DVS, what is it in the car and what is the principle of work?
This marking can often be found on the sites dedicated to automotive themes, and not in vain. After all, there is nothing difficult in deciphering this abbreviation, but means this is a friendly internal combustion engine. DVS its abbreviated version. This is the so-called thermal machine, the main feature of which is the transformation of chemical energy, into mechanical work, by performing a certain list of works, in the appropriate order.
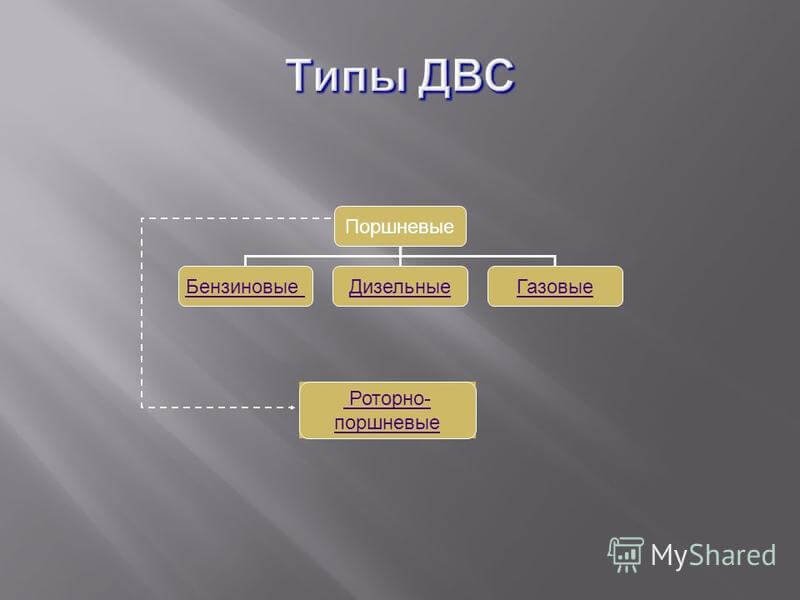
There are several varieties of engines: piston, gas turbine and rotary-piston. Naturally, the currently famous and popular, this is a piston engine. Therefore, the disassembly and study of the principle of work will be considered precisely on its example. And in the general scheme and the nature of the work for all three types have a similar principle.
Among the main advantages of the presented motor, which was widely used, can be noted: versatility, autonomy, cost, low weight, compactness, multi-fuel.
But despite such an impressive percentage of positive sides, the flaws are also enough. These include the noise level, the high frequency of rotation of the shaft, the toxicity of produced gases, a small resource, a small utility work rate.
Depending on the type of fuel used, diesel and gasoline are distinguished. The latter are most in demand and popular. Among alternative fuels, natural gas can be used, the fuel of the so-called alcohol group - ethanol, methanol, hydrogen.
The most promising in the future, it can be a hydrogen engine that, given now increased attention to ecology. After all, this engine does not have harmful emissions. In addition to the engine, hydrogen is used to produce electrical energy for car fuel mechanisms.
DVS device
Among the main elements of the DVS it is worth distinguishing the main building, two main mechanisms (gas distribution and curve), as well as a number of adjacent systems in the formation of fuel, intake, ignition, cooling, control, lubrication, graduation.
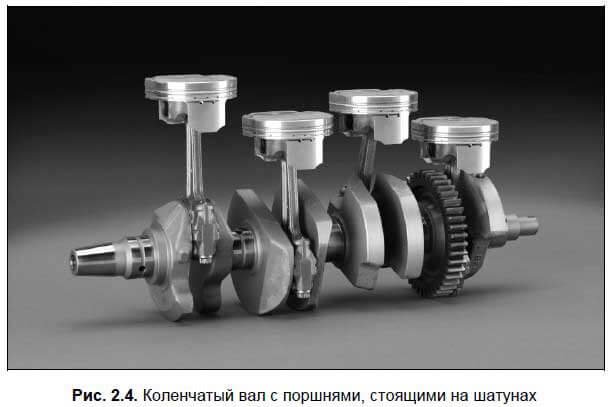
The housing is combined with a block of cylinders and a block of block. The curve mechanism allows you to transform reciprocating piston movements into rotational motions of the crankshaft. The TRM provides timely supply of air or fuel into the system, as well as the release of exhaust gases.
The intake system is responsible for the power of the motor with air, and the fuel for fuel. The joint work of these systems or complexes, ensures the formation of the so-called fuel and air mass. The main place in the fuel system is assigned to the injection system.
The ignition carries out forced ignition of the above mixture in gasoline engines. In diesel, the process is slightly simpler, since the mixture is self-igniting.
Lubrication allows you to remove the voltage from the parts between which friction occurs. In order to cool the mechanisms and parts in time, the cooling system corresponds to the cooling system. Some of the important functions perform an exhaust system, which allows removing spent gases, and also reduces their noise and toxicity.
The court, that is, the engine control system provides electronic control and control, all motor systems and adjacent complexes.
Principle of operation
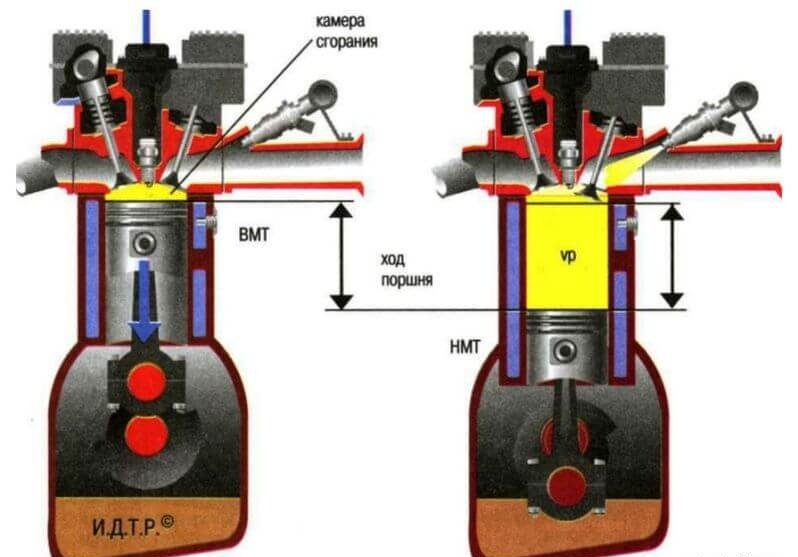
The principle of operation is based on the effect of gas expansion under the influence of heat arising during the combustion of the mixture by an air-fuel system. Due to this, the pistons in the cylinders are moving.
Works in all piston engines are performed cyclically. That is, every cycle occurs for a pair of rolver shaft and, accordingly, includes four clocks. So-called four-stroke engines. List of clocks: inlet, compression, work move, release.
When the work of the inlet and the working stroke is performed, the movement of the piston is carried out in the direction of the bottom. Due to this, cyclicity does not coincide in each of the cylinders. With this in mind, the smoothness and uniformity of the engine is achieved. There are two-stroke motors, in them one combustion cycle includes only compression and work move.
Tact inlet

During this tact, both systems (inlet and fuel) provide the formation of air-fuel mass. Given the different configuration of motors and design, the formation of the mixture can occur directly in the intake manifold or in the combustion chamber itself. At the moment when the GDM intake valves occurs, the air or already the fuel and air mixture moves directly into the combustion chamber, under the influence of the discharge force during the movement of the piston.
Tut compression
During compression, the corresponding intake valves overlap, and the fuel-air mixture is compressed in the cylinders.
Working
This beat is accompanied by the formation of a flame, depending on the type of fuel, as already mentioned forcibly or independently. As a result, the formation of a large number of gases. And those in turn are put on the piston himself, forcing it down. And thanks to the crank-connecting mechanism, the piston movement is converted into the rotational movement, transmitted to the crankshaft, the latter is used in turn to move the car.
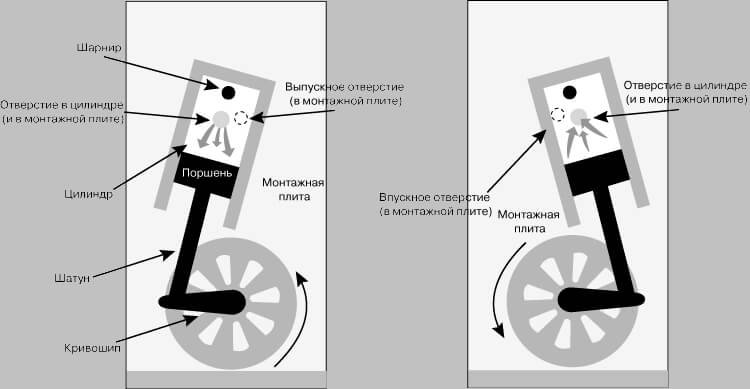
Tact release
During the work of the last tact, the exhaust valves of the mechanism are opened through which the spent gases are removed. In the future, their purification is performed, noise reduction and cooling. Subsequently, gases are sent to the atmosphere.
If you thoroughly analyze your read information, you can understand why the inheritance of the DVS have a small efficiency. Namely, 40%, it is so much work performed at a specific time during the operation of one cylinder. The rest at the same time provide the inlet, compression and release accordingly.