Organization of the work of the maintenance and repair of cars. Organization of maintenance and repair of tractors with the development of a dissemination and washing plot. Organization of maintenance and repair on the site
The organization of the current repairs of rolling stock is one of the most pressing ATO tasks. Easy cars repair and waiting for it are very high, as a result of which up to 25% of the car park is not daily produced on line. Reducing the quality of TP due to its weak organization leads to a decrease in interremary runs and, consequently, to an increase in the volume of TP. In fig. 6.2 shows the scheme of the process of tru cars.
Consequently, the most important task of organizing the repair is to reduce the time of downtime cars in TP and his waiting.
The current car repair is made in one of two methods: aggregate or individual.
For aggregate methodcar repair is made by replacing faulty units with good, previously renovated or new from the revolving fund. Faulty aggregates after repair come to the current fund. In the event that the malfunction of the unit, node, mechanism or part is more expedient to eliminate directly by car during intersdency time (when there is enough intersdial time to repair the repair), the replacement is usually not produced.
The aggregate method allows you to reduce the car downtime in the repair, since the replacement of faulty units and nodes to good, as a rule, requires less time than dismantling and assembly works that are produced without depleting aggregates and nodes.
With an aggregate repair method, it is possible, and often it is advisable to repair aggregates, mechanisms, components and systems to produce outside this organization, in specialized repair organizations.
For individual methodrepair aggregates are not deleasing. Fortified aggregates (nodes) removed from the car after recovery put on the same car. At the same time, the time of downtime of the car in tr is more than in the aggregate method. In this case, the resource of aggregates, nodes and parts is used to more, since the best alight is achieved and fit in the seats.
Organization of production in TP zones is possible on the basis of two methods: universal and specialized posts.
Method of universal postsit provides for the execution of work in one post by the brigade of repair workers of various specialties or highly qualified workers.
Method of specialized postsit provides for the execution of works on several specialized to perform a certain type of work (by engine, transmission, etc.) posts.
The universal post TR is usually a visual ditch equipped with equipment that ensures that any work trial by car.
Each specialized post is equipped with equipment in accordance with the nature of the work performed on it. Specialization of posts TR allows the most mechanization of labor-intensive work, reduce the need for the same type of equipment, improve working conditions, use less skilled workers, improve the quality of work and pile productivity by 20 ... 40%.
Workplaces for replacement and truss engines are usually organized on isolated standard inspection of dead-end channels. Specialized work posts Walking TR engines can be of two types: for removing and installing engines and for trot engines on cars. They differ in the equipment and the number of simultaneously working performers.
Work post for tr engs is advisable to post near the engine (aggregate) site, next to the recruitment area, check and run the engines. The post is advisable to equip diagnostic equipment to ensure control and adjustment after the work of Tr. The nodes and parts of the engine, filmed at the current repair (head of the block, water pump, valves, springs, etc.), purified and repaired in a motor (aggregate) site.
Work posts specialized to repair other aggregates and systems are organized similarly to universal posts, with specialization of equipment. The specificity of the TP gas equipment requires the creation of specialized posts and organizing work on them special repair workers.
Among the specialized posts are created and equipped posts for the production of a number of diagnostic and adjustment work. The need for their organization is caused by the application when performing the works of tr special diagnostic equipment. To such posts, organized on the basis of economic considerations and improving the quality of work, belong:
posts of diagnostics and adjustment of car brakes equipped with roller brake stands;
posts of diagnostics and control the angles of car installation of cars, equipped with optical stands.
When organizing technological processes in production sites, the following principles take into account:
1) the specialization of production sites is carried out using work technology (plumbing, blacksmith, welding, painting, etc.) and in groups of aggregates, nodes, car parts (aggregate, electrical, battery, etc.);
2) ensuring short production links between the TP zone and each production site (spare parts warehouses, aggregates and sections), which seek to achieve in the organization of production sites;
3) Ensuring the technological sequence of operations of current car repair.
The organization of work in each production site is made in accordance with the technological sequence of TR operations. The adopted technological sequence determines the production of organizational and planning solutions of production sites for tru cars. Examples of decisions are further represented by sites and departments.
Aggregate plotit produces the repair of most car units (engine and its assemblies, adhesion gearbox, cardan transmission, rear and front axles, steering, etc.), and mainly replacing faulty parts. Such a distribution allows you to specialize workers on the repair of engines as the most complex unit.
The technological process of repair includes: car wash; pivoting in accordance with the repair volume; washing details and their defects; sorting parts and their complete set after repair; assembly and testing of the unit. Collected assembly works in the aggregate site, as a rule, are carried out on specialized stands, ensuring the possibility of an approach to the repaired unit from different sides, as well as the rotation and slope of the unit for the convenience of work.
Electrotechnical compartment.The electrical branch is carried out repair and control of generators, starters, ignition devices, instrumentation and other equipment. Disassembly assembly of electrical equipment units is carried out mainly on the workbenches using universal tools and special devices. Repair of parts and nodes includes replacing windings and isolation, wiring solder, plumbing work.
Rechargeable compartmentconsists of four zones: acidic (electrolyte cooking); charger; repair (repair and battery check); hardware (for accommodating battery charge equipment). Depending on the size of ATP, the specified zones are placed: in separate four rooms; in two rooms, combining the first with the second and third with the fourth zone; In one room, organizing the work of the first and third zones in the cabinets with individual exhaust ventilation.
Floor-mechanical section.It is restored and the manufacture of relatively simple details and assembly of nodes is mainly for the TP and the aggregate area.
In the mechanical and mechanical section, parts are processed under repair dimensions, make fasteners and other parts (bolts, studs, sleeves, etc.), prepare parts for welding and treated after welding, etc. In the overall laboriousness of TP, mechanical and mechanical works are 4 ... 12%.
Mednitskoy branch.Mednitskiy works are about 2% of the work on TP and are designed to restore the tightness of parts made mainly from color materials. It produces radiators, fuel tubes, tanks and restoration of other parts soldering.
Welding-tinty plot.Welding works are designed to eliminate cracks, breaks, damage, and attaching brackets, corners, etc. Apply electric arc and gas welding.
Carburetor plot.In large atoms, the maintenance of the power supply system can be performed in the carburetor site. In small organizations, these works can be combined with electromechanical work. The carburetor plot specializes in conducting control, adjustment and repair of carburetors, filters, etc. If there are carburetor and diesel engines in the ATO, there may be two geographically separated compartments.
Tire and tire-repair sections.They make disassembly of tires from the wheels, editing of disks and shut-off rings, disk color, control and minor tire repair, vulcanization of cameras, installation and balancing of wheels.
Plot for repair of gas equipment.For the repair of gas equipment of the car, a specialized plot is created. It monitors control, adjustment and repair of high and low pressure gearboxes, gas and gasoline valves, filters and other gas equipment.
Walking plot.It makes repairs and manufacture of pillows, backs, seats and inner upholstery of the bodies, winter covers for radiators and hoods of engines, as well as seat covers and awnings.
Joiner-body portion.It produces repair and production of cargo car bodies, wooden cabins, hooks and other details. Further work (repair of windows, door handles, loops, locks, etc.) are also carried out.
Blacksmith plot.In the blacksmith plot, repair and manufacture of parts with the use of heating (edit, hot riveting, forging parts) and springs repair. The main share of work is related to the repair of the springs - the replacement of broken sheets, rattling (restoration of the initial form) of sheets having reduced elasticity. The collected springs are experiencing a load. In addition, in the blacksmith plot, a variety of types of stepladders, crushes, brackets are manufactured.
Malar plot.Painting works are ending in the repair of the car body, therefore, cars come to the greasy section after performing all types of work.
When organizing work in the painting area, the largest number of jobs is created to prepare the car to the color. Coloring and drying cars are produced in special chambers.
To perform certain types or groups of works, the Trustees of rolling stock, taking into account their fire hazard and sanitary requirements, it should be provided for a separate premises for the following groups of work and trot of rolling stock:
a) washing, cleaning and other works of the EO complex, except for refueling cars in fuel;
b) post-work of MOT-1, T-2, general diagnosis, collapsible assembly and adjustment works of TR;
c) depth work of in-depth diagnostics;
d) aggregate, mechanical and mechanical, electrical and radio repair work, repair work, repair and manufacturing of technological equipment, fixtures and manufacturing equipment;
e) engine tests;
(e) repair of instruments of the system of carburetor and diesel engines;
g) repair batteries;
h) tire and vulcanization work;
k) blacksmith-free, mednico-radiator, welding, tires and reinforcement works;
l) woodworking and wallpaper work;
m) painting works.
Techno-economic indicators of the work of enterprises are largely dependent on the state and performance of equipment, the organization of its operation and care for it, timely and high-quality repairs.
An important role in the organization of maintenance and repair of equipment is given to the implementation of the planned maintenance and repair of equipment (PTOR).
The appointment of the PTOR system is to ensure the planning and implementation of maintenance and repair within certain time in the necessary sequence and scope of work.
The system of scheduled maintenance and repair of equipment is a set of organizational and technical measures to maintain documentation of maintenance and repair; Providing personnel supporting equipment in good condition and providing high-quality indicators of machines and devices established by regulatory documentation.
The PTOR system includes several types of maintenance and repair, which differ from each other in the content and use of technical means.
The PTLOR system provides: systematic observation and periodic inspection, allowing to identify and eliminate equipment malfunctions; maintenance of equipment maintenance during its operation in the established modes; planning and maintenance and repair; The use of progressive repair methods using mechanization and advanced methods for the restoration of parts and nodes.
Responsibility for the overall organization and conducting activities PTLOR is assigned to the chief engineer and the main mechanic (energy) of the enterprise.
The PTOR system includes two types of work: interremmer maintenance and scheduled repair work on time.
Maintenance of equipment. Maintenance (MA) is a range of operations to maintain the health and performance of equipment when used to be prescribed and stored; Performed during the work of the equipment, in the days of the disinfection of operational personnel and duty personnel of the repair service.
Maintenance In the process of using assignment equipment is performed in accordance with the instruction manual (maintenance instructions) developed by the enterprise. The cost of maintenance is due to operating costs.
The condition and performance of the equipment are recorded on the journal of acceptance and delivery of equipment for shifts. The correctness of the journal is controlled by the mechanic of the plant (shop) 1 time per day with compulsory written confirmation of control.
Regulated maintenance is carried out in a planned manner in accordance with the annual schedule. The complex of work on regulated maintenance includes: control over the technical condition of the equipment; inspection; elimination of detected defects; adjustment; replacement of individual components of equipment parts; Cleaning, lubrication.
The results of the inspection of equipment performed with the regulated maintenance are marked in the journal. These logs are the source material to establish the volume of work performed during the next planned repairs.
To control the condition of the equipment at the enterprise at least 1 time a quarter (on certain types of equipment - monthly) there are inspections of equipment engineering and technical staff of the main mechanic and energy service.
Types of repair. The PTOR system provides for the following types of repair: current (t 1; t 2) and capital (K).
Current equipment repairs are carried out both during the repair period and during the operation of the equipment to ensure the restoration of its performance; Consist in restoring or replacing individual parts and assembly units.
Depending on the nature and scope of work, the current repairs are divided into the first current (t 1) and the second current (t 2).
Overhaul is carried out in order to fully restore or close to full equipment resources with a replacement or without replacing its parts.
The cost of the current and capital repairs refers to the funds of the repair fund created at enterprises on repairs to repairs costs.
The nature and scope of work performed during capital and current repairs are established in accordance with the mortars of defects and are clarified in the process of disassembling and repairing equipment. Works aimed at improving technical and technological parameters relate, depending on the volumes, to modernization or reconstruction. They are planned at the time of major repairs and are funded by capital investments with an increase in the book value of fixed assets. Responsibility for their holding is assigned to the main engineer of the enterprise.
Forms of organization of repair. In the alcohol industry, intra-water and inter-wave forms of the organization of repair production are adopted.
In case of intracellular form, the centralized carrying out of the equipment repairs by the forces of the repair and mechanical workshop (electrical) of the enterprise is envisaged.
In the repair period to achieve high productivity, increasing the responsibility of performers for the repair of specific equipment into the repair team include workers serving this equipment. At the same time, the brigades should select the same type of equipment, which will allow you to more rationally use the qualifications of workers, devices and tools. The distribution of work among the members of the brigade is carried out by a brigadier in coordination with the mechanic of the plant (shop). Repair objects are distributed by the main mechanic in coordination with the chief engineer of the plant. Lists of repair brigades with fixed objects of repair are approved by order of the director.
In the inter-wave form of the organization of repair work, it is envisaged:
carrying out the aggregate repair of complex, large-sized and unique equipment in general and individual nodes on specialized repair factories, in shops and commissioning enterprises;
centralized provision of enterprises with spare parts and assembly units of sectoral purposes, as well as unified details and assembly units coming from machine-building factories producing relevant types of equipment, and from specialized plants for the production of spare parts.
Forms of repair in the enterprises of the alcohol industry, depending on the conditions of the organization of repair services.
The enterprises use the following repair methods:
the impersonal, in which the belonging of the recovered components to a specific instance of the equipment is not preserved. By organizing execution, this repair method may be aggregate (defective units are replaced by new or advanced) and detailed (replaced or restored separate parts, failed);
unreacted repair method, in which belonging to the restored component parts to a specific instance of the equipment is preserved.
The choice of the method is carried out on the basis of the conditions of the largest manufacturing and economic effect.
Planning and execution of repairs. All types of repair work are planning. The implementation of the repair plan is mandatory for enterprises as well as the fulfillment of the output plan of the main products.
The plan for repairing the equipment controlled by the Gosgortkhnadzor is made up separately from the plan for repairing the technological, energy and generalized equipment, should not be linked to it.
Annual repair plan is an integral part of technhpromplannov. The volume and range of repair work should ensure uninterrupted and efficient operation of the fleet of technological, energy and generalized equipment. The laboriousness and cost of work are compared with the corresponding techniques of technhpromplan and provide for the loading of workers and equipment to repair and attracted to the repair of services. Repair begins after the end of the production period.
The transfer of the period of stopping equipment for repairs is made in exceptional cases with the permission of the chief engineer of the enterprise, and for the equipment subordinate to the Gosgortkhnadzor, is agreed with the regional authorities of the Gosgortkhnadzor.
The annual repair plan is drawn up by the main mechanic service (energy), taking into account data on the availability of equipment and a list of works (form 5); equipment affairs; Acceptance and delivery of equipment for shifts, the results of its inspection with planned maintenance; Vedomosti defects; reports of previously executed repairs; standards of frequency and duration of current and capital repairs (forms 3, 4); applications manufacturing workshops; Duration of stopping enterprise for repairs.
Based on the annual plan for the repair of equipment, the total volume of repair work on the enterprise as a whole is determined.
Each enterprise is obliged to draw up annual and monthly scheduled schedules.
An annual schedule of planned enterprise repairs is made up by the main mechanic service (energy) and is approved by the chief engineer.
Monthly graphics are made up by the main mechanic basis on the basis of the annual with the refinement of the duty of stops for repair and their duration. In a monthly schedule, if necessary, the repairs not provided for by the annual.
The monthly schedule is approved by the main engineer of the enterprise and is the main document regulating the repair of equipment and planning the work of production in this month.
For each unit of equipment to be capital or current repairs with a periodicity of one year and more, the main mechanic service makes up the estimate of the cost of repairs.
The calculation of the estimates is made by expense articles: the main wages of workers; premiums; materials, semi-finished products, finished products (purchased and own production); workshop costs; Hostess expenses.
Salary and premiums are calculated in accordance with the provisions current on the enterprises on the tariff grid and the provision on the award for the qualitative performance and reduction of the repair time.
The costs of the article "Materials, semi-finished products, finished products" are determined by object standards of material consumption on the repair of this type of equipment or on the basis of the existing experience of organizing the equipment repair at the enterprise.
Workshop and public expenditures are determined as a percentage of the main wage of repair workers in accordance with the technical enterprise technologicalplane.
Tariffation of work during the repair of equipment is carried out according to the tariff qualification director, containing the production characteristics of all types of work with tariff discharges established for them.
For the conditional unit, the scope of work on overhaul with the established standard of labor costs (in the person-h) per unit of repair (Table 1) is taken.
Norms of spare parts for repair and operation. The range of spare parts is established based on the analysis of their consumption and based on the timing of the service and assembly units.
The nomenclature of spare parts includes:
details and assembly units whose service life does not exceed the length of the interrontal period;
parts and assembly units consumed in large quantities and the life of which exceeds the duration of the interrontal period;
details and assembly units, labor-intensive manufacturing, ordered by third party organization and limiting equipment operation;
details and assembly units to imported equipment, regardless of service life;
purchased products (ball bearings, cuffs, belts, chains).
The cost of consumption is developed according to the nomenclature of spare parts and are calculated based on the number of parts or assembly units per unit of equipment and their service life.
The range of spare parts for each type of equipment is made up by the main mechanic service and is made to the equipment.
Storage rates of spare parts. During the year in the warehouse of the enterprise, spare parts are stored, purchased products and materials in the amount that ensures the repair and operation of the equipment. As they spend, their stock is restored.
Storage rates are determined in accordance with the norms of annual demand in spare parts for each type of equipment. In determining the norms of the stock, it is not allowed to form an unjustifiably large reserves of individual parts.
The reserve standards are calculated based on the analysis of the range of spare parts, taking into account the averaged terms of the service of parts per unit of equipment, as well as the renewal time.
The number of spare parts of one name to be stored in the warehouse of the enterprise is determined by the formula
S \u003d BOH / C 3,
where in is the number of the same type of stock parts per unit of equipment; O - the number of units of the same type of equipment; And - the frequency of receipt of parts from the manufacturer, months (usually 3, 6, 12 months); K is a lowering coefficient, taking into account the same type of parts in the equipment group; C 3 - service life of the spare part, month.
The value K is shown below.

The revision and adjustment of the nomenclature and storage standards of the storage of spare parts, the company produces on proposals of the main mechanic service at least once a year, in the initial period of creating a spare parts fleet (for the first two or three years) and at least 1 time in two years - in the future .
Responsibility for the timely and complete support of the enterprise by all the necessary materials and spare parts is assigned to the head of the material and technical supply service, and for providing spare parts manufactured in repair and mechanical workshops (RMM), on the main mechanic of the enterprise.
Control over the storage conditions and the state of the park of spare parts at the enterprise carries out the service of the main mechanic.
Content task for coursework 1 Introduction2 2.1 Source data for calculation2.2 Selection and adjustment of source maintenance and repair standards2.3 Determination of the project coefficient of technical readiness and production ratio2.4 Annual mileage of all cars2.5 Calculation of quantity That and the cr of the entire park for the year 2.6 Definition of daily programs2.7 Determination of the consideration of that, tr and quantities of the main and auxiliary workers2.8 Determination of the number of posts and lines TO AND TR8.1 Determination of rhythm and potato production for KAMAZ5320 and KAMAZ-2.9 Determination of the number of posts in zones Tr 2.10. Distribution of workers on the posts of the zone2.11 Selection of technological equipment for the engine3 Organizational part3.1 Organization of production management TOP and TR3.2 Organization of the technological process of repair of aggregates3.3 Calculation of lighting3.4 Calculation of ventilation3.5 Fire safety3.6 Safety 4 List of sources used1 Introduction Transportation is one of the key sectors of the national economy. In modern conditions, the further development of the economy is unthinkable without well-established transport support.
From its clarity and reliability, the labor rhythm of the enterprises of industry, construction and agriculture, the mood of people, their performance is largely dependent. Socio-economic transformations that occurred in our country over the past 10 to 12 years have violated the working air and management system of the transport sector.
Most public transport facilities in the regions of Russia are currently privatized, a sufficiently large number of individual carriers and small private enterprises participating in the development of passengers transport appeared. The demonopolization of public transport led to the fact that the system of its management has become a lesser extent managed and more expensive.
Currently, transport works in conditions when there was a tendency to stabilize the real sector of the economy and income of the population.
Passenger transport is one of the significant branches of the economy.
In the absence of many citizens of personal vehicles, the problem of timely and qualitative satisfaction of the demand for transportation develops from a purely transport to a social, determining population relations not only to the quality of transport services provided, but in general, the processes that occur in the region and the country. Such conditions are needed to joint efforts by the specialists of transport workers, the central and regional governments, which should be aimed at improving the functioning of the transport complex.
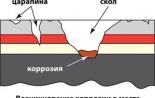
During the operation of the car, its working properties are gradually deteriorating due to the wear of parts, as well as corrosion and fatigue of the material from which they are made. There are failures and malfunctions that are eliminated during maintenance (COM) and repair. And the car is considered to be a car that meets all the requirements of regulatory and technical documentation.
A working car, in contrast to the serviceable, must meet only the requirements, the execution of which allows it to be used to appoint it without a threat to traffic safety. Damage is called the transition of the car into a faulty, but efficient condition; Its transition to an inoperable condition is called refusal. The repair is a set of operations to restore the health or working capacity of products and the restoration of product resources and their components.
The need and feasibility of car repair are due primarily to the inequality of their components (assembly units and parts). It is known that creating an equalization car, all the details of which would wear evenly and had the same service life, it is impossible. Therefore, in the process of operation, cars undergo periodicals and, if necessary, the current repair (TR), which is carried out by replacing individual parts and aggregates.
This allows you to support cars in a technically good condition. Current repairs must ensure the guaranteed operation of the car on mileage until another scheduled repair, and this mileage must be no less run to the next TO-2. In case of failures, non-planned tr, in which they replace or restore partsand assembly units in the volume determined by the technical condition of the car. Capital repairs must ensure health and full (or close to the full) resource of the car or the unit by restoring and replacing any assembly units and parts, including the basic.
Much attention was constantly paid to the organization of car repair in our country. In the early years of Soviet power, the car park in our country consisted of only several thousand cars, mainly foreign production. For the organization of car production in the young Soviet Republic, there was no material base, no experience or trained personnel, so the development of auto repair production is historically ahead of development domestic automotive industry. 2. Calculator2.1 Initial data for calculation The section provides all the necessary data based on analysis.enterprises and accounting prospects for development.
The source data is presented as table 2.1.
What we will do with the material obtained:
If this material has proven to be useful for you, you can save it to your social networking page:
| Tweet |
More abstracts, coursework, thesis on this topic:
Draft Point of Technical Services and Current Repair of Cars with the development of the technological process of the car clutch gas - 3110
It has greater maneuverability, good adaptability and permeability in various climatic and biographical conditions. Automobile transport plays an important role in the country's transport system. The operation of road transport is ensured by the normal functioning of enterprises.
Course work Maintenance and repair of electrical equipment and cars
We will read the site: "Coursework maintenance and repair of electrical equipment and cars"
Course work "Designing a brigade organization and remuneration at the enterprise Maintenance Station LLC Tambovskaya Stara
Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education .. Moscow State Agroennisher .. Named in Goryachkin ..
Design of the automotive site for the organization of maintenance and repair of car brand GAZ-33021
The intensive growth of the automotive park requires a sharp increase in production work when servicing and repairing rolling stock, and complication .. These costs and losses can be significantly reduced by broad mechanization. Project tasks of the project task is to carry out calculations related to technical and economic functioning.
Car repair. a common part
Methodical guidelines for the course and thesis design on discipline Methodical instructions are intended to provide practical assistance to students when performing a course project on discipline Repair of vehicles .. on course and graduation design .. section technological part ..
Design of the maintenance and repair of fuel equipment on ATP
The main task of organizing and planning production in each motor transport company is a rational combination and use of all .. enterprises of road transport in their purpose are divided into .. Automotive enterprises are integrated enterprises carrying out freights or ..
Calculation of the manufacturing program for maintenance and repair of cars
Rechargeable and paints and varnishes are individually from others, like lubricating, warehouse for storing spare parts and materials. Post .. The leaf indicates the following conditions (all the designations are listed in .. in this area 7 posts. There are posts in 2 rows, the 2nd row is at an angle of 30 degrees relative to ..
Maintenance and maintenance of electrical equipment of cars
On the road, follow the testimony of control and signaling devices, which characterize the quality of the AB recapinion - when sunbathing a red alarm .. The spots of a white fleet from the spilled electrolyte are easily removed by the rag. With the help of a float, the density of the electrolyte in each bank is checked with a scale. .
Business plan for the production activities of the enterprise for repair and maintenance of cars
The development of this activity will be accompanied by the development and implementation of new equipment intended for repair and diagnostics .. At the first stage, a small staff is formed in an amount of 7 people .. customers of the company are individuals with medium and events that wish to repair either ..
The organization of work on the maintenance of passenger cars is based on their affiliation to the state or individual sector. For maintenance of public sector cars in motor transport enterprises, schedule plans covering the entire rolling stock market. The schedule is a month for a month, the basis of the periodicity corresponding to certain operating conditions, taking into account the actual daily mileage.
The organization of car maintenance work can be a brigade or aggregate-precinct.
The brigade form of maintenance organization provides for the creation of specialized brigades for work on all aggregates and vehicles of the vehicle within this type of maintenance and repair. In aggregate-precinct form, separate production sites are organized, designed to perform all maintenance and repair work and the repair of certain aggregates and nodes of the vehicle attached to these areas.
Maintenance of passenger cars of the individual sector is carried out at car maintenance stations (STA). Cars entered on Staa are subject to a mandatory car wash, and then enter the reception site to determine their technical condition. Adopted cars are sent to the maintenance zone, and then to the issue zone. Before issuing a car, the owner is conducted by checking the volume and quality of work that employees of technical control departments are performed directly related to maintenance and repair processes.
Maintenance and repair of vehicles are distributed between production sites in accordance with the technological scheme of work. At the maintenance stations, two methods of maintenance of maintenance are used depending on their specialization and volumes of work: on universal and specialized posts.
Method of maintenance at universal posts It is to fulfill all the works of this type of service (except for cleaning and washing) in one post by a group of performers of all specialties (locksters, lubricants, electricians) or workers, universal. In the other case, each specialist performs its part of the work in a certain technological sequence. During maintenance at universal posts, it is possible to perform a different scope of work, which is typical for the STA, serving cars of different brands, when various time is required to perform work.
The disadvantages of service on universal posts should include relatively low performance and the need for multiple duplication of the equipment of the same name. The advantage of this method is a clearer responsibility for the quality of the work performed and the possibility of combining maintenance work with current repairs as needed.
During maintenance on specialized posts The volume of work of this type of maintenance is distributed over several posts. Posts and workers on them, as well as equipment equipment specializes, taking into account the homogeneity of operations or rational compatibility.
Maintenance on specialized posts can be a flow and operational posting. With a streaming method, specialized posts are located directly in the direction of movement of cars or in the transverse direction, more often in a straight line. A prerequisite at the same time is the same duration of the stay of the car at each post.
The set of posts is a streamline service line. With this method of maintenance organization, the loss in time for moving (cars and workers) is reduced and manufacturing areas are more economically used. Conveyors are used to move cars from the post to the post in this case.
A well-known disadvantage of any streamline service is the impossibility of changing the list of work on any of the posts. To avoid this, as well as to ensure the movement of the serviced cars from the post to the post in the Tracker installed for the production line, provide for backup "sliding" workers for further emerging operations. Often the functions of the "sliding" workers are assigned to the brigadiers.
To ensure the fulfillment of the installed list (volume) of maintenance work in this post at the regulatory costs of working time and the calculated duration of the car, technological maps can be used that can be operating and technological and posts.
Operational and technological maps are a list of maintenance operations, compiled in the technological sequence, by aggregates, nodes and car systems (engine, clutch, gearbox, power supply system, lubricant, etc.).
Post technology cards include a list of work on each workplace performed at this place.
Based operating and technological card A technological card is compiled for the workplace. It contains a list of operations in their technological sequence performed by this working (performer), tools, equipment, description of the place of execution (from above, from the bottom, on the side), the number of service places of the same name, the time rate and technical conditions.
To ensure convenient access to the car on top, on the side and bottom during maintenance, viewing dials are used, lifts, lifts, etc. The largest distribution at maintenance stations received inspection ditches and electromechanical lifts of various types.
When carrying out car maintenance in motor transport enterprises and at maintenance stations, the diagnosis of the technical condition of cars is widely applied.
Diagnostation is a technology for determining the technical condition of the vehicle (unit, node) without its disassembly and issuing a conclusion about the need for prevention or repair. The diagnosis primarily subjected to assembly units affecting the safety of motion, as well as the most responsible and expensive in production and repair. Diagnostics are performed on specialized lines or universal posts. In addition, it is partly possible to organically include in a streamline maintenance line and control the state of the assembly unit in the process of performing work.
To diagnose the technical condition of the units and components of the car, various stands and instruments are widely used, with which you can estimate the technical condition of the car before carrying out maintenance operations and monitor the quality of the work performed.
Questions theme: 1. What is the essence of a planned warning system, then passenger cars? 2. What is the order of cargo movement at the maintenance station? 3. What are the tasks of the car diagnostics?
Introduction
1. Technological part
1.3 Determination of the annual work capacity
1.4 Determining the number of production workers
1.5 Determination of the number of posts
1.7 Definition of the production area of \u200b\u200bthe site
1.8 Planning Decisions of Buildings
2. Organizational part
3.1 Compliance with safety requirements when performing work in the site
4. Energy saving in the site
4.2 Max of thermal energy saving
Conclusion
Literature
Introduction
Automotive passenger transport is the main type of transport for trips to short and medium distances. Automobile transport is one of the largest industries of the national economy with complex and diverse equipment and technology, as well as a specific organization and management system.
For the normal operation of road transport and its further development, it is necessary to systematically update the car park and maintain it in good technical condition. Ensuring the necessary number of rolling stock fleet can be carried out in two direction:
purchase of new cars;
park accumulation due to car repair.
Car repair is an objective necessity, which is due to technical and economic reasons.
Firstly, the needs of the national economy in cars is partially satisfied by the operation of renovated cars.
Secondly, the repair ensures further use of those elements of cars that are not completely worn out. As a result, a significant amount of previous labor remained for the manufacture of these parts is preserved.
Thirdly, the repair contributes to saving materials going to the manufacture of new cars.
The technical perfection of cars from the point of view of their durability and labor-intensity of repair should be assessed not from the position of the possibility of correction and restoration of worn items in the conditions of repair enterprises, but from the position of the need to create cars requiring only minorly integrated collaborations related to the change of interchangeable rapidly wear parts and nodes.
An important element of the optimal organization of repair is the creation of a necessary technical base, which predetermines the introduction of progressive forms of labor organization, an increase in the level of mechanization of work, equipment productivity, reducing labor costs and means.
The goal of the course project is the design of the electrical department, the determination of the complexity of work, the number of workers, the selection of equipment, the development of a technological card.
1. Technological part
1.1 Selecting source data for design
The initial data for technological calculation is selected from the task for design and from regulatory literature.
Initial data from the design task:
Number of population in the service area - p \u003d 9000 people;
The number of cars for 1000 inhabitants - Aud. \u003d 225 units;
Middle Annual Mileage of the Car - LG \u003d 14000 km;
The regulatory specific complexity of that and tr per 1000 km of mileage - TN TO AND TR \u003d 2.43 CH / 1000KM;
The coefficient that takes into account the number of customers using the service of the auto repair organization - KKP \u003d 0.81
The climate is moderate for a warm.
Initial data from regulatory literature:
Days of downtime cars at that and repair, dto and tr, day / 1000 km;
Standard of labor intensity of diagnostic works, person-h;
Periodicity standards, km;
Interremmer mileage, km;
Number of days of car downtime in major repairs, DK, DN.
1.2 Determination of the number of cars served in a given area
Annual car service serviced in a given area is determined by the formula
car maintenance equipment
where P is the number of residents in the serviced area;
Aud. - the number of cars for 1000 people accepted according to traffic police;
KKP - a coefficient that takes into account the number of customers using the PAS service, which is assumed to be 0.75-0.90;
1.3 Determination of the annual labor complexity of work
Annual work on both TR for urban pass is determined by the formula
Where LG is the annual mileage of the car;
Asto - the number of cars serviced;
tTO, TR - the specific complexity of that and tr per 100 km of mileage, a person of hours / 1000;
the specific complexity of that and tr per 100 km of mileage, the person's hours / 1000 is determined by the formula
Where tnto, Tr - the regulatory specific complexity of the way and tr per 1000 km of mileage, the person-hours;
K1 is a coefficient that takes into account the number of work posts (up to 5-1.05, from 6 to 10-1.0, from 16 to 26-0.9, from 26 to 35-0.85, over 35-08);
K3 - coefficient taking into account the climatic zone
tTO, Tr \u003d 2,4310,9 \u003d 2,19 people
The post is performed 50% of the work, repair of nodes, systems and aggregates is 14.9%
TTO, Tr \u003d 502820,50,147 \u003d 2891 people-
1.4 Calculation of the number of production workers
For the Zone and TR, in which work is performed directly by car, the technologically necessary number of workers' RT, people. Determine the formula
where the FM is the annual workplace time fund, h. (from the production calendar);
kN - coefficient of uneven loading of posts,
The utilization factor of the working hours of the post, (Table 9).
we accept 2 people.
1.5 Calculation of the number of posts Zone TO-2
Number of posts n are determined by the formula
where TN is the annual volume of posting, a person-hours,
Coefficient of unevenness of cargo receipt for post, (\u003d 1.15),
RSR is an average number of workers in one post, (Table 8),
FP - Annual Fund of Working Time Post, Human Hours,
The utilization factor of the work time (\u003d 0.94-0.95)
take 1.
1.6 Selection of technological equipment, technological and organizational equipment
Table 11 - Technological equipment, technological and organizational equipment
|
Name |
Sizes in terms of, mm |
Footprint, |
Notes |
||||
|
Pneumo-rogging for nuts wheels |
|||||||
|
Hydropodetener |
|||||||
|
Dvigotel removal device |
|||||||
|
PPP removal fixture |
|||||||
|
Installation for removing oil and refueling from the engine system |
|||||||
|
Installation for refueling and removing coolant |
|||||||
|
Installation for removal of the spring front suspension |
|||||||
|
Truck for transportation of units |
|||||||
|
Tool trolley |
UNIOR EUROPLUS_920PLUS1. |
||||||
|
Merchant workshop |
|||||||
|
A set of keys |
|||||||
|
The device for removing the exhaust gases |
VEGA 3515/100 UEH |
||||||
|
Installation for removing the rear axle gear |
|||||||
|
Washbasin |
|||||||
|
Selection stelezh |
|||||||
|
Installation to replace steering mechanisms |
|||||||
|
Capacity for oil drain (polyethylene) |
1.7 Calculation of the production area of \u200b\u200bthe plot TR
Plot area Determine by the formula
F3 \u003d FA HZ CPL,
Where the density coefficient of the density of the equipment and posting posts, [p. 54,14],
xs - coefficient
fA - Square occupy a car in terms of m2.
F3 \u003d 9.6 6,52 \u003d 124.8 m2
2. Organizational part
Technological card removal of gearbox from a passenger car
|
Name |
Rate of time |
Intrification |
Technical conditions and punishment |
||
|
Remove the intermediate cooler and engine cover |
|||||
|
Remove the battery |
|||||
|
Disconnect the air rash sensor connector |
|||||
|
Remove the air filter hose and weaken the bolt of the clamp |
|||||
|
Remove the clamp and then the top cover of the air filter |
|||||
|
Unscrew the mounting bolt and then remove the air filter assembly |
|||||
|
Unscrew four bolts and then remove the battery shelf |
|||||
|
Remove the negative terminal from the gearbox |
|||||
|
Disconnect the vehicle speed sensor connector and turn off the reverse lamp |
|||||
|
Remove the management cable assembly removing locking pins and clamps |
|||||
|
Remove the coaxial executive cylinder tube |
|||||
|
Unscrew the four mounting bolts of the top of the gearbox |
|||||
|
Maintain the engine and gearbox |
Using special equipment |
||||
|
Unscrew the bolts and then remove the isolation of the gearbox |
|||||
|
Remove the front wheels |
|||||
|
Raise vehicle |
|||||
|
Unscrew the connecting bolt of the steering column |
|||||
|
Remove the lower protection of the vehicle |
|||||
|
Drain the liquid of the steering mechanism system through the return tube |
|||||
|
Disconnect the injection hose of the steering steering system from the pump |
|||||
|
Merge gearbox transmission oil through a drain hole |
|||||
|
Disconnect the lower lever, the ball support of the tip of the transverse steering thrust, the traction of the transverse stability stabilizer from the front swivel fist |
|||||
|
Replete mounting bolt roller support |
|||||
|
Unscrew the mounting bolts from the subframe, support the subframe |
With the help of jackt |
||||
|
Disconnect drive shafts from gearbox |
|||||
|
Disconnect the connector from the starter and remove the starter |
|||||
|
Remove the gearbox cover |
For all-wheel drive car remove the gearbox body assembly |
||||
|
Replete assembly bolts of the lower part of the gearbox and the left side cover and remove the gearbox assembly supporting it |
With the help of jackt |
3. Labor protection and the environment
3.1 Compliance with safety requirements when performing work in the department
General Safety Requirements include the technical readiness of the machine, its start, inspection after the end of work and troubleshooting. The workplace should be convenient and ensure a good overview of the work front, equipped with fences, protective and safety devices and devices.
Increased safety degree is achieved by the use of safety devices.
Before ademing to the operation of mechanics and their helpers, receipt receive instructions containing also safety requirements. Every year, persons serving machines check knowledge in the volume of manufacturing instructions. The results of the knowledge check are drawn up and enter the certification and verification of knowledge. Before starting work, you must submit a warning beep. It is impossible to start working with insufficient lighting.
Work should be discontinued during damage to safety devices and in emergency situations. At the end of work, all combustible and lubricants must be passed onto the warehouse. The switch before the main power cable of the power plant with the electric drive must be turned off and closed on the lock. When an accident or accident, stop the power plant before the administration representative comes. Failure to comply with safety regulations can lead to industrial injuries.
Modern machines and equipment are equipped with means of protecting workers from vibration, concussions, industrial noise, dust.
To prevent electric shock in the lighting or control network, the electrical current voltage up to 36 V is used; isolate and fencing electrical equipment and wires under voltage; Install the protective equipment that turns off electrical equipment at hazardous loads in the electrical circuit; Ground electrical equipment.
3.2 Compliance with the requirements of industrial sanitation
Production sanitation is a system of organizational events and technical means that prevent or reducing the impact on working harmful production factors. The main dangerous and harmful production factors are: increased dust and gas supply of the working area; increased or reduced air temperature of the working area; increased or reduced humidity and air mobility in the working area; increased noise; increased level of vibration; elevated level of various electromagnetic emissions; lack or lack of natural light; Insufficient illumination of the working area and others.
Dangerous and harmful production factors:
Physical;
Chemical;
Biological;
Psychophysiological.
Borders of production sanitation:
Air healing and normalization of microclimate parameters in the working area;
Protection of noise, vibration, electromagnetic emissions, etc.;
Ensuring the required standards of natural and artificial lighting;
Maintaining in accordance with the sanitary requirements of the territory of the organization, the main production and auxiliary premises.
Production microclimate is one of the main factors affecting the human health and human health. Meteorological factors strongly affect the vital activity, well-being and human health. An unfavorable combination of factors leads to a violation of thermoregulation.
In accordance with GOST 12.0.003-74 "SSBT. Dangerous and harmful production factors. Classification »Increased dust and gas surgery working area refers to physically hazardous and harmful production factors.
Many things get into the body lead to acute and chronic poisoning. The ability of the substance to cause harmful actions on the vital activity of the body is called toxicity.
3.3 Ensuring Environmental Protection
Automobile transport is one of the powerful sources of environmental pollution. The direct negative impact of cars on the environment is associated with emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere. The indirect influence of road transport on the environment is due to the fact that the automotive roads, parking, service enterprises occupy an increasing and daily increase in the area necessary for human life.
Work on environmental protection on each AP should provide for the following basic activities:
Training staff of UP and drivers the basics of environmental safety;
Improving the technical condition of the rolling stock produced on line, fuel economy, reduce the empty mileage of cars, the rational organization of the road;
Organization of warm parking, electric heating of cars and other activities in order to improve the environment;
Ensuring the serviceability of cars, the correct adjustment of the operation of the engines;
Elimination of fuel, oil, antifreeze in the parking lot;
Cleaning the resulting protesters of operational materials, filling with sand or sawdust;
Collecting spent oils, other liquids and passing them on prefabricated items;
Periodic verification on the smoke and prohibition of the release of cars on line with a large smoke of gases;
Organization and ensuring the effective purification of effluent of household, industrial and stormwater with the help of treatment facilities, the introduction of revolving water supply on the AP;
Systematic control over the state of components and assemblies of cars in order to reduce noise;
If there is an active boiler in the territory of the existing boiler, it is necessary to provide measures to reduce the contamination of the atmosphere of harmful emissions (smoke, soot, gases), in the future - the boiler house in the territory of the ATO and the transition to central heating.
Territory, industrial, auxiliary, sanitary household premises and car storage sites must comply with applicable sanitary standards and rules. Garbage, production waste, etc. It is necessary to take timely to be removed in specially reserved places. The territories of enterprises must be equipped with drainage. Where acids, lumps and petroleum products are used, the floors should be resistant to the effects of these substances and do not absorb them.
Premises for the storage and maintenance of cars, where it is possible to rapidly increase the concentration of toxic substances in the air, the automatic control system for the state of the air in the working area and the alarms should be equipped.
The organization should be equipped with economic and drinking and industrial water supply, as well as industrial sewers in accordance with the norms.
4. Energy saving in the electromechanical site
4.1 Events to save electricity
The main routes of reduction of electricity losses in industry are:
Rational construction of the power supply system;
Laying networks in polyurethane foam isolation;
Wiping the electric light bulb from dust;
Do not leave electrical appliances in standby mode;
Painting walls and ceilings in white;
Maximize natural lighting;
Using solar panels;
Replacement of incandescent bulbs by energy-saving lamps;
Transfer of loads from the hour of the maximum power system to other hours;
Application of 2 tariff counters;
Reducing the growth of energy tariffs;
Development of a methodology for determining specific energy consumption.
4.2 Events to save thermal energy
The successful use of energy-saving technology is largely predetermined by the norms of technological and building design of buildings and, in particular, the requirements for the parameters of internal air, specific heat, moisture-, steam, gas divisions.
Significant reserves of fuel savings are concluded in the rational architectural and construction design of new public buildings. Savings can be achieved:
Appropriate selection of shape and orientation of buildings; - voluminous planning solutions; - the choice of heat-protective qualities of exterior fences; - Selecting the walls differentiated on the sides of the walls and size of windows.
Careful installation of systems, thermal insulation, timely adjustment, observance of the timing and composition of maintenance and repair of systems and individual elements are important reserves of SER savings.
For a radical change in the state of affairs using heat for heating and hot water supply of buildings, we need to implement a whole range of legislative measures that determine the procedure for designing, construction and operation of structures for various purposes.
There must be clearly formulated requirements for design solutions of buildings that provide reduced power consumption; Revised methods for rationing use of energy resources. The tasks of economy of heat for heat supply of buildings should also be reflected in the relevant plans of the social and economic development of the republic.
Equipment of heat consumers with means of control and consumption control makes it possible to reduce energy costs at least by 10-14%. And when taking into account the change in wind speed - up to 20%. In addition, the use of phasadane regulation systems of heat for heating makes it possible to reduce heat consumption by 5-7%. Due to the automatic regulation of the work of central and individual thermal points and reduce or eliminate the loss of network water, it is achieved up to 10%.
With the help of regulators and tools for operational control of temperature in heated rooms, you can consistently withstand comfortable mode while reducing the temperature by 1-2C. This makes it possible to reduce to 10% of the fuel consumed on heating. Due to the intensification of heat transfer of heating devices with the help of fans, a reduction in thermal energy consumption is reached up to 20%.
The heat insulation of the ceiling by fiberglass mats reduces heat loss by 69%. Payback to the cost of an additional thermal insulation device - less than 3 years. During the heating season, savings were achieved compared with regulatory solutions - in the range of 14-71%.
The use of low-density concrete with perlite type fillers or other lightweight materials for the manufacture of enhancement structures of buildings allows 4-8 times to increase the thermal resistance of organizations.
The main directions of work on saving thermal energy in the systems of heat supply of buildings is:
Development and application when planning and in the production of technically and economically well-founded progressive heat-consumption rates for the implementation of the economy regime and their most effective use;
Organization of effective discount of vacation and consumption of heat;
Optimization of operational regimes of thermal networks with the development and implementation of commissioning events;
Development and implementation of organizational and technical measures to eliminate non-production thermal losses and leaks in networks.
Conclusion
In this course project, the following tasks were resolved:
The initial data is selected;
Determined the number of cars serviced in a given area;
The annual labor-intensity of work is determined;
The number of production workers is determined
Determined the number of posts of the site;
The selection of technological equipment, technological and organizational equipment;
The production area of \u200b\u200bthe projected diagnostic area is determined;
The layout of the site is made
List of sources used
Standards
1 GOST 2.105-95. ESKD. General requirements for text documents.
2 GOST 21.204-93 Conditional graphic notation and images of elements of master plans and transportation structures.
3 TKP 248-2010 (02190). Maintenance and repair of automotive vehicles. Norms and rules for conducting.
Literature
Main literature
Internet sources.
5 Kovalenko N.A. Technical operation of cars: Tutorial / N.A. Kovalenko, V. Plobach, N.V. Veprintsev. - MN, 2008.
6 Kovalenko N.A. Technical operation of cars. Course and graduation design: Tutorial / N.A. Kovalenko, ed. ON THE. Kovalenko - Mn., 2011.
7 Lochnitsky I.A. Energy saving / I.A. Lochnitsky. - Mn., 2004.
9 Methodical guidelines for the course design of technical operation of cars.
10 Designing road transport enterprises: textbook / M.M. Bollard; Ed. MM Bollard. - Mn., 2004.
11 Falcon T.S. Labor protection: Tutorial / TS. Falcon; Under total. N.V. Ovchinnikova. - Mn., 2005.
12 Sukhanov B.N. Maintenance and repair of cars: a guide on the graduation design / B.N. Sukhanov, I.O. Borzov, Yu.F. Bedlev. - M., 1991.
additional literature
13 Turkevsky I.S. Labor protection in road transport: Tutorial / I.S. Turkevsky. - M., 2009.
14 Novovehina L.I. Handbook on technical drawing / L.I. Novichikhina. - Mn., 2004.
Similar documents
Annual car service. Determination of the approximate value of annual labor intensity. Determining the number of work posts of the maintenance and repair station. The total annual labor complexity of cleaning and washing works.
course work, added 11.02.2011
Rationale of the capacity of the designed car maintenance station. Calculation of the annual volume of maintenance stations and the determination of the number of production workers. Development of the technological process of engine diagnostics.
thesis, added 14.07.2014
Justification of the choice of the territory on which it is planned to place a car maintenance station. Calculation of the production program. Determination of the annual work, the selection of technological equipment and the calculation of the number of workers.
coursework, added 04.06.2012
Draft Maintenance Maintenance Station: Annual Work, Personnel, Production Areas and Support Services. Technological equipment for diagnosis and repair: principle of operation, device.
course work, added 01/23/2011
Indicators of the use of cars in the farm. Calculation of the number of current repairs and maintenance, replacement program, the annual time consideration of work, the number of workers, the area of \u200b\u200bthe plot. Determination of the cost and price of one norm-hours and Tr.
thesis, added 02/16/2016
Characteristics of the technical service station of LLC Transmission. Cars served for a hundred. Calculation of the annual labor-intensity of maintenance and repair of cars, selection of equipment. Calculation of the number of production workers.
test work, added 01/22/2014
Faults of nodes, connections and parts affecting the safety of motion. Determination of the technical condition of the vehicle and the establishment of the volume of repair work at the service station. Maintenance and repair of cars.
thesis, added 06/18/2012
Justification of the expediency of opening a maintenance station. Overview of VAZ cars, ZAZ sold and serviced at a hundred. Place of location, profile and goal of STR. Sales Market Analysis, Competition, Marketing Strategy.
thesis, added 06.06.2011
Calculation of the source data and production program. Distribution of complexity of maintenance work and auxiliary work on industrial zones and sites. Annual schedule for cars. Calculation of technological equipment.
coursework, added 11/02/2011
Technological calculation of the car maintenance station. Annual work, distribution of it by species and place of implementation. Calculation of the number of posts and the automale offer of the projectable STA. Determining the need for technological equipment.