Principle of operation and device of the car engine. Maintenance of the car engine
Most concept drivers do not have, what is the engine of the car engine. And it is necessary to know this, because it is not for nothing in training in many driving school students tell the principle of operation of the OI. Each driver should have an idea of \u200b\u200bthe engine work, because these knowledge can be useful on the road.
Of course, there are different types and brands of car engines, whose work differs among themselves in the trifles (fuel injection systems, the location of cylinders, etc.). However, the basic principle for all types of FEA remains unchanged.
Car engine device in theory
The DVS device is always appropriate to be considered on the example of the operation of one cylinder. Although most often passenger cars have 4, 6, 8 cylinders. In any case, the main part of the motor is a cylinder. It contains a piston that can move up-down. At the same time, there are 2 borders of its movement - upper and lower. Professionals are called NTC and NMT (upper and lower dead dots).
The piston itself is connected to the connecting rod, and the connecting rod - with the crankshaft. When the piston is moving up and down, the connecting rod transmits the load on the crankshaft, and that rotates. The load from the shaft is transmitted to the wheels, as a result of which the car begins to move.
But the main task is to make the piston work, because it is he who is the main driving force of this complex mechanism. This is done with gasoline, diesel fuel or gas. A drop of fuel flammable in the combustion chamber discards the piston with a lot of power down, thereby leading it in motion. Then the piston on inertia returns to the upper border, where the explosion of gasoline occurs again and the cycle is repeated constantly until the driver stops the motor.
So the engine of the car engine looks like. However, this is only the theory. Let's consider in more detail the cycles of the motor operation.
Four-stroke cycle
Almost all engines operate on a 4-stroke cycle:
- Fuel intake.
- Fuel compression.
- Combustion.
- The output of exhaust gases beyond the combustion chamber.
Scheme
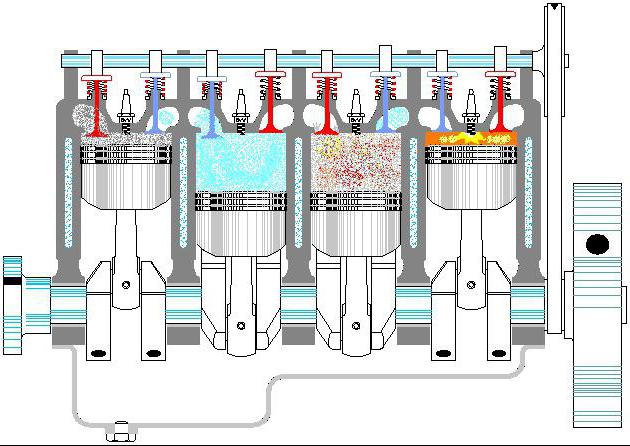
Below, the figure shows the typical scheme of the car engine device (one cylinder).
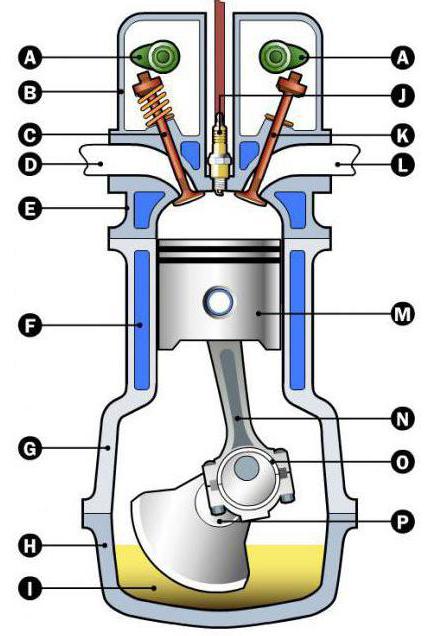
This scheme clearly shows the main elements:
A - camshaft.
B - valve cover.
C - exhaust valve through which gases from the combustion chamber are discharged.
D - exhaust hole.
E - cylinder head.
F is the coolant cavity. Most often there is antifreeze, which cools the heating housing of the motor.
G - motor block.
H - oil collector.
I - pallet where all the oil flows.
J is an ignition candle forming a spark for a lift of the fuel mixture.
K - intake valve through which the fuel mixture falls into the combustion chamber.
L - inlet.
M is a piston that moves up and down.
N is the rod connected to the piston. This is the main element that transmits an effort on the crankshaft and transforms a linear movement (up-down) into the rotational.
O - rod bearing.
P - crankshaft. It rotates due to the movement of the piston.
It is also worth highlighting such an element as piston rings (they are also called oilmaging rings). They are not in the figure, however they are an important component of the car engine system. These rings are enveloped by piston and create a maximum seal between the cylinder walls and the piston. They prevent fuel from entering the oil pan and oil into the combustion chamber. Most of the old engines of VAZ cars and even the motors of European manufacturers have worn rings that do not create an effective seal between the piston and the cylinder, which is why the oil can fall into the combustion chamber. In such a situation, the increased consumption of gasoline and "Zhor" oil will be observed.
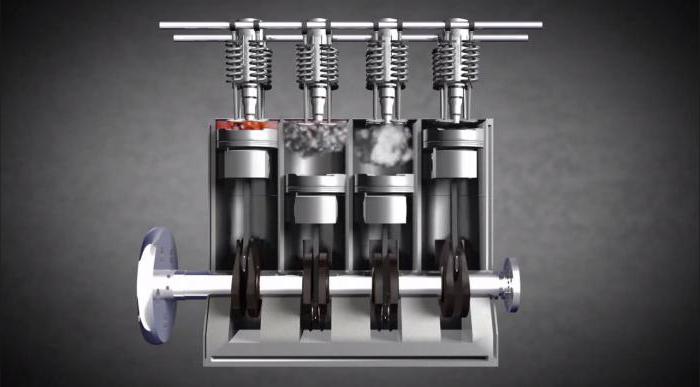
These are the main elements of the design, which take place in all internal combustion engines. In fact, it is much more elements, but we will not touch the subtleties.
How does the engine work?
Let's start with the initial position of the piston - it is at the top. At the moment, the inlet is opened with a valve, the piston begins to move down and sucks the fuel mixture into the cylinder. In this case, only a small drop of gasoline enters the cylinder capacity. This is the first tact of work.
During the second tact, the piston reaches the lowest point, while the inlet is closed, the piston starts upwards, as a result of which the fuel mixture is compressed, since it has nowhere to go in a closed chamber. Upon reaching the piston of the maximum top point, the fuel mixture is compressed to a maximum.
The third stage is the ignition of a compressed fuel mixture with a candle that emits a spark. As a result, the combustible composition explodes and pushes the piston with a big force down.

At the final stage, the detail reaches the lower boundary and inertia returns to the upper point. At this time, the exhaust valve opens, the exhaust mixture in the form of gas leaves the combustion chamber and through the exhaust system hits the street. After that, the cycle, starting from the first stage, repeats again and continues throughout the time until the driver stops the engine.
As a result of the explosion of gasoline, the piston moves down and pushes the crankshaft. It is spinning and transfers the load on the car's wheels. This is how the engine of the car engine looks like.
Difference in gasoline engines
The method described above is universal. According to this principle, the work of almost all gasoline engines was built. Diesel engines are distinguished by the fact that there is no candle - an element that fills fuel. The detonation of diesel fuel is carried out due to the strong compression of the fuel mixture. That is, on the third cycle, the piston rises up, strongly compresses the fuel mixture, and the one explodes naturally under the action of pressure.
Alternative to DVS
It should be noted that the electric cars have recently appear on the market - cars with electric motors. There, the principle of operation of the motor is completely different, since the source of energy is not gasoline, but electricity in batteries. But so far the automotive market belongs to cars with DVS, and the electrical engines cannot boast of high efficiency.
A few words in conclusion
Such a device of DVS is practically perfect. But every year new technologies that increase the efficiency of the motor work are being developed, the characteristics of gasoline are improved. With the right maintenance of the car engine, it can work for decades. Some successful Motors of Japanese and German Concern "run out" million kilometers and come into disrepair solely because of the mechanical obsolescence of parts and steam of friction. But many engines even after a million mileage successfully pass over the overhaul and continue to fulfill their direct purpose.