in the manufacture of plates to increase the strength of their material and improving its injection properties in lead, antimony is added (over 4.5%). This leads to the fact that the decomposition of the electrolyte (with the simultaneous loss of water) occurs at low (14.3-14.4 c) voltages. To compensate for water consumption, it has to be periodically adding through holes closed by traffic jams. If the moment of a sharp decrease in the level of electrolyte is missed, the irreversible lead sulfate will begin, and, as a result, the destruction of the active mass of the plates. Low-service rechargeable batteries
The low-service batteries possess both pronounced advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include small water consumption, high corrosion resistance of plates and small self-discharge. The disadvantage is the irreversible formation of calcium sulfate during rearrangements (conjugate with discharge of electrolyte) and deep discharges. To reduce the last phenomenon, some manufacturers make the combined design batteries: negative plates are performed from a calcium lead alloy, positive - from a minority (like older served batteries). The overwhelming majority of batteries manufactured by domestic plants are low-serviceable. In Europe, as in the whole world, low-service batteries are displaced by challenging.
Unqualified batteries
According to DIN standards, the "non-serving" battery means water consumption less than 6 g / a * hour. In practice, the maintenance-free batteries include those in the design of which a set solution aimed at achieving an extremely low flow of water consumption. As a result, it is assumed that the duration of the battery critical for the efficiency of the battery exceeds the battery life to its natural failure due to the natural corrosion destruction of the grilles. The fraction of antimony in the lead plates of non-servant batteries is less than 2.5%.
Parameters of batteries
The battery possesses 100% efficiency at 27 o C. with minus 18 o with battery efficiency drops by 40%. Therefore, in the conditions of the cold climate, the values \u200b\u200bof the operating parameters are attached to a special value.
Marking of batteries
Designations are applied to the battery, allowing you to unambiguously determine their basic parameters: Capacity, Cold Start current, type of housing. Designations of the date and / or place of production are not binding, therefore not standardized. The labeling can be divided (in relation to our conditions) into two large groups:
marking according to GOST;
marking according to DIN.
For example, according to the standard GOST Marking Battery 6st-55Pma The following information bears: 6 - the number of elements (2V) in the battery; ST - Purpose of the battery (starter); 55 - nominal capacity in the amps * hours; P - monoblock material (polyethylene copolymer with polypropylene); M - separator material (Miplast); A - general lid; Z - produced in a flooded and charged form. According to DIN standard labeling 5 74 012 068 carries the following information: 5 - a digit showing the "order" of the capacity of the tank; (5 - up to 100 a * hour, 6 - from 100 to 200 a * hour, 7 - over 200 a * hour); 74 - Capacity 74 A * Hour; 012 - the factory designation of the type of body, from which the size of the case is followed, the type of fastening, the location of the conclusions; 068 - Starting current 680 A according to EN standard. A number of foreign battery manufacturers label their batteries in a specific way, indicating not a capacity in the marking, but the value of the Cold start current to which the catalog can be compared the value of the nominal container. Batteries produced in the United States or manufactured for sale in the US market are also peculiarly marked. Additional code, its own for each manufacturer, allows you to find out the place and date of the battery production.
Operation of the battery
Operation of the battery on vehicles is allowed only with a serviceable relay controller (at a voltage of 13.8V to 14.2V), the leakage current is not more than 25mA, the electrolyte density according to Table 1 and the electrolyte level is not lower than the top edge of the plates.
When starting the engine, the starter duration of the starter should not exceed 10 seconds for carburetor cars, 15 seconds for diesel. If the start attempt failed, it is necessary to take a break for 1 minute.
When operating the battery at least once a month, it is necessary:
check and, if necessary, clean the battery from dust and dirt. The electrolyte that fell to the surface of the battery is removed by a rag moistened in a 10 percent solution of ammonia or soda;
check and, if necessary, clean the ventilation holes on the battery case;
check the level of electrolyte and, if necessary, to top up distilled water to a normal level (for batteries having traffic jams); You can add the electrolyte into the battery only in cases where it is precisely known that the decrease in the electrolyte level occurred due to its splashing (in the batteries served);
check the reliability of attachment of the battery in the installation socket and the fastening density of the connecting terminals on the pole termination of the battery; Connecting terminals to lubricate technical vaseline.
in the winter period, check the battery status is more common.
At least once a quarter check the degree of charges of the battery. If necessary, charge the battery according to the "CARING BATTERY" section.
The deep discharge of the battery at negative temperatures is unacceptable! This leads to the freezing of electrolyte and the destruction of the battery case.
Rechargeable batteries (AKB) are used everywhere as mobile and stationary power sources: in lifting and transport equipment, as elements of emergency and reserve energy supply, are the basis for autonomy of a huge diversity of portable devices. Understanding how the battery works, helps to properly charge the smartphone and extend the battery life of the car.
Historical Overview
The development of the first galvanic element is attributed to the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta. He conducted a series of experiments with electrochemical phenomena during the 1790s and approximately in the 1800th created the first battery, which contemporaries called "volt pillar". The device consisted of alternating zinc and silver disks separated by layers of paper or tissues that were moistened in sodium hydroxide solution.
These experiments became the basis of work on the quantitative laws of electrochemistry for Michael Faraday. He described the principle of operation of the battery and the first commercial electrical elements were created on the basis of the works of the scientist. . Further evolution looked like this:

Device and principle of operation
 The battery is called a device that converts the energy of chemical reactions into electrical. Although the term "battery" and means an assembly of two or more galvanic elements capable of such a transformation, in a broad sense, it also applies to a single element of this type.
The battery is called a device that converts the energy of chemical reactions into electrical. Although the term "battery" and means an assembly of two or more galvanic elements capable of such a transformation, in a broad sense, it also applies to a single element of this type.
Each such cell has a cathode (positive electrode) and anode (negative). These electrodes are separated by electrolyte, providing the exchange of ions between them. Electrode materials and components of the electrolyte are selected in such a way as to ensure sufficient electromotive power Between battery terminals.
Since electrodes contain limited potential of chemical energy, the battery will be exhausted during operation. Type of electroplating elements that are adapted to replenish after partial or full dischargeis called batteries. Assembly of such connected cells - a battery. The work of the ACB assumes the cyclic change of two states:
- Charging - the battery works as an electricity receiver, inside the cells of electrical energy is implemented in chemical changes.
- Discharge - the device functions as an electric current source due to the transformation of chemical reaction energy into electric.
Charging and Discharge Features
 The energy used to restore the capacity of the ACB comes from chargerconnected to the electrical network. To force the current to leak inside the elements, the source voltage should be higher than that of the battery. Significant exceeding the calculated charging voltage can lead to the output of the battery.
The energy used to restore the capacity of the ACB comes from chargerconnected to the electrical network. To force the current to leak inside the elements, the source voltage should be higher than that of the battery. Significant exceeding the calculated charging voltage can lead to the output of the battery.
Charging algorithms directly depend on how the battery is arranged and what type it refers. For example, some batteries can safely replenish their capacity from constant voltage sources. Others work only with an adjustable current source capable of changing parameters depending on the level of charge.
An incorrectly organized charge process can damage the battery. In extreme cases, it is possible to fire ankb or an explosion of its contents. There are intelligent batteries equipped with voltage control devices. The main parameters that should be considered when operating the electroplated batteries:

Types of batteries
Constructive batteries differ depending on the purpose and on the type of electrochemical reactions flowing into them. According to the method of their use, the AKB can be divided into two main categories:

In addition to the ability to recharge, rechargeable batteries, in comparison with conventional electroplating elements, are characterized by a high power density and good performance even at low temperatures. Depending on the composition of the electrolyte, the materials of the electrodes and design features, three common types of batteries can be distinguished.
Child-acid
These AKBs have a long history of popularity as autonomous power sources. Most of these batteries are made of lead plates or grids, where one of the decisions (positive electrode) is covered with lead dioxide in crystalline form. The electrolyte consisting of sulfuric acid is involved in lead and lead dioxide reactions to the formation of lead sulfate. Moving the ions of the latter forms the discharge current. The charge occurs by recovery of lead dioxide charge on the cathode.

This type of batteries was in demand for more than a hundred years due to the following features:
- a wide range of opportunities both in the production of strong and weak currents;
- reliability for hundreds of cycles in the presence of charge control;
- relatively low cost (lead is cheaper in translating the capacity than nickel, cadmium, lithium or silver);
- large shelf life during storage for rechargeable device;
- high voltage of a single cell;
- ease of manufacture (cast, welding, rolling).
Car battery is the most famous lead-acid rechargeable power supply. Widely applying them as traction in autofurges, loaders and other vehicles. Although most of them are portable, some can weigh several tons.
Alkaline batteries
In this type of batteries, electrical energy is generated as a result of chemical reactions in an alkaline solution using various electrode materials. The most famous of them:

Lithium rechargeable devices
 These include batteries with lithium anode or using lithium ions in the electrochemical reaction. At the time of the advent of the battery based on metallic lithium, we promising thanks to the impressive potential to miniaturization, but turned out to be extremely unstable due to the risk of leaking chemical reactions on the anode. Therefore, the main commercial success of this type of AKB took place with the use of lithium ion technologies, the essence of which was that, together with the refusal of the metal anode, the role of electrolyte was assumed by complex salts of lithium.
These include batteries with lithium anode or using lithium ions in the electrochemical reaction. At the time of the advent of the battery based on metallic lithium, we promising thanks to the impressive potential to miniaturization, but turned out to be extremely unstable due to the risk of leaking chemical reactions on the anode. Therefore, the main commercial success of this type of AKB took place with the use of lithium ion technologies, the essence of which was that, together with the refusal of the metal anode, the role of electrolyte was assumed by complex salts of lithium.
Due to the high density of the accumulated energy and an insignificant self-discharge, this type of battery is popular as a power source of consumer electronics. Chief flaw lithium batteries - Risk of unexpected fire from overheating. Even the most modern ones are equipped with additional electronic control Processes charge-discharge for safety. Lithium polymer batteries are more perfect in their class. Instead of liquid electrolyte, the solid polymer is used instead of liquid electrolyte. These batteries are easier than ordinary lithium ionicBut because of the high prices, they could not fully replace them.
Progress does not stand still. Now engineers and technologists are developing models of the principal device of the batteries of the future, which will replace lithium-ion batteries.
The appearance of nanomaterials can push the new twist of the evolution of batteries with such amazing properties as instant charging, elasticity, ultra-compactness and environmental safety.
The battery is a device that accumulates energy in a chemical form when connected to a DC source, and then gives it to transforming into electricity. It is used repeatedly due to the ability to restore and reversible chemical reactions. Discharged - recover again. Batteries are used as autonomous and backup power sources for electrical equipment and various devices.
Battery device
In cars typically apply. Consider their device. 
All elements are located in the housing, which is made of polypropylene. The housing consists of a container separated by six cells, and the covers equipped with a drainage system for the pressure and gas pressure and removal. Two poles (terminals) are positive and negative on the lid.
The contents of each cell represent a package of 16 lead plates, the polarity of which alternates. Eight positive plates combined by Barteque are a plus electrode (cathode), eight negative - minus (anode). Each electrode is displayed to the corresponding battery terminal.
Packages of plates in cells are immersed in the electrolyte - solution of sulfuric acid and water with a density of 1.28 g / cm3.
Between the plates of the electrodes, separators are inserted - porous plates that do not interfere with the circulation of electrolyte and do not interact with it.
A separate plate of the electrode is a grille made of metal lead, into which the reagent is pressed (namazan). The active mass of the cathode - lead dioxide (PBO2), anode - sponge lead.
The principle of batteries
 The principle of battery operation is based on the formation of the potential difference between two electrodes, immersed by electrolyte. When connecting the load (electrotechnical devices) to the battery terminals, electrolyte and active elements of the electrodes are reacted. There is a process of moving electrons, which is essentially electrical.
The principle of battery operation is based on the formation of the potential difference between two electrodes, immersed by electrolyte. When connecting the load (electrotechnical devices) to the battery terminals, electrolyte and active elements of the electrodes are reacted. There is a process of moving electrons, which is essentially electrical.
When the battery is discharged (load connection), sponge lead anode highlights positive bivalent lead ions in the electrolyte. Excess electrons move along an outer closed electrical circuit to the cathode, where the recovery of tetravalent lead ions is restored to bivalent.
When they are connected to the negative ions of the sulfur residue of the electrolyte, lead sulphate is formed on both electrodes.
Oxygen ions from cathode lead dioxide and hydrogen ions from electrolyte are connected, forming water molecules. Therefore, the electrolyte density decreases. 
When charging, reverse reactions occur. Under the influence of the outer ions of the bivalent lead, the positive electrode is given by two electrons and are oxidized in tetravalent. These electrons move to the anode and neutralize the bivalent lead ions, restoring sponge lead. On the cathode, by intermediate reactions, lead dioxide is formed again.
Chemical reactions In one cell we produce 2 B, so on the terminals of the battery from 6 cells and it turns out 12 V.
From the video you can find out more detail how the battery works: