Skoda liaz truck tractor. Difficult story
The beginning of the history of the company for the production of cars Skoda Liaz is considered the very beginning of the 50s of the last century. It was then that the leadership of Czechoslovakia decided to transfer the production of Skoda trucks from the AVIA plant in Letняany to the city of Liberec, which was located in the north of what was then Czechoslovakia.
The birth of an enterprise
This was preceded by a number of measures for the reconstruction of small enterprises in the settlements of Rynovice, Mnichovo Hradiste, Sviyany-Loukov and Liberec proper. All of them joined the Liberec Automobile Plants association, which, in turn, was part of AZNP, the main Skoda enterprise located in the city of Mlada Boleslav. A year later, LIAZ (Liberec Automobile Plants) gained independence, but the trucks produced had a double brand - Skoda LIAZ - until 1984.
Models 706 D and 706 R Features and Specifications
The base for the first truck, which the enterprise began to produce, was the Skoda 706 D. With a carrying capacity of 7 tons and a power of 110 liters. with., trucks during the war were produced for the needs of the Wehrmacht. Before the resumption of production in 1946, modernization was carried out. The car was equipped with a new cab and increased power by 25 liters. With. The updated version received the 706 R index and was presented in 1949 in Moscow at the Czechoslovak Motor Show. On its basis, vans, buses, dump trucks and special-purpose vehicles were subsequently produced. The use of a common base greatly simplified the ordering of spare parts, regardless of the intended use of the car.
The development and production of Liaz trucks was established even before the war.

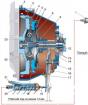
A diesel 6-cylinder engine was installed on the truck, the design features of which made it possible to remove the pistons and connecting rods from the block without dismantling the entire engine. Glow plugs were located in each cylinder. The fuel pump was equipped with a centrifugal distributor that supplies fuel to the injectors. The water cooling system was equipped with a thermostat.
The maximum declared speed of the car was about 53 km / h, in fact, it rarely exceeded 40 km / h with an average fuel consumption of about 30 liters per 100 km. The diesel engine was paired with a 5-speed manual transmission.
The car was equipped with an engine brake, which was not found in most diesel trucks of the time.
The 706 R's cab is spacious, free to accommodate the driver and three passengers, and was made of wood sheathed in steel sheets.

New model - 706 RT and its modifications
In 1957, the 706 R was replaced by a new model - the cabover RT. It was she who soon became a truly massive phenomenon on the roads of the Soviet Union. Based on this model with 160 hp engine. With. and direct fuel injection were produced dump trucks RTS1 (unloading on one side), RTS3 (unloading on three sides), bus chassis RTO, truck tractor Skoda RTTN and other modifications.
In the 60s, mass deliveries of the Skoda 706 RT family began to the USSR. The main type of semi-trailers with which Czech tractors worked in the Soviet Union were refrigerators, the purchases of which began in 1964. RT-based vehicles for various purposes have earned popularity due to their reliability and endurance in operation. The gearbox, engine and main components worked perfectly, and if necessary, it was easy to find spare parts for repair.
The comfort of the driver's seat was incomparable with what domestic manufacturers offered our drivers.
Series 706 MT
In 1966, the production of the Skoda 706 MT series with a 180 hp engine was launched. with., and since 1969 - series MT4 and MT5 with a 210-horsepower engine and a 5-speed gearbox. The MT family also received an updated cab, and in 1973, the production of two-seater cabins for vehicles operating over short distances began.
The end of the series production was the development and release of a new model Liaz 100, the production of which began in 1974 with truck tractors, and subsequently flatbed trucks. Nevertheless, Skoda 706 series dump trucks were produced until 1987.

LIAZ family
The LIAZ 100 family, presented at the Brno exhibition in 1973, at that time consisted of only two cars - a flatbed truck and a truck tractor with indices 100.45 and 100.05, respectively. The mass production of new models began in 1974, and the family update was introduced in 1984. It included the Skoda Liaz 110 series with a forward-folding cab, as well as 122 three-axle vehicles, represented by a 26-ton flatbed truck 122.03 and a 122.48 tractor for 42-ton road trains.
The new generation of Czechoslovakian trucks Skoda Liaz 110 was distinguished by an unusually stylish and thoughtful design. This was preceded by the creation of several prototypes, which ultimately made it possible to create a truly optimal model with perfectly worked out details and unified parts. The new MS638 and MS637 engines designed for Liaz, equipped with 6 turbocharged cylinders, produced 270 and 304 hp at 2000 rpm. With. The mountings of both motors were designed in such a way that each of them can be installed on any modification. A 45-degree tilt of the cylinders allows more room for the middle seat and lowers the floor in the cab. There was also a luggage rack and a berth behind the seats in the cockpit, which the previous model could not boast of.
Interestingly, at about the same time Renault licensed AVIA factories to produce light duty trucks, and LIAZ immediately attempted to install a French cab on its tractors. However, this idea was unsuccessful, and the Czechs returned to their own design.
Soon, Skoda modifications were developed with a shortened cab, three- and four-axle models, an all-wheel drive chassis with a passenger body (Africabus model). Opportunities for cooperation were not missed either. For example, for Tatra trucks, a cab has been developed with a special radiator grille and a high seating position.
After the war, the leadership of Czechoslovakia decided to reduce the range of cars and trucks produced at various factories in the country. As a result, the Škoda car factory began to build railway locomotives, and the production of trucks and buses was transferred to the Avia company in Letnany. By agreement with the designer of the structures, the Škoda company, the same emblem remained on the facings of their radiators and the name of the company was retained.
The first post-war Škoda truck was named Škoda 706 R, its production was established in Letняany from 1946 to 1951, and in June 1951 the production was transferred to a plant in the village. Rynovice, now part of the city of Liberec. In 1952, the new plant, together with branches in the cities of Mnichovo Hradiste and Ganychov, became the center of the "Group of companies for the production of trucks and buses S706". Later, this group of companies became the basis of the LIAZ company (LIAZ - "Liberec Automobile Plants").
Development of the Škoda 706 R began back in 1930, then the model was called Škoda 706. The post-war model from the 1930 model differed in a more spacious cabin, a more powerful diesel engine and had a higher carrying capacity - 7300 kg.
 The diesel engine installed on the Škoda 706 R was a 6-cylinder with wet liners and pre-chamber mixture formation, and had several design features that greatly facilitated its repair and maintenance. The crankshaft was assembled in a seven-piece factory and rotated in a powerful crankcase on seven large-diameter roller bearings. During repair work, the pistons together with the connecting rods could be removed from the block without dismantling the diesel engine from the car. The light alloy pistons contained four compression rings and one oil scraper ring.
The diesel engine installed on the Škoda 706 R was a 6-cylinder with wet liners and pre-chamber mixture formation, and had several design features that greatly facilitated its repair and maintenance. The crankshaft was assembled in a seven-piece factory and rotated in a powerful crankcase on seven large-diameter roller bearings. During repair work, the pistons together with the connecting rods could be removed from the block without dismantling the diesel engine from the car. The light alloy pistons contained four compression rings and one oil scraper ring.

The timing camshaft with pushers and rocker arms was driven from the crankshaft by a gear drive. The diesel was equipped with a compressor that served the air brake system of the car, and was driven by a gear transmission from the crankshaft. Two filters with replaceable paper elements were installed in the oil line. Starting a cold diesel engine was facilitated by glow plugs located in each cylinder. The high-pressure fuel pump with a centrifugal-type distributor supplied fuel through steel pipes to injectors that were easily dismantled during maintenance. The cooling system included a thermostat that regulates the flow of water in the water jacket.
The volume of the diesel engine was 11.781 cm3 and had a power of 135 hp. at 1750 rpm. The maximum speed was 53.5 km / h. In real operating conditions, the speed of the truck rarely exceeded 40 km / h. Average fuel consumption was about 30 liters per 100 km. The oil consumption was also rather big - 1 liter per 100 km of run!
Together with a diesel engine, the Škoda 706 R was equipped with a 5-speed manual gearbox with three pairs of constant mesh gears. The steering included an actuator of the worm-roller type, while a small effort on the steering wheel was achieved by a large gear ratio and a huge steering wheel diameter. The designers installed an engine brake (a flap in the exhaust manifold), the presence of which could not boast of many other European diesel trucks of that time.
The cab of the Škoda 706R trucks was very wide - it could easily accommodate the driver and 3 passengers. The cabin frame was made of wood, sheathed with steel sheets. In 1954, the cab was replaced with an all-metal one, but by 1956 they had already decided to abandon it, because in 1956, a cab-over-engine prototype was introduced. Trucks with such a cab, welded from steel elements, were assigned the index 706RT... The flatbed trucks were equipped with a 5000 × 2350 mm wooden platform with three drop sides and a steel frame at the base of the floor.
 In 1954, trucks of the 706R family underwent modernization: a new radiator grille and fenders became more technologically advanced in manufacturing, and access to the engine for repair and maintenance was facilitated (small areas appeared to the right and left of the hood, located behind the front bumper). The maximum power of the diesel engine increased to 145 hp. With. at 1800 rpm, which made it possible to increase the maximum speed to 68 km / h. The upgraded models with an on-board platform were distinguished by a carrying capacity increased to 7750 kg and consumed 32 liters of fuel per 100 km of run. Production of the 706R continued for three more years - it was discontinued in 1957.
In 1954, trucks of the 706R family underwent modernization: a new radiator grille and fenders became more technologically advanced in manufacturing, and access to the engine for repair and maintenance was facilitated (small areas appeared to the right and left of the hood, located behind the front bumper). The maximum power of the diesel engine increased to 145 hp. With. at 1800 rpm, which made it possible to increase the maximum speed to 68 km / h. The upgraded models with an on-board platform were distinguished by a carrying capacity increased to 7750 kg and consumed 32 liters of fuel per 100 km of run. Production of the 706R continued for three more years - it was discontinued in 1957.
 The 706R is replaced by Škoda-706MT... The model received an updated cab, which differed from the previous one only in the design of the front end. The new cab was installed on vehicles of the MT family and on the continued production of RT. In 1973, a two-seater cab was developed for vehicles operating on short routes - before that, all Škoda-706RT / MTs were equipped with a "long" cab with a berth.
The 706R is replaced by Škoda-706MT... The model received an updated cab, which differed from the previous one only in the design of the front end. The new cab was installed on vehicles of the MT family and on the continued production of RT. In 1973, a two-seater cab was developed for vehicles operating on short routes - before that, all Škoda-706RT / MTs were equipped with a "long" cab with a berth.
Simultaneously with the production of onboard versions, the assembly of dump trucks began. 706RS with metal platforms that unload on three sides. The carrying capacity of the dump truck was limited to 6.5 tons with a curb weight of 7.26 tons. The main area of their application was urban and suburban construction. Another version of the truck was a car. Škoda-706RОК with a front cab, unified with the bus one. Cars, as a rule, were offered as a carrier of specialized equipment (like garbage trucks, etc.) or in the form of a van.
 Dump trucks Škoda-706RS played a significant role in the restoration of destroyed factories and cities in Czechoslovakia in the first post-war decade. Wheels with large tires (12.00-22) and a huge ground clearance (250 mm) in the presence of a high-torque diesel engine provided a loaded car with good cross-country ability, including on dirt roads. The presence of a heater, a relatively small effort on the steering wheel and on the gear lever formed the drivers' opinion of the Škoda-706RS (and in general about the entire line of 706R models) as a machine that is convenient to operate at any time of the year. The design of the engine and transmission, worked out over a decade, and the high quality of car manufacturing guaranteed their excellent reliability and durability.
Dump trucks Škoda-706RS played a significant role in the restoration of destroyed factories and cities in Czechoslovakia in the first post-war decade. Wheels with large tires (12.00-22) and a huge ground clearance (250 mm) in the presence of a high-torque diesel engine provided a loaded car with good cross-country ability, including on dirt roads. The presence of a heater, a relatively small effort on the steering wheel and on the gear lever formed the drivers' opinion of the Škoda-706RS (and in general about the entire line of 706R models) as a machine that is convenient to operate at any time of the year. The design of the engine and transmission, worked out over a decade, and the high quality of car manufacturing guaranteed their excellent reliability and durability.
Since 1969, the series has been produced Škoda-706MT4 and Škoda-706MT5 equipped with a new 210 hp M634 engine. and a five-speed gearbox with a two-stage demultiplier.
In 1970, on the basis of the 706MT series, a new family of LIAZ 100 trucks was created. In 1974, the production of truck tractors of a new family began, and a year later, flatbed trucks. This meant the end of production of the corresponding models of the previous family. However, the production of the Škoda-706MTS24, Škoda-706MTSP24 and Škoda-706MTSP27 dump trucks continued until 1987.
 Cars of the Škoda-706RT and -706MT families were produced in Bulgaria under the LIAZ-Madara brand from 1970 to 1981. Since 1975, drive axles for these cars were produced in Bulgaria, supplied to Czechoslovakia.
Cars of the Škoda-706RT and -706MT families were produced in Bulgaria under the LIAZ-Madara brand from 1970 to 1981. Since 1975, drive axles for these cars were produced in Bulgaria, supplied to Czechoslovakia.
In the USSR, Škoda-706RT cars appeared in the early 1960s. Then truck tractors were handed over to the Soviet Union for testing. Škoda-706RTTN and Praga S5T-2TN with refrigerated semi-trailers.

Subsequently, refrigerated trucks became the main type of semi-trailers with which Czech tractors worked in the USSR. According to the test results, the Škoda-706RTTN were highly praised, but no immediate deliveries followed. It was only in 1964 that a decision was finally made to purchase Czech tractors, and Skoda and Prague with Orličan refrigerated semi-trailers began to arrive in the USSR.

In addition to truck tractors, the USSR received onboard Škoda-706RT and dump trucks Škoda-706RTS (as well as their analogues of the Škoda-706MT family).
 The Škoda-706RT trucks have proven themselves from the very best side. On the basis of the 706RT model, trucks were designed for a wide variety of needs and industries: fire trucks, flatbed trucks, tank trucks, truck cranes and other modifications.
The Škoda-706RT trucks have proven themselves from the very best side. On the basis of the 706RT model, trucks were designed for a wide variety of needs and industries: fire trucks, flatbed trucks, tank trucks, truck cranes and other modifications.



They were respected for their reliability and durability, as well as for the comfort of a driver's workplace unattainable for a domestic manufacturer.
 Many Škoda-706RTs worked until the mid-nineties, and some copies are found on the roads today.
Many Škoda-706RTs worked until the mid-nineties, and some copies are found on the roads today.

In 1973, the production of trucks under the Skoda brand stopped and the production of LIAZ trucks began (although the LIAZ plant became independent in 1953, it produced trucks with the Skoda logo for another 20 years). The debut of the LIAZ brand took place at the World Fair in Brno in 1973.
In September 1995, the LIAZ plant was incorporated into the Škoda heavy engineering concern. Having bought out the shares of the LIAZ factories and closed a number of unprofitable enterprises, he formed a new joint-stock company - Skoda-LIAZ a.s, which had only 4 enterprises at its disposal in the cities of Jablonec na Nis, Liberec, Mnichovo Hradiste and Melnik. At first, the program included all previously produced cars, which received a new trademark "Škoda-LIAZ" and a revised model indexing.

These include the "S", "FZ", "110/150/250", "300" and "MZOO" series with a gross weight of 9 to 40 tons with wheel configurations from 4x2 to 8x4 and diesel engines of our own production or Austrian engines "Steyr "(Steyr) with a capacity of 180-410 hp.
And in 1996 "Škoda-LIAZ" launched a new truck on the market - the main tractor "Xen a 19.47TBV" (for road trains with a gross weight of up to 44 tons, which led the new series "400".
 It is equipped with a Detroit Diesel 6-cylinder turbocharged engine (12,742 cc, 437 or 477 hp), 16-speed Eaton gearbox, imported axles, front disc brakes, ABS, electronically controlled rear air suspension, new spacious a cabin made of multilayer fiberglass on an aluminum frame. In 2000, a new Fox series with a GVW of 19 tons with 290-330 hp engines was added to it. In 2003, production of the Xen a and Fox trucks ceased.
It is equipped with a Detroit Diesel 6-cylinder turbocharged engine (12,742 cc, 437 or 477 hp), 16-speed Eaton gearbox, imported axles, front disc brakes, ABS, electronically controlled rear air suspension, new spacious a cabin made of multilayer fiberglass on an aluminum frame. In 2000, a new Fox series with a GVW of 19 tons with 290-330 hp engines was added to it. In 2003, production of the Xen a and Fox trucks ceased.

In 1999, Skoda, with the help of Truck International AS, acquired the newly organized Skoda Motory from Jablonek, which became a subsidiary. On February 28, 2002 Skoda Motory became JAMOT (Jablonecky Motory) and on June 17 declared itself bankrupt. On July 1, 2003, JAMOT became part of the TEDOM concern. In the same year, TEDOM began bankruptcy proceedings against LIAZ, and in 2002, the engine plant in Yablonets, the main supplier of power units for the conveyors of the former giant SKODA-LIAZ, was declared insolvent. In just 50 years of its existence, Skoda-LIAZ has produced about 350 thousand trucks and bus chassis.
The Skoda-706RT truck can be safely called one of the most successful solutions of the Czech car manufacturers, and in the USSR of the “pre-Kamaz” era it was a legendary car, most of them worked in “Sovtransavto” on international cargo transportation.
The history of this car began in 1957, when the car was presented to the general public, which aroused well-deserved interest. The first thing that caught my eye was the layout. The bonnet over the engine was a rarity in the 50s, at a time when “bonnets” still reigned in Europe. Only now the cockpit did not tilt, and the engine was accessed directly from the cockpit.
Diesel (direct injection) six-cylinder engine with a volume of 11.76 liters and a capacity of 160 hp. allowed the production of this truck in many different modifications, the most massive of which was the Skoda-706RTTN truck tractor.
The car is quickly gaining popularity both in the countries of the socialist camp and in Europe. It is appreciated for its endurance, unpretentious maintenance, high speed, simple and highly reliable design, easy to repair.
Mass deliveries of Skoda-706RT to the USSR begin in the mid-60s. Basically, these were Skoda-706RTTN tractors, working in tandem with a Czech, single-axle refrigerated semitrailer.
It is such a machine that appears in the frames of the famous Soviet film "Prisoner of the Caucasus"
By the way, since we are talking about cinematography, we should also mention the "Race with Pursuit", where Skoda-706RTTN actually plays one of the main roles, occasionally occurs in the films "Mirage" and "Amphibian Man", "Adventures of Electronics".
Skoda-706RTTN gave the Soviet driver an unprecedented level of comfort, because the cabin was equipped with a sleeping bag. The first Soviet truck with a sleeping bag was "Kolkhida", but calling a "circus horse" a full-fledged tractor will not work, no matter what one wants. By the way, when designing the Kolkhida's cockpit, the designers were clearly inspired by the Skoda.
In 1966, the Skoda-706 receives a new 180 hp engine, and in 1969 even more powerful modifications of the Skoda-706MT4 and Skoda-706MT5 appear, with a 210 hp engine. a five-speed gearbox with a splitter and a slight restyling. Skoda-706RT, however, continued to be produced.
In 1973, a shortened cab appears, without a sleeping bag. The cab was installed on a chassis for special equipment, dump trucks and other modifications, the operating conditions of which did not imply frequent long trips.
The Soviet "dalnoboschiks" already had their own traction, MAZ-500, but Skoda was still popular and loved, and in Bulgaria even the production of Skoda-706RT under the LIAZ-Madara brand began. It was produced from 1970 to 1981.
Skoda-706RT lasted in production until 1985, and Skoda-706MT in dump truck modifications lasted in production right up to 1987. In total, about 250 thousand different modifications of the Skoda-706 RT and MT truck were produced. They had such a safety margin that the car was quite common on the roads until the mid-90s. Now they are no longer to be found except at the exhibitions of oldtimers, only a good memory of the car remains.
Skoda Liaz
Date of birth of the car manufacturer Skoda LIAZ it is considered to be 1951, since before that time both enterprises - LIAZ and Skoda - existed separately. At different periods of time, the company included up to 12 enterprises of various profiles located in different cities, and in the 70s of the last century Skoda LIAZ was the largest manufacturer of trucks in Czechoslovakia.
The following video tells about the rich history of LIAZ-Skoda:
Lineup LIAZ Skoda
Skoda 706
At the end of 1951, the government of Czechoslovakia decided to resume production of aircraft at the Avia plant, and transfer the production of buses and heavy trucks Skoda-706 to a plant in the village of Rynovice, which is part of the LIAZ group of companies (Liberec Automobile Plants). Although LIAZ became independent from Skoda in 1953, it still continued to use its name (Skoda LIAZ) until 1984. The photos of the first Skoda LIAZ 706 trucks have been preserved:

Skoda LIAZ 706 is one of the first truck models produced by LIAZ
Since 1957, Skoda LIAZ factories have produced Skoda 706RTS dump trucks, Skoda 706RTTN truck tractors, as well as Skoda 706RT chassis, on the basis of which flatbed trucks, buses and various specialized vehicles were produced. All 706RT vehicles were equipped with a 160-horsepower direct injection diesel engine.

Skoda LIAZ 706 RTTN tractor unit

Fire truck based on Skoda 706 LIAZ RT chassis
In 1966, a new series of Skoda 706MT trucks was launched into production, equipped with six-cylinder in-line 180-horsepower M630 diesel engines and a 210-horsepower engine modification, designated M634, developed 3 years later.

Skoda LIAZ 100
In 1974, a new car was added to the existing model range - Skoda LIAZ 100, developed on the basis of the 706MT trucks.
The first on the conveyor were two-axle trucks with a gross weight of up to 19 tons and Skoda LIAZ 100.42 truck tractors designed for road trains weighing up to 38 tons. shown in the photo):

Skoda LIAZ 100.05 flatbed truck
Technical characteristics of the Skoda LIAZ 100.42 truck
- Type: truck tractor
- Overall dimensions (length / width / height), mm: 6350/2500/2810
- Curb weight (kg): 6800
- Engine make and type: MS 634, diesel R6
- Engine displacement, see cubic: 11940
- Power, hp: 201 at 2000 rpm.
- Maximum moment, Nm: 751 at 1400 rpm
- Gearbox type: manual, 5-speed
- Maximum speed, km / h: 98
- Fuel consumption, l / 100 km: 35-40
- The volume of fuel tanks: 2 to 175 l
Skoda LIAZ 110
Ten years later, the car changed, it received a new design, a reclining cab, rear air suspension and a new designation - Skoda LIAZ 110. Initially, the truck was equipped with one of five modifications of the M630 engine with a capacity of 210 to 320 hp. In 1992, the Skoda LIAZ 110.573 truck tractors appeared, equipped with a large-volume Maxi cab and an anti-lock braking system.

Skoda LIAZ 110.57 tractor unit
Both models were actively exported to the Soviet Union. Compared to domestic trucks, Skoda LIAZ 100-110 cars were considered more comfortable and reliable. Quite a few of them are still in operation on intercity routes in the countries of the former Soviet Union.
Skoda LIAZ Xena and Fox
Unfortunately, even the modernized versions of Czechoslovak trucks could not compare with the models of competitors from Western Europe, and the collapse of the USSR put the car factory on the brink of ruin. In 1995, the Skoda concern bought out the shares of the LIAZ factories, forming the Skoda-LIAZ a.s. Joint Stock Company. In addition to the already produced models, it was planned to develop and launch a new series of trucks.
The first vehicle created by the new joint-stock company was the Skoda LIAZ Xena 19.47TBV mainline truck tractor. The novelty was intended for road trains weighing up to 44 tons. The tractor was equipped with a fiberglass cabin on an aluminum frame, foreign-made axles, a 16-speed Eaton gearbox, ABS, disc brakes at the front and an electronically controlled air suspension at the rear. Photo and video review of the cargo Skoda LIAZ Xena 19.47 TBV gives an idea of the scale of the changes made to the design:

Skoda LIAZ Xena 19.47 TBV trunk tractor
In 2000, Fox series trucks, equipped with engines of up to 330 hp, were added to the company's lineup, but their release did not change the company's difficult financial situation.

Tipper Skoda LIAZ Fox
The last truck was produced by LIAZ on September 1, 2003. It was a technical assistance car for Martin Masik's racing team, who participated in the Dakkar Rally.

The last truck produced at the LIAZ plant