How the inner combustion gasoline engine works
On our roads, you can most often find cars consuming gasoline and diesel fuel. The time of electrocars has not yet come. Therefore, we consider the principle of operation of the internal combustion engine (DVS). A distinctive feature is the transformation of the energy of the explosion into mechanical energy.
When working with gasoline power plants, several methods for forming a fuel mixture are distinguished. In one case, this happens in the carburetor, and then this is all served in the engine cylinders. In another case, gasoline through special nozzles (injectors) is injected directly into the collector or combustion chamber.
To fully understand the work of the engine, it is necessary to know that there are several types of modern motors that have proven their effectiveness in the work:
- gasoline engines;
- engines consuming diesel fuel;
- gas installations;
- gas diffraction devices;
- rotary options.
The principle of operation of the DVS of these types is almost the same.
BACKS OF DVS
Each has a fuel that blowing up in the combustion chamber is expanding and pushing the piston mounted on the crankshaft. Next, this rotation through additional mechanisms and nodes is transmitted to the vehicle wheels.
As an example, we will consider a gasoline four-stroke motor, since it is precisely the most common variant of the power plant in the machines on our roads.
So you:
- the inlet opens and filling the combustion chamber by the prepared fuel mixture
- camera sealing and reduce its volume in compression tact
- the mixture is exploding and pushes the piston that receives a mechanical energy pulse
- camera combustion is released from burning products
In each of these stages of the operation of the engine, several simultaneous processes are laid. In the first case, the piston is at the very bottom of its position, while all the valves are open, admissive fuel. The next step begins with the complete closure of all the holes and move the piston to the maximum top position. In this case, everything is compressed.
Having reached the extreme top position of the piston, the voltage comes on the candle, and it creates a spark, burning the mixture for an explosion. The strength of this explosion pushes the piston down, and at this time the outlet openings open and the camera is cleared of gas residues. Then everything is repeated.
Work carburetor
The formation of the fuel mixture in the machines of the first half of the last century occurred using a carburetor. To understand how the internal combustion engine works, you need to know that the automotive engineers constructed the fuel system so that the combustible mixture was supplied to the combustion chamber.
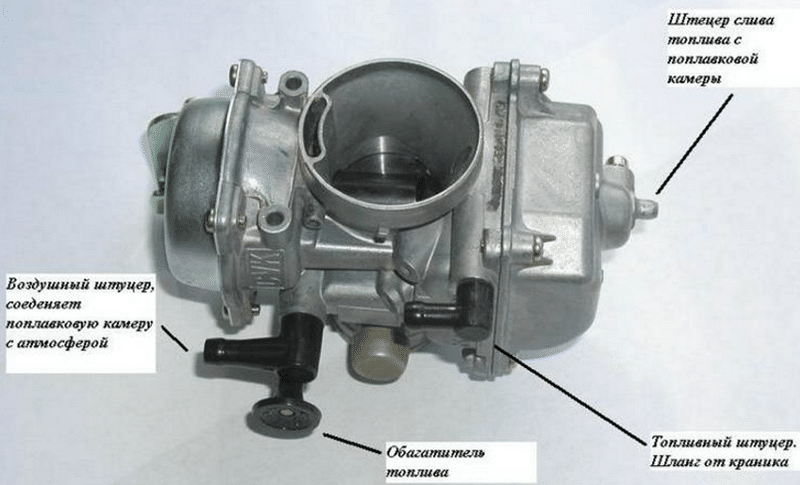
Carburetor device
Her formation was engaged in the carburetor. In the right relations, he stirred gasoline and air and sent it all into cylinders. Such a relative simplicity of the system design allowed him for a long time to remain indispensable part of the gasoline units. But later, his shortcomings began to prevail over the advantages and not to ensure the rising requirements for cars in general.
Disadvantages of carburetor systems:
- there is no possibility to provide economical modes in sudden change of driving modes;
- excess of the limits of harmful substances in exhaust gases;
- low car power due to non-compliance with the prepared mixture of the vehicle.
Compensate these drawbacks tried direct gasoline through injectors.
Work of injection engines
The principle of operation of the injection motor is to direct gasoline injection into the intake manifold or combustion chamber. Visually, everything is similar to the operation of the diesel installation, when the feed is performed dosed and only in the cylinder. The only difference is that injector units have candles for ignition.
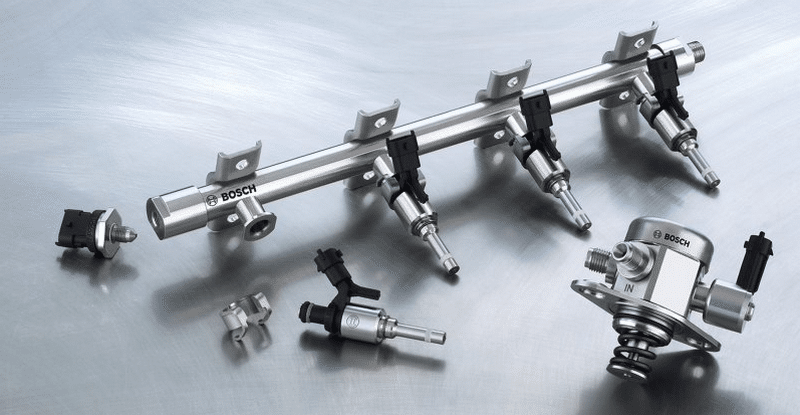
Injector design
Stages of gasoline engines with direct injection are not different from the carburetor option. The difference is only at the place of formation of the mixture.
Due to this design, the designs are ensured by the advantages of such engines:
- an increase in power up to 10% with similar technical characteristics with carburetor;
- noticeable savings of gasoline;
- improving environmental emission characteristics.
But with such advantages there are disadvantages. The main maintenance, maintainability and configuration. Unlike carburetors who can independently disassemble, collect and adjust, injectors require special expensive equipment and a large number of different sensors in the car.
Fuel injection methods
During the evolution of fuel supply to the engine, a constant convergence of this process with a combustion chamber took place. In the most modern ICE, the fusion of the gasoline supply and place of combustion occurred. Now the mixture is no longer formed in the carburetor or intake manifold, but is injected into the chamber directly. Consider all the variants of injection devices.
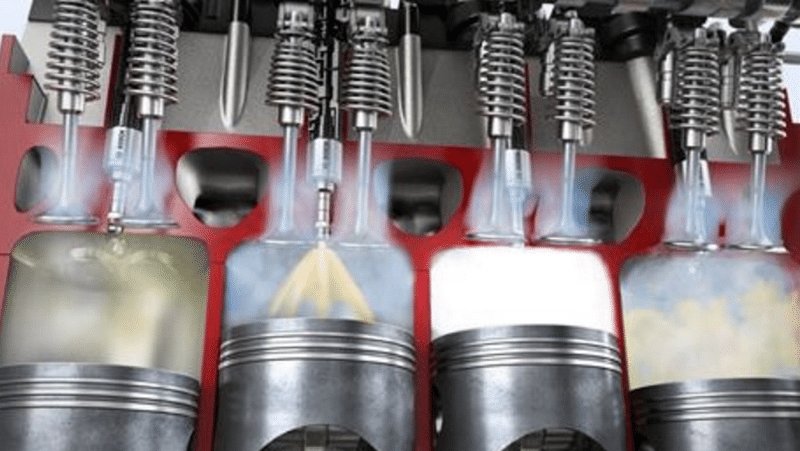

Single-point injection option
The simplest design version looks like fuel injection through one nozzle in the intake manifold. The difference with the carburetor is that the latter supplies a ready-made mixture. In the injection version passes the fuel through the nozzle. The benefit is to obtain savings at expenses.
Monotinic Fuel Feed
This method also forms a mixture outside the camera, but sensors are involved, which provide the feed directly to each cylinder through the intake manifold. This is a more economical use of fuel.
Straight injection into the chamber
This option is still the most effectively uses the possibilities of the injection structure. The fuel is directly sprayed in the chamber. Due to this, the level of harmful exhaust is reduced, and the car receives except for greater savings of gasoline increased power.
Increased system reliability reduces negative service factor. But such devices need high-quality fuel.