Batteries: what voltage to charge and how to do it
Autonomous power supplies - rechargeable batteries - are seen in modern technologies as an integral part of almost any project. For automotive technology, the battery is also a constructive part, without which full-fledged operation of the vehicle is inconceivable. The general usefulness of batteries is obvious. But technologically these devices are still not completely perfect. For example, frequent recharging of the batteries is a clear imperfection. Of course, the question is, with what voltage to charge the battery in order to reduce the frequency of recharging and preserve all its working properties for a long period of time?
To thoroughly understand the intricacies of the charging / discharging processes of lead-acid batteries (automobile) will help to determine the basic parameters of batteries:
- capacity,
- electrolyte concentration,
- discharge current strength,
- electrolyte temperature,
- self-discharge effect.
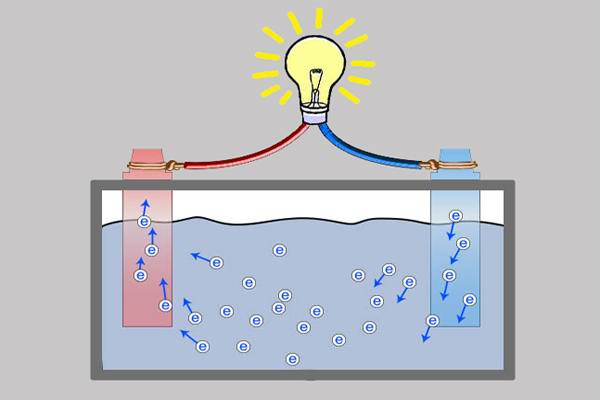
Under the capacity of a battery of accumulators, electricity is received, given by each individual battery bank in the process of its discharge. Typically, the capacity value is expressed in ampere-hours (A / h).
 On the case of the storage battery for the car, not only the nominal capacity is indicated, but also the starting current when the car is started on a cold one. An example of marking - a battery produced by the Tyumen plant
On the case of the storage battery for the car, not only the nominal capacity is indicated, but also the starting current when the car is started on a cold one. An example of marking - a battery produced by the Tyumen plant The discharge capacity of the battery, indicated on the technical label by the manufacturer, is considered a nominal parameter. In addition to this figure, the parameter of the charge capacity is also significant for operation. The required charge value is calculated by the formula:
Sz = Iz * Tz
where: Ic - charging current; Tz - charge time.
The figure indicating the discharge capacity of the battery is directly related to other technological and design parameters and depends on the operating conditions. From the constructive and technological properties of the battery, the discharge capacity is influenced by:
- active mass,
- the electrolyte used,
- thickness of electrodes,
- geometrical dimensions of electrodes.
Among the technological parameters, the degree of porosity of active materials and the recipe for their preparation are also significant for the capacity of the battery.
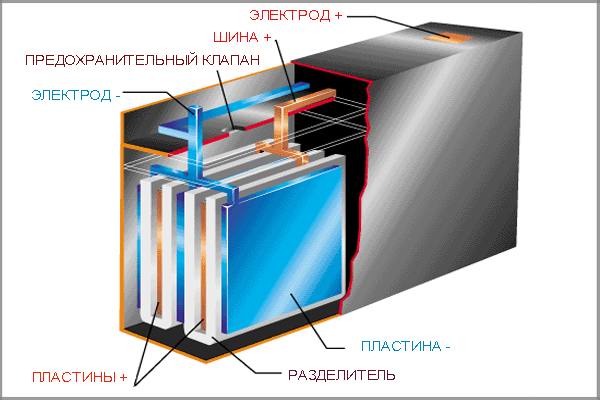 The internal structure of a lead-acid car battery, which includes the so-called active materials - plates of negative and positive fields, as well as other components
The internal structure of a lead-acid car battery, which includes the so-called active materials - plates of negative and positive fields, as well as other components Operational factors also do not stand aside. As practice shows, the strength of the discharge current paired with the electrolyte is also capable of influencing the battery capacity parameter.
Effect of electrolyte concentration
Excessive electrolyte concentration will shorten the battery life. Operating conditions of the battery with a high concentration of electrolyte lead to an intensification of the reaction, which results in the formation of corrosion on the positive electrode of the battery.
Therefore, it is important to optimize the value, taking into account the conditions in which the battery is used and the manufacturer's requirements for such conditions.
 Optimizing the concentration of the electrolyte of the battery is seen as one of the important points in the operation of the device. Monitoring the concentration level is imperative
Optimizing the concentration of the electrolyte of the battery is seen as one of the important points in the operation of the device. Monitoring the concentration level is imperative For example, for conditions with a temperate climate, the recommended electrolyte concentration level for most car batteries is adjusted to a density of 1.25 - 1.28 g / cm 2.
And when the operation of devices is relevant in relation to a hot climate, the electrolyte concentration should correspond to a density of 1.22 - 1.24 g / cm 2.
Batteries - Discharge Current
It is logical to divide the battery discharge process conditionally into two modes:
- Long.
- Short.
The first event is characterized by a discharge at low currents over a relatively long time period (from 5 to 24 hours).
The second event (short discharge, starter discharge), on the contrary, is characterized by large currents in a short period of time (seconds, minutes).
An increase in the discharge current provokes a decrease in the capacity of the battery.
 Charger Teletron, which is successfully used to work with lead-acid car batteries. Simple electronic circuit, but high efficiency
Charger Teletron, which is successfully used to work with lead-acid car batteries. Simple electronic circuit, but high efficiency Example:
There is a battery with a capacity of 55 A / h with an operating current at the terminals of 2.75A. Under normal environmental conditions (plus 25-26 ° C), the battery capacity is within 55-60 A / h.
If the battery is discharged with a short-term current of 255 A, which is equivalent to an increase in the nominal capacity by 4.6 times, the nominal capacity will decrease to 22 A / h. That is, almost doubled.
Electrolyte temperature and battery self-discharge
The discharge capacity of storage batteries naturally decreases if the temperature of the electrolyte drops. A drop in the temperature of the electrolyte entails an increase in the degree of viscosity of the liquid component. As a consequence, the electrical resistance of the active substance increases.
Disconnected from the consumer, completely inactive, has the ability to lose capacity. This phenomenon is explained by chemical reactions inside the device, taking place even in conditions of complete disconnection from the load.
Both electrodes - negative and positive - fall under the influence of redox reactions. But to a greater extent, the self-discharge process involves the electrode of negative polarity.
The reaction is accompanied by the formation of hydrogen in gaseous form. With an increase in the concentration of sulfuric acid in the electrolyte solution, an increase in the density of the electrolyte from 1.27 g / cm 3 to 1.32 g / cm 3 is noted.
This is commensurate with a 40% increase in the rate of self-discharge effect at the negative electrode. An increase in the self-discharge rate is also provided by metal impurities included in the structure of the negative-polarity electrode.
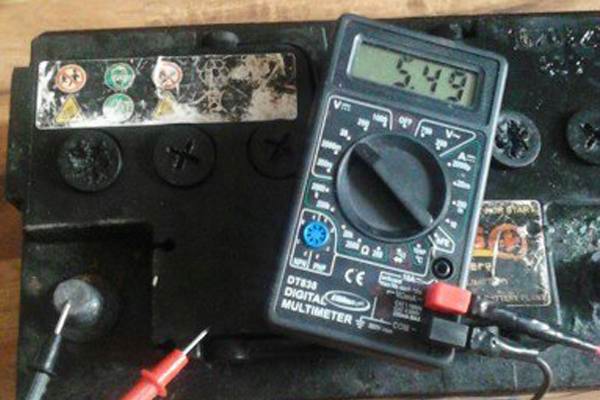 Self-discharge of a car battery after long-term storage. With complete inactivity, with no load, the battery has lost a significant part of its capacity
Self-discharge of a car battery after long-term storage. With complete inactivity, with no load, the battery has lost a significant part of its capacity It should be noted: any metals present in the electrolyte and other components of batteries enhance the self-discharge effect.
When these metals come into contact with the surface of the negative electrode, they cause a reaction, as a result of which the release of hydrogen begins.
Some of the existing impurities play the role of a charge carrier from the positive electrode to the negative one. In this case, the reactions of reduction and oxidation of metal ions take place (that is, again, the self-discharge process).
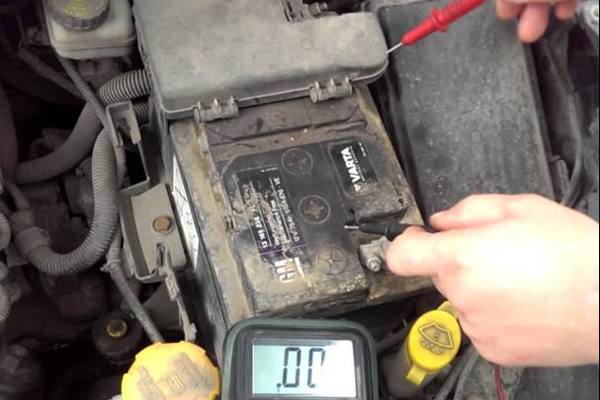 There are also cases when the battery loses its charge from contamination on the case. Contamination creates a conductive layer that closes the positive and negative electrodes
There are also cases when the battery loses its charge from contamination on the case. Contamination creates a conductive layer that closes the positive and negative electrodes In addition to the internal self-discharge, the external self-discharge of the car battery is not excluded. The reason for this phenomenon can be a high degree of contamination of the surface of the battery case.
For example, electrolyte spilled on the case, water or other technical liquids. But in this case, the self-discharge effect is easily eliminated. It is enough just to clean the battery case and keep it always clean.
Car battery charging
Let's start from the situation of inactivity of the device (in the off state). With what voltage or current to charge the car battery when the device is in storage?
In storage conditions of the battery, the main purpose of charging is aimed at compensating for self-discharge. In this case, charging is usually done with low currents.
The range of charge values is typically 25 to 100 mA. In this case, the charge voltage must be maintained within the range of 2.18 - 2.25 volts in relation to a single battery bank.
Selecting Battery Charge Conditions
The battery charging current is usually adjusted to a certain value depending on the set float time.
 Preparation of a car battery for recharging in a mode that needs to be determined taking into account the technological properties and technical parameters during the operation of the battery
Preparation of a car battery for recharging in a mode that needs to be determined taking into account the technological properties and technical parameters during the operation of the battery So, if it is supposed to charge the battery for 20 hours, the optimal parameter of the charging current is a value equal to 0.05C (that is, 5% of the nominal capacity of the battery).
Accordingly, the values will increase proportionally if you change one of the parameters. For example, with a 10-hour charge, the current strength will already be 0.1C.
Charge in a two-stage cycle
In this mode, initially (the first stage) is charged with a current of 1.5C until the voltage on a separate bank reaches 2.4 volts.
After that, the charger is transferred to the charge current mode of 0.1C and continues to charge until the full capacity is set for 2 - 2.5 hours (second stage).
The charge voltage in the second stage mode varies from 2.5 to 2.7 volts for one can.
Boost charge mode
The principle of forced charging involves setting the value of the charging current at the level of 95% of the nominal capacity of the battery - 0.95C.
The method is quite aggressive, but it allows you to charge the battery almost completely in just 2.5-3 hours (in practice, 90%). Up to 100% capacity charging in a forced mode will take 4 - 5 hours.
Control-training cycle
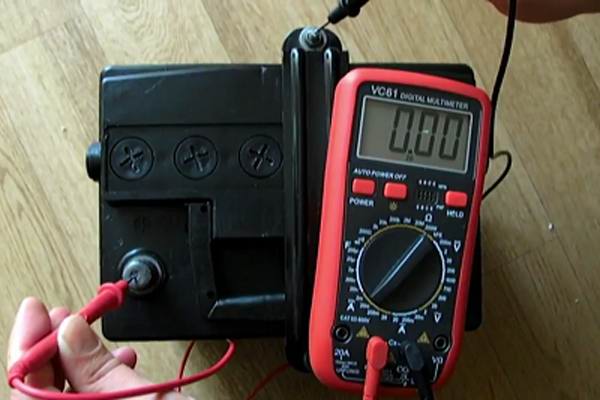 The practice of operating car batteries notes a positive result when the control-training cycle is applied to new batteries that have not yet been in operation.
The practice of operating car batteries notes a positive result when the control-training cycle is applied to new batteries that have not yet been in operation. For this option, charging with parameters calculated by a simple formula is optimal:
I = 0.1 * C20;
Charge until the voltage on a single bank is 2.4 volts, after which the value of the charging current is reduced to the value:
I = 0.05 * C20;
With these parameters, the process is continued until fully charged.
The control-training cycle also covers the practice of discharge, when the battery is discharged with a small current of 0.1C to a total voltage level of 10.4 volts.
In this case, the degree of density of the electrolyte is maintained at the level of 1.24 g / cm 3. After discharge, the device is charged according to the standard procedure.
General principles of charging lead-acid batteries
In practice, several methods are used, each of which has its own difficulties and is accompanied by a different amount of financial costs.
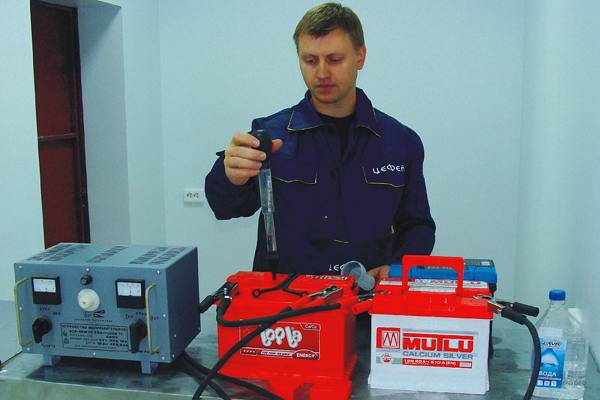 It is not difficult to decide in what way to charge the battery. Another question is what result will be obtained from the application of this or that method.
It is not difficult to decide in what way to charge the battery. Another question is what result will be obtained from the application of this or that method. The most accessible and simple method is considered to be a constant current charge at a voltage of 2.4 - 2.45 volts / bank.
The charging process continues until the current value remains constant for 2.5-3 hours. Under these conditions, the battery is considered fully charged.
Meanwhile, the combined charge technique has received greater recognition among motorists. In this version, the principle of limiting the initial current (0.1C) is applied until the specified voltage is reached.
Then the process continues at constant voltage (2.4V). For this circuit, it is permissible to increase the initial charge current to 0.3C, but no more.
It is recommended to charge batteries in buffer mode at low voltages. Optimal charge values: 2.23 - 2.27 volts.
Deep discharge - remediation
First of all, it should be emphasized: the restoration of the battery to the nominal capacity is possible, but on condition that there were no more than 2-3 deep discharges.
The charge in such cases is carried out with a constant voltage equal to 2.45 volts per cell. It is also allowed to charge with a (constant) current of 0.05C.
 The battery recovery process may require two to three separate charge cycles. Most often, to achieve full capacity, charging is carried out exactly in 2-3 cycles.
The battery recovery process may require two to three separate charge cycles. Most often, to achieve full capacity, charging is carried out exactly in 2-3 cycles. If the charge is carried out with a voltage of 2.25 - 2.27 volts, it is recommended to perform the process twice or three times. Since at low voltages, it is not possible to reach the capacity rating in most cases.
Of course, the influence of the ambient temperature should be taken into account during the recovery process. If the ambient temperature is in the range of 5 - 35 ° C, the charge voltage does not need to be changed. In other conditions, a charge adjustment will be required.
Video on the battery control and training cycle
Tags: