Rotary-piston Vankel engine (15 photos + 3 video)
Steam machines and internal combustion engines have one common disadvantage - the reciprocating movement of the piston must be transformed into the rotational movement of the wheels. From here and knowingly low efficiency, and high wear of the elements of the mechanism. Many wanted to build an internal combustion engine so that all moving parts in it only rotate - as it happens in electric motors.
However, the task was not simple, successfully solved it only by the mechanical self-taught, which in all his life did not receive a higher education or even a working specialty.
Felix Henrich Wankel (Felix Heinrich Wankel, 1902-1988) was born on August 13, 1902 in the small German town of Lar. During the First World War, Felix's father died, because of which the future inventor had to throw a gymnasium and to work to work as a student of the seller in a publisher's book shop. Thanks to this work, Vankel was addicted to reading books by which he independently studied technical disciplines, mechanics and automotive industry.
There is a legend that the solution to the task came to seventeen-year-old Felix in a dream. True, this or not - unknown. But it is obvious that Felix possessed very outstanding abilities to mechanics and a "unreasonable" look at things. He understood how all four cycles of the usual internal combustion engine (injection, compression, combustion, exhaust) can be carried out during rotation.
Quite quickly, Vankel came to the first engine design, and in 1924 he organized a small workshop, which also served and improvised "laboratory." Here Felix began to conduct the first serious research in the area of \u200b\u200brotary-piston engine.
Since 1921, Vankel has been an active member of the NSDAP. He spoke for party ideals, was the founder of the Allegmer Military Youth Association and Jungfürer of various organizations. In 1932, he left the party, accusing one of his former colleagues in political corruption. However, on the oncoming charge, he himself had to spend six months in prison. Freed from imprisonment thanks to the intercession of Wilhelm Keppler (Wilhelm Keppler), he continued on the engine. In 1934, he created the first prototype and received a patent. It constructed new valves and combustion chambers for their engine, created several different options for its options, developed a classification of kinematic schemes for various rotary-piston machines.

In 1936, the prototype of the Vankel engine was interested in BMW - Felix received money and his own laboratory in Lindau to develop experienced aircraft engines.
However, until the defeat of fascist Germany, no Vankel engine went to the series. Perhaps to bring the design to mind and creating mass production was required too much time.
After the war, the laboratory was closed, the equipment was exported to France, and Felix was left without work (the former membership in the National Socialist Party had affected). However, NSU Motorenwerke AG, which is one of the oldest manufacturers of motorcycles and cars, soon received Vankel.
In 1957, the joint efforts of Felix Vankel and the lead engineer NSU Walter Freede (Walter Froede), a rotary-piston engine was first installed on the NSU Prinz car. The initial design was far from perfection: even to replace the candles, it was necessary to disassemble almost the entire "engine", the reliability left to desire the best, and about economy at this stage of development and was sinful. As a result of tests, the series went on a car with traditional engine. Nevertheless, the first rotary-piston engine DKM-54 has proven its fundamental performance, opened the directions for further finishing and demonstrated the enormous potential of Rototnikov.
Thus, the new type of DVS received, finally, his way into life. In the future, he is still waiting for a lot of improvements and improvements. But the prospects for a rotary-piston engine are so attractive that engineers have no longer stopped in bringing the design to operational perfection.

Before disassembling the advantages and disadvantages of rotary-piston DVS, it is still more detailed to consider their design.
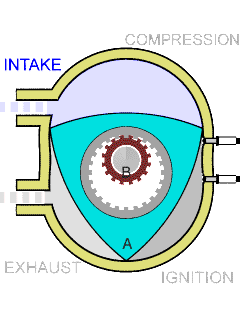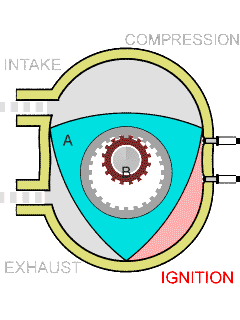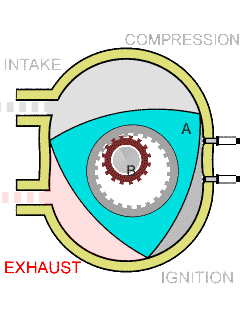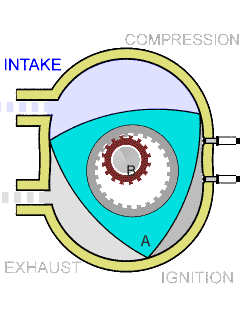
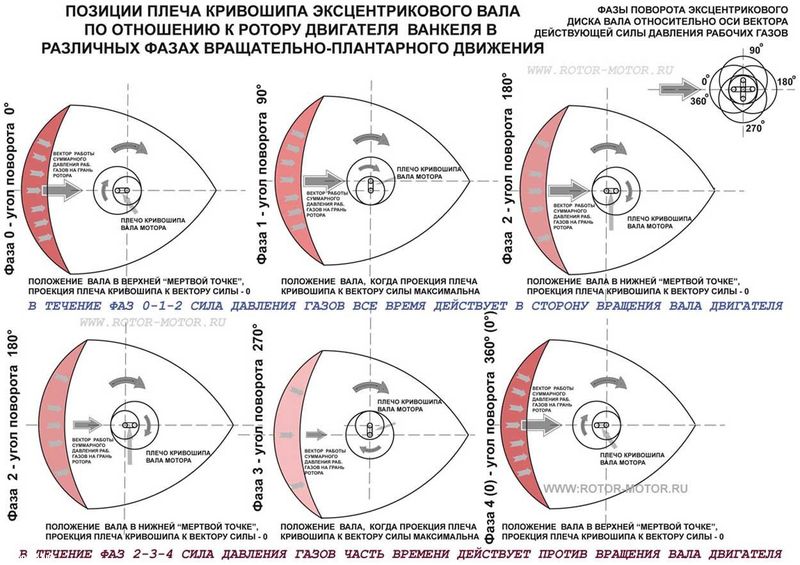
In the center of the rotor, a round hole has been done, from the inside the teeth covered like a gear. The rotating shaft of smaller diameter is inserted into this hole, also with teeth, which ensures no slipping between it and the rotor. The relationship of the diameters of the hole and the shaft is chosen so that the vertices of the triangle move along the same closed curve, which is called "Epitrohoid," the art of Vankel as an engineer was to first understand that it was possible, and then accurately calculate. As a result, the piston having the shape of the belt belt, cuts off in the chamber repeating the shape found by the curve, three alternating and position cameras.
The design of rotary-piston DVS allows you to implement any four-stroke cycle without the use of a special gas distribution mechanism. Thanks to this fact, the "Rotornik" is much easier than the usual four-stroke piston engine, in which an average of almost a thousand parts is greater.
Sealing the working chambers in the Rotary-piston DVS is provided by radial and end sealing plates, pressed against the "cylinder" with tape springs, as well as centrifugal forces and gas pressure.
Another technical feature is a high "labor productivity". For one full turn of the rotor (that is, behind the cycle "Injection, compression, ignition, exhaust"), the output shaft makes three full turns. In the usual piston engine, such results can only be achieved using six-cylinder engine.
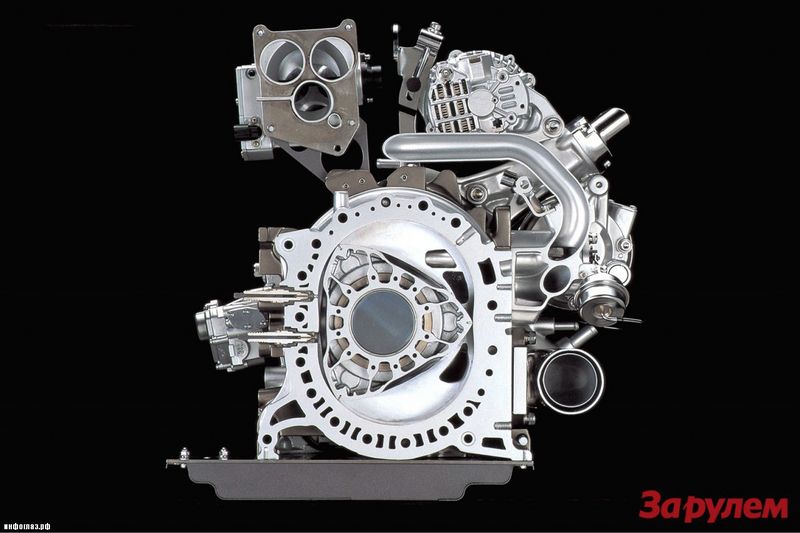
After the first successful demonstration of rotary DVS in 1957, the largest auto hydriants began to develop increased interest in developing. First, the engine license, which received the informal name "Vankel", bought Curtiss-Wright Corporation, after a year, Daimler-Benz, Man, Friedrich Krupp and Mazda. In total, about a hundred companies in the world, including monsters such as Rolls-Royce, Porsche, BMW and Ford, are acquired for a very short period of time, including monsters such as Rolls-Royce, Porsche, BMW and Ford. Increased interest in Vanka - In a rotary-piston engine, 40% less details, it is easier in repair and production.
In addition, Vankel is almost twice as compact and lighter than traditional piston engine, which in turn improves car handling, facilitates the optimal location of the transmission and allows you to make a more spacious and comfortable interior.
Picture clickable:
The rotary-piston engine develops high power at a rather modest fuel consumption. For example, a modern "Vankel" volume of only 1300 smі develops the capacity of 220 hp, and with a turbocharger - all 350. Another example is a miniature engine OSMG 1400 weighing 335 g (working volume 5 sm) develops a capacity of 1.27 liters .from. In fact, this crumble is 27% stronger than horse.
Another important advantage is a low level of noise and vibrations. The rotary-piston engine is perfectly balanced mechanically, moreover, the mass of moving parts (and their number) is significantly less in it, so that Vankel works much quieter and does not vibrate.
And finally, the rotary piston engine is distinguished by excellent dynamic characteristics. At low gear, it is possible without a special load on the engine to overclock the car up to 100 km / h on high engine speeds. In addition, the design of "Vankel" due to the lack of a mechanism for the transformation of the reciprocating movement into the rotational, is able to withstand large revs than traditional engine.

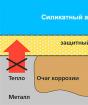
After the NSU Spyder released in 1964, the legendary model NSU RO 80 (there are still many clubs of owners of these machines in the world), Citroen M35 (1970), Mercedes C-111 (1969), Corvette XP (1973). But the only mass manufacturer was the Japanese Mazda, which since 1967 sometimes 2-3 new models with RPD. Rotary engines put on boats, snowmobiles and light aircraft. The end of Euphoria came in 1973, in the midst of the oil crisis. It was then that the main drawback of rotary engines was manifested - non-economic. With the exception of Mazda, all automakers turned rotary programs, and the Japanese company selling on America decreased from 104960 sold cars in 1973 to 61192 - in 1974. Along with indisputable advantages, Vankel also possessed a number of very serious flaws. First, durability. One of the first prototypes of rotary-piston engines on testing has developed its resource in just two hours. The next, more successful DKM-54 has already extended a hundred hours, but this is not enough for normal operation of the vehicle. The main problem was covered in uneven wear of the inner surface of the working chamber. In the process of operation, transverse grooves appeared, which received the speaker name "Devil Tags".

In Mazda, after acquiring a license to Vankel, a whole department was formed, engaged in the improvement of a rotary-piston engine. Quite soon it turned out that when the triangular rotor rotates, the plugs on its vertices begin to vibrate, as a result of which the "devil labels" are formed.
Currently, the problem of reliability and durability has finally decided by applying high-quality wear-resistant coatings, including ceramic.
Another serious problem is an increased toxicity of Vankel exhaust. Compared to conventional piston DVS "Rotornik" allocates less nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, but much more hydrocarbons, due to incomplete combustion of fuel. Pretty fast Mazda engineers who believed in the brilliant future of Vankel, found a simple and effective solution and this problem. They created the so-called thermal reactor, in which the residues of hydrocarbons in the exhaust gases simply "surrendered". The first car that implemented such a scheme was Mazda R100, also called Familia Presto Rotary, released in 1968. This car, one of the few, immediately passed very hard environmental requirements, put forward by the United States in 1970 for the auto imported cars.
The next problem of rotary-piston engines partially follows from the previous one. This is economy. The fuel consumption of the standard "Vankel" due to the incomplete combustion of the mixture is significantly higher than that of standard FRO. And again, Mazda engineers began to work. With the help of a whole complex of measures, including the processing of thermo-actor and carburetor, add a heat exchanger to the exhaust system, developing a catalytic converter and the introduction of a new ignition system, the company has achieved a decrease in fuel consumption by 40%. As a result of this undoubted success in 1978, the Mazda RX-7 sports car was released.

It is worth noting that at this time all over the world of cars with rotary-piston engines produced only Mazda and ... AvtoVAZ.
It was in the failure of 1974 that the Soviet government creates a special design bureau of the RPD (SKB RPD) - the socialist economy is unpredictable in the Volga Auto Plant. In Tolyatti, work began on the construction of workshops for the mass production of Vankels. Since the VAZ was originally planned as a simple copier of Western technologies (in particular, Fiatovsky), the factory specialists decided to reproduce the Mazda engine, completely throwing off all the ten-year-old developments of domestic engineering institutions.
Soviet officials spent a long time negotiating with Felix Vankel for the purchase of licenses, and some of them took place right in Moscow. Money, however, did not find, and therefore it was not possible to take advantage of some branded technologies. In 1976, he earned the first Volzhsky single-section engine VAZ-311 with a capacity of 65 hp, another five years left for the design of the design, after which an experienced party was released in 50 pieces of rotary "units" VAZ-21018, instantly separated among Vase workers. Immediately it turned out that the engine only outwardly resembled the Japanese - he became painted very much in Soviet. The plant's management was forced for six months to replace all engines on serial piston, cut half the staff of SKB RPD and suspend the construction of workshops. The salvation of the domestic rotary engine started from the special services: they were not very interested in fuel consumption and the resource of the engine, but strongly - dynamic characteristics. Immediately of two VAZ-311 engines, a two-section RPD was made with a capacity of 120 hp, which began to be installed on Special Confection - VAZ-21019. It was this model that received the unofficial name "Arkan", we are obliged to countlessly by the Militia "Cossacks", catching up with "Mercedes", and many guards of order are orders and medals. Until the 90s, an externally unpretentious "Arkan" really dismissed all the cars. In addition to the VAZ-21019, small batch cars VAZ-2105, -2107, -2108, -2109, -21099 are also available on AvtoVAZ. The maximum speed of the rotary "eight" is about 210 km / h, and until hundreds of it accelerates in just 8 seconds.
The ripped on special orders of SKB RPD began to make engines for water and motor sports, where cars with rotary engines became so often to conquer prizes that sports officials were forced to ban the use of RAP.
In 1987, the head of SKB RPD Boris Pospelov died and Vladimir Shnyakin was chosen at the general meeting - a person who came to the automotive of aviation and the disliked ground transport. The main direction of SKB RPD becomes the creation of engines for aviation. It was the first strategic mistake: the aircraft we produce incommensurable less cars, and the plant lives with the engines sold.
The second mistake was the orientation in the preserved production of automotive RPDs on low-power engines VAZ-1185 in 42 hp For "Oka", although more voracious, but more dynamic rotary engines are asked for the fastest domestic machines - for example, on the "eights". The same Japanese install "Vankels" only on sports models. As a result, there were only a few rotary microllers "Oka" on Russian roads. In 1998, a civil version of the two-cylinder rotary 1,3-liter engine VAZ-415 was finally prepared, which began to be installed on VAZ-2105, 2107, 2108 and 2109.
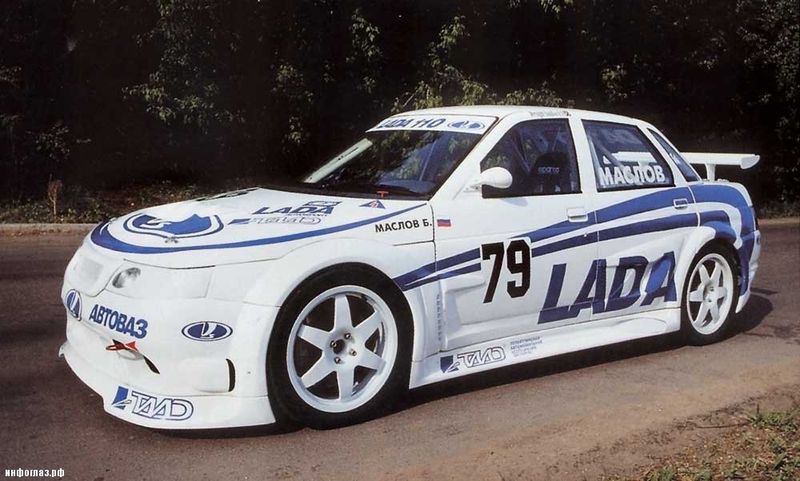

In May 1998, the annular VAZ-110 "RPD-Sport" (190 l., 8500 rpm, 960 kg, 240 km / h) was organized. Alas, on the only sample, which is more often demonstrated at exhibitions than the starting in races, it did not go. The 110th was the most powerful in the Peloton, but frankly raw design every time she did not give her to demonstrate all his potential. However, it is offended by all the fact that on the "vase" quickly cooled to the rotary direction, and the unique "Lada" was redested in the rally-car with ordinary DVS.
So why are all the leading car manufacturers have not yet moved to "Vankels"? The fact is that for the production of rotary-piston engines, it is required, firstly, an honed technology with many of a wide variety of nuances and not every company is ready to pass the path of the same Mazda, passing by numerous "rake". And secondly, we need special high-precision machines capable of pulling the surfaces described by such a tricky curve as an epitrohyoid.
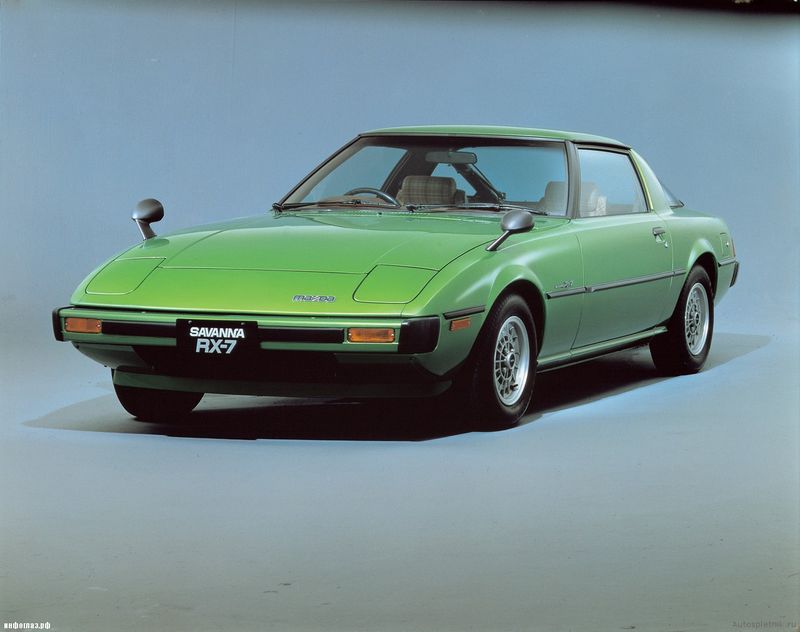

Mazda RX-7 is one of the first cars on which the Vankiel rotary-piston engine was put. In the history of Mazda RX-7 there were four generations. The first generation from 1978 to 1985. The second generation - from 1985 to 1991. The third generation - from 1992 to 1999. Last, the fourth generation - from 1999 to 2002. The first generation of RX-7 appeared in 1978. It had a mid-door layout and was equipped with a rotary engine with a capacity of only 130 liters. from.
Currently, only Mazda is engaged in serious research in the field of rotary-piston engines, gradually improving their design, and most of the pitfalls in this area are already passed. Vankeli comply with world standards for the level of exhaust toxicity, fuel consumption and reliability. For modern surface machines, the epitrohyoid described are not a problem (as they are not a problem and much more complex curves), new structural materials allow you to increase the service life of the rotary-piston engine, and its cost is already lower than that of standard DVS due to the smaller amount used details.
Like NSU, Mazda in the 60s. There was a small company with limited technical and financial resources. The basis of its model range was delivered trucks and family small bars. Therefore, there is nothing surprising that the sports coupemazda 110s cosmo (982 cm cu., 110 l., 185 km / h) was created for more than 6 years and turned out to be very capricious and expensive. Yes, the reputation of the NSU RO80 reputation did not contribute to the stir (in 1967-1972 found their owners only 1175 "spaces"), but world interest in 110s contributed to an increase in sales of the rest of the company's other products!
To prove that RPD is just as reliable (its superiority in power has already become obvious to everyone), Mazda almost for the first time in life took part in competitions, and chose the most difficult and long-lasting race - 84-hour Marathon de La Route, held on Nürburgring. As the crew from Belgium managed to take the 4th place (the second car came down from the distance three hours before the finish line because of the jammed brakes), losing only the "grew up" on the "Nordshaife" Porsche 911, it seems to remain a mystery.

Vankel Workshop in Lindau
Although since then, the Japanese Rototniks have become regulars of racing routes, major success in Europe they had to wait for 16 years. In 1984, the British on the RX-7 won a prestigious daily race in Spa Francoschamp. But in the USA, the seven market, its racing career was much more successful: since the debut in the IMSA GT championship in 1978 and in 1992 she won in its class more than a hundred stages, and from 1982 to 1992. He first marked in the main race series - 24 hours of daytona.
In the rally, "Mazda" everything went so smoothly. As it often happened to the Japanese teams (Toyota, Datsun, Mitsubishi), they performed only at the individual stages of the Rural Championship of the World (New Zealand, United Kingdom, Greece, Sweden), which are primarily interested in marketing departments of concerns. National titles have enough: so, in 1975-1980. Millen won the whole five in New Zealand and the United States. But in WRC, successes were exclusively local: the best, which was shown by the RX-7, - the 3rd and 6th place in the Greek "Acropolis" of 1985.
Well, the loudest success of Mazda in general and the RPD in particular became the victory of her sportsprototype 787b (2612 cm cu., 700 l., 607 nm, 377 km / h) in Le Mana in 1991. Moreover, not only fast pilots and competitive techniques helped to defeat the factoryporsche, Peugeot and Jaguar: the persistence of Japanese managers played their role, regularly "knocked out" for rotorists all sorts of relaxation in the regulations. So, on the eve of the victory of the 787th, the organizers of the race agreed to compensate the voraciousness of the "rotorniks" 170 kilogram (830 against 1000) with a decrease in mass. The paradox was that, in contrast to gasoline engines, the "appetite" of the RPD with further forcing growing a much more modest pace than the usual piston motors, and the 787th turned out to be more economical than its main competitors!
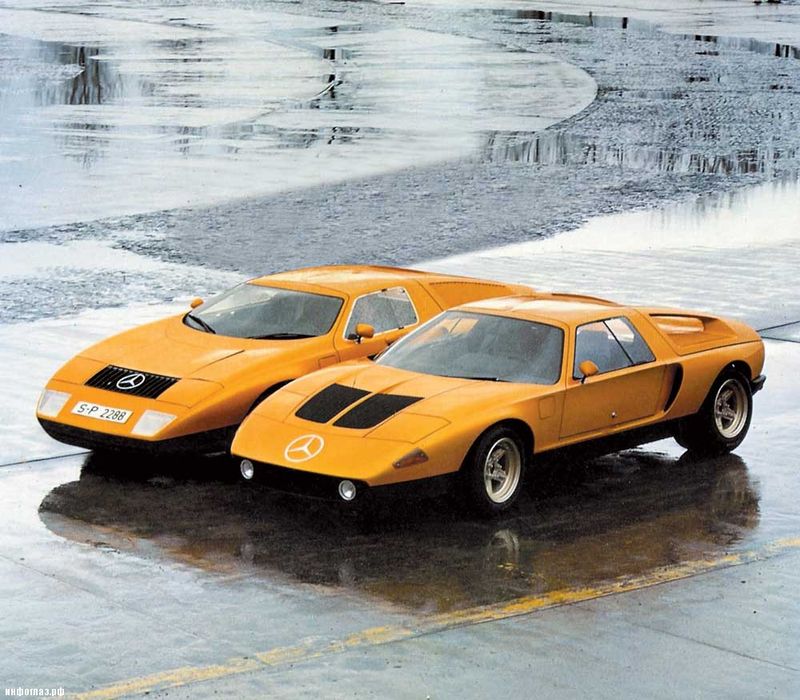

It was shock. Mercedes, which Stern magazine for conservatism called no other than the "car manufacturer for 50-year-old Lords in hats," in 1969 presented super-car, hitting the imagination even with color. Causeing a bright orange color, an underlined wedge-shape, a medium-engine layout, the door "Seagulls" and heavy duty three-section RPD (3600 cm cubic meters, 280 l., 260 km / h) - for conservative Mercedes it was something!
And since the company did not build concepts, everyone believed that C111 had only one way: a small (ologogenic) assembly and a big racing future, because since 1966 FIA made RPD to official competitions. And at the headquarters of Mercedes, checks were sprinkled with a request to enter the right amount for the right to possess C111. Stuttgartsa also got an interest in Esk, in 1970, presenting a second coupe generation with an even more fantastic design, a 4-section rotor and breathtaking characteristics (4800 cm cubic meters, 350 liters., 300 km / h). For the refinement, Mercedes built five layouts that were attempted and spent the night on Hockenheimring and Nürburgring, preparing to establish a series of speed records. The press saved the upcoming "Battle of Titans" between the rotor Mercedes, the atmospheric Ferrari and the upgrade Porsche in the World Racing Championships. Alas, the return to the big sport did not take place. First, C111 was very expensive even for Mercedes, secondly, the Germans could not put so much crude design. And after the Caribbean oil crisis, they generally covered the project, focusing on diesel engines. They equipped the latest versions of C111, which established several world records.

Non-finished technical education, in the end of the life of Felix Vankel, has reached worldwide recognition in the field of engine engineering and sealing equipment, which won a lot of awards and titles. His name is named streets and squares of German cities (Felix-Wankel-Strasse, Felix-Wankel-Ring). In addition to engines, Vankel has developed a new concept of high-speed vessels and independently built several boats.
The most interesting thing is that the rotary engine that made it with a millionaire and brought him world famous, Vankel did not like, considering it with "guffic duckling." Real working RPDs were made on the so-called "concept of the CCM", providing for the planetary rotation of the rotor and requiring the introduction of external balances. A significant role was played by the fact that this scheme was not suggested by Vankel, but the engineer NSU Walter Freud. Vankel himself, until the last day, considered the perfect engine scheme "with rotating pistons without uneven rotating parts" (Drehkolbenmasine - DKM), conceptually much more beautiful, but technically complex, requiring, in particular, installing spark plugs on a rotating rotor. Nevertheless, rotary engines worldwide are associated with the name of Vankel, since everyone who closely knew the image, in one voice, claim that without the irrepressive energy of the German engineer, the world would not see this amazing device. Felik Vankel left in 1988.
Curious story with Mercedes 350 SL. Vankel really wanted to have a rotary Mercedes C-111. But Mercedes did not meet him. Then the inventor took the serial 350 SL, thrown out from there a "native" engine and installed the rotor from C-111, which was a lighter than the former 8-cylinder by 60 kg, but developed significantly higher power (320 hp at 6500 rpm). In 1972, when engineering genius finished work on his next miracle, he could sit behind the wheel of the SL-class very fast at that time. The irony concluded that Vankel's driver's license was never received.

With the revival of interest in the RAP, we are obliged to a new engine Mazda Renesis (from Re - Rotary Engine - and Genesis). Over the past decade, Japanese engineers managed to solve all the main problems of the RPD - exhaust toxicity and non-economic. Compared to the predecessor, it was possible to reduce oil consumption by 50%, gasoline by 40% and bring the emission of harmful oxides to the norms corresponding to EURO IV. A two-cylinder engine with a volume of only 1.3 liters outputs the power of 250 hp And it takes much less space in the engine compartment.
Especially under the new engine was developed by the Mazda RX-8 car, which, according to the Brand manager of Mazda Motor Europe Martin Brink, was created on a new concept - the car was "built" around the engine. As a result, the rave of the RX-8 axes is ideal - 50 to 50. The use of a unique shape and small size of the engine made it possible to put the center of gravity very low. "RX-8 is not encouraged by a racing monster, but this is the best car in management, which I have ever drove," Popular Mechanics Martin Brink said with delight.
Barrel honey ...
Without doubt, at first glance, the rotary-piston engine has a lot of advantages over traditional internal combustion engines:
- less than 30-40% by the number of parts;
- smaller in 2-3 times with dimensions and mass, compared with the corresponding standard in the power of the DVS;
- smooth characteristic of torque in the entire turn range;
- the absence of a crank-connecting mechanism, and, consequently, a much smaller level of vibration and noise;
- high level of revolutions (up to 15000 rpm!).
A spoon of tar…
It would seem that if Vankel has such superiority over the piston engine, then who needs these bulky, heavy, rattling and vibrating piston engines? But, as it often happens, in practice everything is not so chocolate. No ingenious invention, coming out for the laboratory threshold, went to the basket with a note "for garbage". Serial production has not found on one stone, but for a whole browsery of granite:
- testing of the combustion process in the chamber of unfavorable form;
- ensuring sealing sealing;
- ensuring work without charging in conditions of uneven heating;
- Low thermal efficiency due to the fact that the RPD combustion chamber is much larger than that of traditional DVS;
- high fuel consumption;
- high toxicity of gaseous combustion products;
- Narrow temperature zone for RPD operation: at low temperatures, the engine power drops sharply, with high - fast wear of the rotor seals.