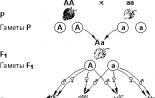
Ratio with complete dominance. Analysis cross
Analysis cross
What are the genotypes of the parents in a dihybrid test cross?
1) AABB x BbBb
2) AaBb x aabb
3) AABB x AABB
4) Bb x Aa
The genotype of one of the parents will be AaBb if, during an analyzing dihybrid crossing and independent inheritance of traits, a splitting in phenotype is observed in the offspring in the ratio
General
Select the genetic symbols that characterize the dihybrid cross.
1) AaB x aabb 3) AA x BB
2) Aa x aa 4) AB x AB
How are the genotypes of individuals designated during dihybrid crossing?
Signs by type
Identify recessive traits in pea seeds
1) yellow and smooth
2) green and smooth
3) yellow and wrinkled
4) green and wrinkled
Gametes
What gametes do individuals with the aaBB genotype have?
1) aa
2) aaBB
3) aBB
4) aB
How many types of gametes are formed in diheterozygous pea plants during dihybrid crossing (the genes do not form a linkage group)?
1) one
2) two
3) three
4) four
What types of gametes does a dihomozygous organism produce (dominance for each pair of alleles)?
What types of gametes are formed in an organism with genotype AaBb with independent inheritance of genes?
1) АВ, ab 3) АВ, Ab, аВ, ab
2) Aa, Bb 4) AA, Bb, Aa, BB
Types of gametes in an individual with the AABb genotype
1) AB, Ab
2) AA, Bb
3) Aa, bb
4) Aa, Bb
An individual with the Aabb genotype produces gametes
1) Ab, bb
2) Ab, ab
3) Aab
4) Aa, bb
An organism with the AABBCc genotype produces gametes
1) ABC and ABC
2) ABC and ABC
3) ААВВСС and ААВВССs
4) A, B, C, s
How many types of gametes does the following zygote produce: AaBvSS?
1) two 2) one 3) four 4) three
Problems
In dogs, black hair (A) is dominant over brown hair (a), and short legs (B) are dominant over normal leg length (b). Select the genotype of a black short-legged dog that is heterozygous only for leg length
1) AABb
2) Aabb
3) AaBb
4)AABB
When crossing individuals with genotypes AaBb with AaBb (the genes are not linked), the proportion of heterozygotes for both alleles in the offspring will be
1) 75%
2) 50%
3) 25%
4) 0%
When crossing two guinea pigs - a black (AA) smooth-haired (bb) male with a white (aa) wavy-haired (BB) female, a genotype ratio was obtained in F1
1) 100% AaBb
2) 50% AaBb: 50% Aabb
3) 25% AaBb: 50% Aabb: 25% Aabb
4) 25% AaBb: 50% Aabb: 25% AABB
Determine the percentage of genotypes in F1 hybrids at
crossing a gray rabbit (Aa) with a white one (aa).
1) 25% A a: 75% aa
2) 25% aa: 75% aa
3) 50% A a: 50% aa
4) 25% AA: 50% AA: 25% AA
The marriage of a woman with large eyes and a straight nose and a man with small eyes and a Roman nose produced four children, half of whom had large eyes and a Roman nose. Determine the mother's genotype if large eyes (A) and a Roman nose (B) are dominant traits.
1) Aabb 2) AaBB 3) AABB 4) AaBb
Two homozygous pumpkin plants with white oval fruits and yellow round fruits were crossed (A - white color dominates over yellow, B - round fruit shape over oval). Determine the F1 genotype.
In cattle, black color (A) is dominant over red, and polledness (B) is dominant over hornedness. When crossing a black polled cow with a red horned bull, 50% of the offspring turned out to be black polled, 50% - red polled.
Indicate the genotypes of the parents.
1) AaBb and aabb
2) AABB and aabb
3) AaBB and aabb
4)AABb and aabb
Brown-eyed, dark-haired parents (dominant traits) have a blue-eyed, fair-haired daughter. Determine the genotypes of her parents.
1) AABB, aaBB
2) AABb, aaBB
RELATIONSHIP OF PHENOTYPES IN F1
When crossing heterozygous tomato plants with red and round fruits with individuals recessive for both traits (red A and round B are dominant traits), offspring with genotypes AaBb, aaBb, Aabb, aabb will appear in the ratio
1) 3: 1
2) 9: 3: 3: 1
3) 1: 1: 1: 1
4) 1: 2: 1
The black color of the rabbit (B) is dominant over the white one (b), and the shaggy fur (A) is dominant over the smooth one (a). What kind of phenotypic split should be expected from crossing heterozygous individuals for two pairs of traits?
With dihybrid crossing and independent inheritance of traits in
parents with genotypes AABb and aabb in the offspring is observed
splitting in ratio
What will be the ratio of the splitting of traits according to phenotype in
offspring obtained from crossing a diheterozygous black,
shaggy rabbit AaBv with a white, smooth-haired rabbit AaBv
1) 1:2:1 2) 9:3:3:1 3) 1:1:1:1 4) 1:2:2:1
Determine the ratio of character segregation according to phenotype in the offspring obtained from crossing diheterozygous pea plants.
F1 genotypes
When crossing yellow smooth and green wrinkled peas in F1, all yellow smooth peas were obtained. Determine the genotype of pea seeds in F1
1) Aabb
2) aaBb
3) AaBB
4) AaBb
When crossing homozygous tomato plants with round red fruits and with pear-shaped yellow fruits (red - A, yellow - a, round - B, pear-shaped - b), offspring with the genotype will be obtained
1) bbAA
2) Bbaa
3) BBAA
4) BbAa
What genotype does the offspring have in F1 when crossing tomato plants with genotypes AAbb and aaBB?
1) aaBv
2) AaBv
3) AaBB
4) Aavv
Determine the percentage of genotypes in F1 hybrids when
crossing a gray rabbit (Aa) with a white one (aa).
1) 25% Aa: 75% aa
2) 25% aa: 75% aa
3) 50% Aa: 50% aa
4) 25% AA: 50% AA: 25% AA
Numerous experiments have confirmed the correctness of the patterns established by Mendel. At the same time, facts have emerged showing that the numerical relationships obtained by Mendel during the splitting of the hybrid generation were not always observed. This indicated that the relationships between genes and traits are more complex. It turned out that the same gene can influence the development of several traits; the same trait can develop under the influence of many genes.
It should be noted that the interaction of genes is of a biochemical nature, that is, it is not genes that interact with each other, but their products. The product of a eukaryotic gene can be either a polypeptide, tRNA, or rRNA.
TYPES OF INTERACTION OF ALLELIC GENES
There are complete dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance, and allelic exclusion.
Allelic genes are called genes located in identical loci of homologous chromosomes. A gene can have one, two, or more molecular forms. The appearance of the second and subsequent molecular forms is a consequence of gene mutation. If a gene has three or more molecular forms, it is said to be multiple allelism. Of the entire set of molecular forms, only two can be present in one organism, which is explained by the pairing of chromosomes.
Complete Domination
Complete Domination- this is a type of interaction of allelic genes in which the phenotype of heterozygotes does not differ from the phenotype of homozygotes in terms of dominance, that is, the product of a dominant gene is present in the phenotype of heterozygotes. Complete dominance is widespread in nature and occurs during inheritance, for example, of the color and shape of pea seeds, eye color and hair color in humans, Rh antigen, and many others. etc.
The presence of the Rh antigen (Rh factor) of erythrocytes is determined by the dominant Rh gene. That is, the genotype of a Rh-positive person can be of two types: either RhRh or Rhrh; The genotype of a Rh negative person is rhrh. If, for example, the mother is Rh-negative, and the father is Rh-positive and heterozygous for this trait, then with this type of marriage, both Rh-positive and Rh-negative children can be born with equal probability.
An Rh conflict may occur between an Rh-positive fetus and an Rh-negative mother.

This is the name of the type of interaction of allelic genes in which the phenotype of heterozygotes differs from both the phenotype of dominant homozygotes and the phenotype of recessive homozygotes and has an average (intermediate) value between them. Occurs when inheriting the color of the perianth of the night beauty, snapdragon, color of the fur of guinea pigs, etc.
Mendel himself encountered incomplete dominance when he crossed a large-leaved pea variety with a small-leaved one. The first generation hybrids did not repeat the trait of any of the parent plants; they had medium-sized leaves.
When crossing homozygous red-fruited and white-fruited strawberry varieties, the entire first generation of hybrids has pink fruits. When crossing these hybrids with each other we get: by phenotype - 1/4 red-fruited, 2/4 pink-fruited and 1/4 white-fruited plants, by genotype - 1/4 AA, 1/2 Aa, 1/4 aa (and by phenotype, and by genotype the ratio is 1:2:1). The correspondence of segregation by genotype to segregation by phenotype is characteristic of incomplete dominance, since heterozygotes are phenotypically different from homozygotes.
Codominance
Codominance- a type of interaction of allelic genes in which the phenotype of heterozygotes differs from both the phenotype of dominant homozygotes and the phenotype of recessive homozygotes, and the heterozygote phenotype contains products of both genes. Occurs during the formation, for example, of the IV blood group system (AB0) in a person.
In order to imagine how the inheritance of blood groups occurs in humans, you can look at the birth of children with what blood group is possible from parents who have one blood group, the other a third, and are heterozygous for this trait.
| R | ♀I A i 0 II (A) |
× | ♂I B i 0 III (B) |
||
| Types of gametes | I A | i 0 | I B | i 0 | |
| F | i 0 i 0 I (0) 25% |
I A i 0 II (A) 25% |
I B i 0 III (B) 25% |
I A I B IV (AB) 25% |
|
Allelic exclusion
Allelic exclusion called the absence or inactivation of one of a pair of genes; in this case, the phenotype contains the product of another gene (hemizygosity, deletion, heterochromatization of the chromosome region in which the desired gene is located).
TYPES OF INTERACTION OF NON-ALLELIC GENES
Complementarity, epistasis, polymerization.
Non-allelic genes- genes located either in non-identical loci of homologous chromosomes, or in different pairs of homologous chromosomes.
Test crossbreeding is a type of genetic research carried out to determine the heterozygosity of an organism.
Essence of the method
Test crossbreeding was studied by Gregor Mendel and one of the founders of genetics, William Bateson.
To determine heterozygosity, an analyzer is used - a recessive homozygous organism (aa).
The analyzed individual has a dominant trait in the phenotype. For example, this is a solid coat color in cats.
In the genotype it can be:
- homozygous (AA);
- heterozygous (Aa).
We cross:
R A? (solid colored cat) x aa (Siamese cat)
TOP 4 articleswho are reading along with this
G Huh? aa
First option F1: Aa Aa (all kitten colors are solid)
Second option F2: Aa aa (Siamese and solid colors in a 1:1 ratio)
The accuracy of the analysis depends on the number of descendants. The more descendants, the higher the accuracy.
Thus, in the first variant, the analyzed organism produced only A - gametes. This means he is homozygous (pure breed). In the second case of analysis, the cat gave both A - gametes and a - gametes, i.e. it is a heterozygote. Thus, the genotype with complete dominance is determined by the ratio of characteristics during analyzing crossing.
In the case of incomplete dominance in the offspring there are observed intermediate (mixed) signs:
- in the first generation by 100%;
- in the second generation 1:2:1, where 2 is a mixed trait.

Rice. 1. Scheme of analytical crossing.
Determination of a diheterozygote (AaBb) during test crossing occurs when the ratio of phenotypes and genotypes (F) is 1:1:1:1.
R AaVv x aavv
G AB Av aV av av
F AaBv Aavv aaBv aavv
Backcrossing
Sometimes backcrossing is carried out - with the parent individual. Its goal is to saturate the hybrid with valuable parental genes.
Sample task
It is known that black color in rabbits is dominant over white. Is it possible to get white rabbits from black parents?
The recessive trait manifests itself in the homozygous state (aa). Such a homozygote can result if each parent has a recessive gene a.

Rice. 2. Drawing of crossing a white and a black rabbit.
Since both parents are black, then gene a will be in both gametes if each of them is heterozygous (Aa).
P Aa x Aa
F AA Aa aA aa
25% of the offspring of heterozygous black rabbits will be white.
Practical use
Test crossbreeding is of great importance in all sectors of animal husbandry. With its help, you can determine the purebred of an individual.
If the dominant trait is economically significant and determines the productivity or other value of animals, early determination of homozygosity helps prevent financial losses.
The fact is that one or more male sires can be the fathers of the entire livestock of the country. Therefore, the requirements for the selection of such animals are very stringent.
The Ukrainian sire of the Podolsk breed, Repp, fathers 50,000 calves every year. The mass of this bull is 1500 kg.

Rice. 3. Bull Repp.
What have we learned?
While studying analytical crossbreeding in 10th grade, we learned that this is an important method of genetic analysis. The ratio of genotypes and phenotypes during test crossing depends on the homozygosity or heterozygosity of the parent individual. If an individual is homozygous, then uniformity in phenotype and genotype is observed in the offspring. If the original organism is heterozygous, then in the offspring there is a divergence in both genotype and phenotype (1:1). Heterozygotes are of less value in livestock production if an economically important trait is associated with the dominant gene.
At monohybrid cross is being studied
- one sign;
- one gene;
- one pair of alternative genes;
- one pair of alternative signs (they are all the same).
Monohybrid splits
1) There is no splitting (all children are the same) - two homozygotes AA x aa were crossed (Mendel’s first law).
2) Segregation 3:1 (75% / 25%) – two heterozygotes Aa x Aa were crossed (Mendel’s second law).
3) Segregation 1:2:1 (25% / 50% / 25%) – two heterozygotes Aa x Aa were crossed at .
4) Segregation 1:1 (50% / 50%) – a heterozygote and a recessive homozygote Aa x aa were crossed (analysis crossing).
Mendel's first law
(law of uniformity, law of dominance)
When pure lines (homozygotes) are crossed, all offspring are identical (uniformity of the first generation, no splitting).
PAA x aa
G (A) (a)
F 1 Aa
All descendants of the first generation (F 1) exhibit a dominant trait (yellow peas), and the recessive trait (green peas) is in a latent state.
Mendel's second law (law of segregation)
When self-pollination of first-generation hybrids (when crossing two heterozygotes) results in a 3:1 split in the offspring (75% dominant trait, 25% recessive trait).
F 1 Aa x Aa
G (A) (A)
(a) (a)
F 2 AA; 2Aa; aa
Analysis cross
When crossing a heterozygote Aa with a recessive homozygote aa, a 1:1 split (50% / 50%) is obtained.
P Aa x aa
G (A) (a)
(a)
F 1 Aa; aa
PROBABILITY OF GENOTYPE WHEN CROSSING Aa x Aa
1. Determine the percentage probability of the appearance of a recessive homozygote in the offspring of crossing heterozygous plants with complete dominance. Write your answer as a number.
Answer
PROBABILITY OF PHENOTYPE WHEN CROSSING Aa x Aa
1. What is the probability of white chickens from cream heterozygous parents (Aa)? Write your answer as a percentage; there is no need to write the % sign.
Answer
2. What is the percentage of dwarf forms during self-pollination of a heterozygous tall pea plant (tall stem - A)? Write down only the percentage in your answer.
Answer
3. Determine the probability (%) of obtaining offspring with a dominant manifestation of the trait in a monohybrid crossing of heterozygous hybrids with each other with complete dominance of this trait. Write your answer as a number.
Answer
4. What is the probability of dark-haired parents (Aa) having children with blond hair (dark color dominates light color)? Write your answer as a number only.
Answer
5. In chickens, the presence of a comb (C) dominates over its absence (c). When a heterozygous rooster and hen that have combs are crossed, what percentage of the chicks will be combless? Please indicate only the number in your answer.
Answer
6. Phenylketonuria is inherited as a recessive trait. Determine the probability of having healthy children from parents heterozygous for this trait. Write your answer in %.
Answer
7. What is the probability (in%) of the appearance of offspring with a recessive trait during self-pollination of heterozygous plants? Write down only the corresponding number in your answer.
Answer
PROBABILITY OF GENOTYPE WHEN CROSSING Aa x aa
1. What is the probability (in%) of the birth of homozygous offspring when crossing homozygous and heterozygous organisms? Write down only an integer in your answer.
Answer
PROBABILITY OF PHENOTYPE WHEN CROSSING Aa x aa
1. What is the probability that a pathological gene will appear in the offspring if an organism that is heterozygous for a given trait (the genes are not linked) is crossed with an organism that has a recessive genotype for this trait? Write your answer as a number (in %) showing the desired probability.
Answer
2. The individual under study has dark hair color and is homozygous for this trait. When conducting an analysis cross, what is the probability of the birth of offspring with light hair color (A - dark hair color, a - light hair color)? Please indicate only the number in your answer.
Answer
3. What is the probability (%) of obtaining brown puppies in a monohybrid test cross of a heterozygous black dog with complete dominance of the trait? Write your answer as a number.
Answer
4. Myoplegia (attacks of paralysis of the limbs) is inherited as a dominant trait. Determine (in%) the probability of having children with anomalies in a family where the father is heterozygous and the mother does not suffer from myoplegia. Write down only the corresponding number in your answer.
Answer
RELATIONSHIP OF GENOTYPES Aa x Aa
1. What ratio of genotypes will be obtained by crossing two heterozygotes with complete dominance? Write the answer as a sequence of numbers in descending order.
Answer
2. Determine the ratio of genotypes in the offspring when crossing Aa x Aa. In your answer, write down the sequence of numbers in decreasing order.
Answer
3. Determine the ratio of genotypes in the offspring formed by crossing two heterozygous pumpkin plants with yellow fruits with complete dominance. Write your answer as a sequence of numbers arranged in decreasing order.
Answer
RELATIONSHIP OF GENOTYPES Aa x aa
1. Determine the ratio of genotypes in descendants when crossing organisms heterozygous and homozygous for a recessive allele with complete dominance. Write the answer as a sequence of numbers arranged in descending order.
Answer
2. Determine the ratio of genotypes when crossing a heterozygous pea plant with smooth seeds and a plant with wrinkled seeds. Write your answer in the form of numbers showing the ratio of the resulting genotypes, arranged in decreasing order.
Answer
RELATIONSHIP OF PHENOTYPES Aa x Aa
1. Determine the ratio of phenotypes in hybrids obtained by crossing parental forms with genotypes Aa x Aa. Write the answer as a sequence of numbers arranged in descending order.
Answer
2. Determine the ratio of phenotypes in the offspring formed by crossing two heterozygous pumpkin plants with yellow fruits with complete dominance. Write your answer as a sequence of numbers showing the ratio of phenotypes in descending order.
Answer
3. Determine the ratio of phenotypes in the offspring of a monohybrid crossing of two heterozygous organisms with complete dominance. Write your answer as a sequence of numbers showing the ratio of the resulting phenotypes, in descending order.
Answer
RELATIONSHIP OF PHENOTYPES Aa x aa
1. In guinea pigs, the black gene is dominant over the white gene. Determine the ratio of phenotypes in the offspring obtained by crossing a heterozygous female and a white male. Write your answer as a sequence of numbers showing the ratio of the resulting phenotypes.
Answer
2. Determine the ratio of phenotypes in the offspring of a monohybrid crossing of a heterozygous individual with a homozygous individual having a phenotypic manifestation of the recessive trait. Write the answer as a sequence of numbers arranged in descending order.
Answer
NUMBER OF PHENOTYPES
1. What number of phenotypes is formed in the offspring when crossing Aa x Aa in the case of complete dominance? Please indicate only the number in your answer.
Answer
2. How many phenotypes will the offspring get from an analyzing monohybrid cross of a heterozygous organism? Write down only the corresponding number in your answer.
Answer
3. How many different phenotypes will be obtained when crossing a black heterozygous female and a white male rabbit? Write down only the corresponding number in your answer.
Answer
DIFFICULT
Plants of pure tomato lines with round and pear-shaped fruits were crossed (A – rounded fruit shape). The resulting offspring in F1 were crossed with each other. Determine the ratio of descendants by phenotype in the second (F2) generation with complete dominance of the trait. Write your answer as a sequence of numbers showing the ratio of the resulting phenotypes, in descending order.
Answer
From crossing black rabbits, the offspring produced seven black and two white rabbits. What is the probability of obtaining white rabbits from subsequent crosses of the same parents? Write your answer as a number showing the probability of getting white rabbits in subsequent generations in %.
Answer
Determine the ratio of phenotypes in second-generation hybrids during monohybrid crossing (complete dominance). In your answer, write down a sequence of numbers showing the ratio of the resulting phenotypes, in descending order.
Answer
Determine the probability (in%) of having a child with blood group II if the parents have blood group IV. Write down only the corresponding number in your answer.
Answer
Establish a correspondence between the ratio of phenotypes and the type of crossing for which it is typical: 1) monohybrid, 2) dihybrid (genes are not linked)
A) 1:2:1
B) 9:3:3:1
B) 1:1:1:1
D) 3:1
Answer
All of the characteristics given below, except two, are used to describe the results of an analytical crossing of an individual with genotype Aa. Identify these two characteristics that “fall out” from the general list, and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) the number of offspring with a recessive genotype is 75%
2) the ratio of phenotypes was 1: 1
3) gene linkage appears
4) the second parent has the genotype - aa
5) among the descendants, 50% have a dominant trait in the phenotype
Answer
The statements below, except two, are used to describe the results of crossing individuals with genotypes Aa x Aa with complete dominance. Identify these two statements that are out of the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) 75% of offspring have a recessive trait in their phenotype
2) the phenotype ratio was 3:1
3) the law of splitting of characteristics is manifested
4) genotype splitting was 1:2:1
5) 25% of offspring have a dominant trait in the phenotype
Answer
All the characteristics given below, except two, are used to describe monohybrid crossing of heterozygotes with complete dominance. Identify two characteristics that “fall out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) the offspring are phenotypically monotonous
2) there is a splitting according to the genotype 1: 2: 1
3) parental individuals produce two types of gametes
4) 25% of the offspring have a heterozygous genotype
5) 75% of the offspring have a dominant phenotype
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. Determine the genotype of the parent pea plants if their crossing resulted in 50% of plants with yellow and 50% with green seeds (recessive trait)
1) AA x aa
2) Aa x Aa
3) AA x Aa
4) Aa x aa
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. When crossing Drosophila flies with long and short wings, an equal number of long-winged and short-winged offspring was obtained (long wings B dominate over short wings b). What are the genotypes of the parents
1) bb x Bb
2) BB x bb
3) Bb x Bb
4) BB x BB
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. What is the genotype of the parents if a 1:1 phenotypic ratio was observed during the test cross?
1) Aa and aa
2) Aa and Aa
3) AA and aa
4) Aa and AA
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. From hybrids of the first generation in the second generation, 1/4 of individuals with recessive characteristics are born, which indicates the manifestation of the law
1) linked inheritance
2) splitting
3) independent inheritance
4) intermediate inheritance
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. What number of phenotypes is formed in the offspring of an Aa x Aa cross in the case of complete dominance?
1) 1
2) 2
3) 3
4) 4
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. “When crossing two homozygous organisms that differ in one pair of traits, the new generation of hybrids will be uniform and will be similar to one of the parents.” This is the wording
1) the law of splitting
2) hypotheses of gamete purity
3) rules of dominance
4) the law of independent distribution of genes
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. According to the law of segregation, the ratio of phenotypes in F2 (with complete dominance) is equal to
1) 1:1
2) 3:1
3) 1:2:1
4) 1:1:1:1
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. Determine what genotypes children can have if the heterozygous mother has wavy hair and the father has straight hair (complete dominance of the trait).
1) BB, Bb, bb
2) Bb, bb
3) BB, Bb
4) BB, bb
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. When self-pollinating a heterozygous pea plant with yellow colored seeds, the phenotypic cleavage will be
1) 1:1
2) 3:1
3) 1:2:1
4) 9:3:3:1
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. When a monohybrid crossing of a heterozygous individual with a homozygous recessive individual occurs in their offspring, the characteristics are split according to the phenotype in the ratio
1) 3:1
2) 9:3:3:1
3) 1:1
4) 1:2:1
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. If, when crossing two homozygous organisms in the second generation, a recessive trait is found in 1/4 of the offspring, then the law has manifested itself
1) linked inheritance
2) independent inheritance
3) intermediate nature of inheritance
4) splitting of signs
Answer
Choose one, the most correct option. Phenotypic cleavage in the second generation in a ratio of 3:1 is typical for crossing
1) dihybrid
2) analyzing
3) monohybrid
4) polyhybrid
Answer
Consider the crossover patterns presented in the figure and determine the ratio of phenotypes in F2. In your answer, write down a sequence of numbers showing the ratio of the resulting phenotypes, in descending order.
Answer

Using the pedigree shown in the figure, determine the probability (in percentage) of the birth of parents 1 and 2 of a child with the trait indicated in black, with complete dominance of this trait. Write your answer as a number.
Answer
All of the characteristics given below, except two, are used to describe an analysis cross. Find two characteristics that “fall out” from the general list and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) crossing is carried out with recessive individuals for all genes
2) phenotypic cleavage is observed in the ratio 9:3:3:1
3) genotypes of individuals with dominant traits are studied
4) if the individual under study is heterozygous, then splitting is observed
5) the manifestation of traits is determined by several genes
Answer
© D.V. Pozdnyakov, 2009-2019
Task No. 1
Consider the proposed scheme. Write down the missing term in your answer, indicated by a question mark in the diagram.
Explanation: Let's consider a cross section of the stem of a woody plant.

The stem can be divided into 4 large parts: pith, wood, cambium and bark. The bark consists of bast (sieve tubes), peel and cork.
The correct answer is bark.
Task No. 2.
Below is a list of research methods. All of them, except two, are used in genetics. Find two methods that “fall out” from the general series and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1. Centrifugation
2. Hybridization
3. Karyotype analysis
4. Crossbreeding
5. Monitoring
Explanation: Among the listed methods, geneticists do not use only monitoring; this method is more related to zoology. The authors of the textbook from which we took this option consider centrifugation to be another non-genetic method, but the education of a biologist (and during my studies I studied methods of genetics, among other things) allows me to say with confidence that geneticists practically every day precipitate nucleic acids. acids by centrifugation. The correct answer is 5.
Task No. 3.
How many nucleotides make up the tRNA anticodon?
Explanation: An anticodon, like any codon, consists of three nucleotides.
The correct answer is 3.
Task No. 4.
All of the following characteristics, except two, can be used to determine the processes of the light phase of photosynthesis. Identify two characteristics that “drop out” from the general list, and write down in the table the numbers under which they are indicated.
1. Photolysis of water
2. Reduction of carbon dioxide to glucose
3. Synthesis of ATP molecules using the energy of sunlight
4. Formation of molecular oxygen
5. Use of the energy of ATP molecules for the synthesis of carbohydrates
Explanation: Here is a list of processes that occur during the light and dark phases of photosynthesis.
Light phase processes:
1. Chlorophyll activation
2. Photolysis of water
3. ATP synthesis
4. Creation of NADPH H2
5. Formation of free oxygen
Dark phase processes:
1. Carbon dioxide fixation
2. Glucose formation (Calvin cycle)
The correct answer is 25.
Task No. 5.
Establish a correspondence between the processes and the method of cell division: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column
Processes
A. Somatic cell division occurs
B. The chromosome set is halved
B. A new combination of genes is formed
D. Conjugation and crossing over occur
D. Bivalents are located along the equator of the cell
Division method
1. Mitosis
2. Meiosis
Explanation: meiosis is the process of formation of germ cells (from a diploid cell, four haploid cells are formed in two divisions). Mitosis is the process of division of somatic cells, in which two diploid cells are formed from one diploid cell, the process occurs without changing the DNA of the original cell. Therefore, we will classify the division of somatic cells as mitosis, and meiosis as the rest. Bivalents are pairs of homologous chromosomes connected by special proteins; this structure is formed during meiosis.
The correct answer is 12222.
Task No. 6.
What ratio of genotypes will be obtained by crossing two heterozygotes with complete dominance? Write the answer as a sequence of numbers in descending order.
Explanation: Let's take two heterozygotes: Aa and Aa and see what happens when they are crossed. The following genotype options are obtained: AA: 2Aa: aa. That is, let's write down - 211.
The correct answer is 211.
Task No. 7.
Below is a list of terms. All of them, except two, are used to describe genetic processes and phenomena. Find two terms that “fall out” from the general series and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table.
1. Polyploidy
2. Decomposer
3. Symbiosis
4. Homozygote
5. Karyotype
Explanation: The terms polyploidy, homozygote and karyotype refer to genetics. Polyploidy is a multiple increase in the number of chromosomes. Homozygote is an organism in which both alleles of a given trait are the same. A karyotype is a set of chromosomes that is individual for each type of living organism. And decomposer and symbiosis are concepts related to ecology. A decomposer breaks down organic substances into mineral ones, and symbiosis is a mutually beneficial relationship between living organisms. The correct answer is 23.
Task No. 8.
Establish a correspondence between the method of reproduction and a specific example: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column
Example
A. Fern sporulation
B. Formation of gametes by Chlamydomonas
B. Formation of spores in sphagnum
D. Yeast budding
D. Fish spawning
Reproduction method
1. Asexual
2. Sexual
Explanation: sporulation, both in ferns and in mosses (sphagnum), refers to the asexual type of reproduction, budding is also asexual reproduction, and the formation of gametes and the spawning of fish refer to sexual reproduction.
The correct answer is 12112.
Task No. 9.
1. Development of larvae in the host body
2. Sexual reproduction
3. The presence of a dense cuticle
4. The presence of bilateral body symmetry
5. Presence of a skin-muscle bag
6. Formation of a large number of eggs
Task No. 10.
Establish a correspondence between the characteristic and the kingdom of organisms: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column.
Characteristic
A. The cell wall contains chitin
B. Autotrophic nutrition type
B. Form organic substances from inorganic substances
D. The reserve nutrient is starch.
D. In natural systems they are decomposers
E. The body consists of mycelium
kingdom organisms
1. Mushrooms
2. Plants
Explanation: fungi are characterized by the following characteristics: the presence of chitin in the cell wall, the decomposition of organic substances to inorganic ones, that is, they are decomposers, and their body consists of mycelium. This means that plants include: autotrophy, starch as a reserve nutrient, the formation of organic substances from inorganic ones. The correct answer is 122211.
Task No. 11.
Establish the sequence of systematic categories used in classifying animals, starting with the smallest. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers in the table.
1. Tiger
2. Felines
3. Predatory
4. Mammals
5. Ussuri tiger
6. Chordates
Explanation:
Species - Ussuri tiger
Rod - tiger
Family - felines
Squad - predatory
Class - mammals
Type - chordates
The correct answer is 512346.
Task No. 12.
When the sympathetic nervous system is excited, as opposed to when the parasympathetic nervous system is excited
1. Arteries dilate
2. Blood pressure increases
3. Intestinal motility increases
4. The pupil narrows
5. Blood sugar increases
6. Heart contractions become more frequent
Explanation: the sympathetic and parasympathetic sections of the nervous system are antagonists, if the sympathetic nervous system dilates the pupil, increases pressure, narrows the arteries, increases the amount of sugar in the blood, increases heart rate, reduces intestinal motility, then the parasympathetic system, on the contrary, constricts the pupil, lowers pressure, dilates the arteries , reduces the amount of sugar in the blood, slows the heartbeat, enhances intestinal motility.
The correct answer is 256.
Task No. 13.
Establish a correspondence between the meaning of the reflex and its type: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column.
Reflex meaning
A. Provides instinctive behavior
B. Provides adaptation of the organism to the environmental conditions in which many generations of this species lived
B. Allows you to gain new experience gained throughout life
D. Determines the behavior of the organism in changed conditions
Type of reflex
1. Unconditional
2. Conditional
Explanation: First, let's understand the terminology. Reflex is the body’s response to the action of stimuli or the external environment. An unconditioned reflex is a reflex that is present in a species (or group of species) from birth, developed (reinforced from generation to generation (for example, sucking, swallowing, sneezing, etc.). The reflex arc of such reflexes primarily passes through the spinal cord. Conditioned reflex - a reflex that occurs in the human body (or animals) during life in a certain habitat, as an adaptation to this environment. Conditioned reflexes for each organism are individual and when moving to another territory (or when the reflex is not used) the reflex arc of such reflexes disappears. through the brain. Therefore, the correct answer is 1122.
Task No. 14.
In what order are the parts of the lower limb skeleton located in humans, starting with the pelvic girdle? Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers in the table.
1. Fingers
2. Metatarsus
3. Thigh
4. Shin
5. Tarsus
Explanation: Consider the skeleton of a human lower limb.

The correct answer is 34521.
Task No. 15.
Choose three correct answer options out of six and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table. What embryological evidence of evolution supports human kinship with other vertebrates?
1. Anlage of gill slits in the embryo
2. The presence of 46 chromosomes in the cells of the human embryo body
3. Development of the caudal region in the embryo
4. Presence of homologous organs
5. Development of vestigial organs
6. Division of the body into the head, trunk, and caudal sections
Explanation: The Haeckel-Müller biogenetic law says that ontogeny is a repetition of phylogeny, that is, in the process of embryonic development we go through all stages of evolution, from a single cell to a multicellular highly organized organism, at some stage we have a tail, gills, etc. . Therefore, embryonic evidence includes: the formation of gill slits, the development of the tail, and the division of the body into three sections (at the embryonic stage). The correct answer is 136.
Task No. 16.
Establish a correspondence between an example of the struggle for existence and the form to which this struggle relates: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column.
Example
A. Determination of nesting sites in the forest by crossbills
B. Use of cattle as a habitat by the bovine tapeworm
B. Competition between males for dominance
D. Replacement of a black rat by a gray rat
D. Fox hunting for field mice
Fight form
1. Intraspecific
2. Interspecific
Task No. 17.
Choose three correct answers out of six and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table.
What biotic factors can lead to an increase in the number of mouse-like rodents in a spruce forest?
1. Reduction in the number of owls, hedgehogs, foxes
2. Large harvest of spruce seeds
4. Tree cutting
5. Deep snow cover in winter
The correct answer is 126.
Task No. 18.
Establish a correspondence between a characteristic of the environment and its factor: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column.
Characteristic
A. Constancy of the gas composition of the atmosphere
B. Changing the thickness of the ozone screen
B. Change in air humidity
D. Change in the number of consumers
D. Change in the number of producers
Environmental factors
1. Biotic
2. Abiotic
The correct answer is 222111.
Task No. 19.
Establish the sequence of processes occurring during the reproduction and development of flowering plants, starting from the moment of pollen formation. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers in the table.
1. Penetration of sperm into the embryo sac
2. Formation of a triploid cell
3. Pollen tube germination
4. Formation of a seed from an ovule
5. Formation of generative and vegetative cells
Explanation: Let's arrange the processes in the correct order. It all starts with the formation of generative and vegetative cells, then the pollen tube grows, then the sperm penetrates the embryo sac, the sex cells fuse, a triploid cell is formed and, finally, the seed is formed from the ovule. The correct answer is 53124.
Task No. 20.
Analyze the table. Fill in the empty cells of the table using the concepts and terms, examples given in the list. For each lettered cell, select the appropriate term from the list provided.
List of terms and concepts:
1. Biological progress
2. The presence of webbed limbs in waterfowl
3. Presence of warm-bloodedness in chordates
4. Aromorphosis
5. Divergence
6. Biological regression
Correct answer: 142.
Task No. 21.
Study the graph of reaction rate versus enzyme concentration. Select statements that can be formulated based on the analysis of the proposed schedule. Write down the numbers of the selected statements in your answer.

1. The rate of an enzymatic reaction does not depend on the concentration of the enzyme
2. The rate of an enzymatic reaction depends significantly on the concentration of the enzyme
3. As the enzyme concentration increases, the reaction rate increases
Explanation: The graph shows that as the concentration of the enzyme increases, the reaction rate also increases, so answer options 2 and 3 are suitable for describing this dependence. The correct answer is 23.
Task No. 22.
It is known that when growing clover, soybeans, and beans, fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers is not required. Explain why.
Explanation: All of these plants are legumes, and nodule bacteria live in symbiosis with leguminous plants, which fix molecular nitrogen and process it into a form digestible by plants.
Task No. 23.
Using a drawing of the process of sexual reproduction of Chlamydomonas, explain the essence of sexual reproduction and how it differs from asexual reproduction. As a result of what process are gametes formed, what are their features? What number in the picture indicates the zygote? How is it different from gametes?

Explanation: during asexual reproduction, the contents of a single-celled Chlamydomonas are divided into 4 parts using meiosis, resulting in the formation of zoospores, which perform the function of dispersal, then small cells grow to the size of the mother cell and divide again by meiosis. And in unfavorable conditions, sexual reproduction occurs, and biflagellate gametes are formed in the mother cell (3), they leave the mother cell and merge in pairs with other individuals, the zygote is covered with a dense shell and overwinters (survives unfavorable conditions), then the zygote divides, as a result which results in the formation of 4 diploid chlamydomonas, which grow to maternal size.
The zygote in the figure is indicated by the number 5. It differs from haploid gametes in its diploidity.
Task No. 24.
Find errors in the given text. Indicate the numbers of the sentences in which errors were made and correct them.
1. The body of the cockchafer, covered with skin and cuticle, is divided into the head, trunk and abdomen. 2. The digestive system of beetles begins on the head with a mouth opening with a piercing mouthpart. 3. Metabolic products are secreted through green glands. 4. Gas exchange occurs directly through the walls of the trachea. 5. The open circulatory system consists of the heart and blood vessels.
Explanation: sentence 1 - the body of the cockchafer is not covered with skin with a cuticle, but with a chitinous covering, and it is divided into the head, chest and abdomen. Sentence 2 - the mouthparts of the May tongue are not piercing, but gnawing. Proposition 3 - green glands are not organs of the excretory system, since the metabolic products of the cockchafer are secreted through the Malpighian vessels and the fat body.
Task No. 25.
Explain what organ of a flowering plant a head of cabbage is a modification of.
Explanation: a head of cabbage is a modified bud, since in the second year of life an adult plant is formed from the head of cabbage, which has all the generative organs, that is, a flower and fruits with seeds. Also, a head of cabbage resembles a bud in structure: the stump is a modified stem, with thick leaves and rudimentary buds located on it.
Task No. 26.
Which ecosystem, a potato field or a meadow, has longer and more diverse food chains? Explain your answer.
Explanation: a potato field is an artificial ecosystem, and a meadow is a natural ecosystem. Longer and more diverse food chains are found in a natural ecosystem, since there are more plants, animals and microorganisms in the meadow and monoculture (potatoes) does not predominate.
Task No. 27.
All types of RNA are synthesized on a DNA template. The fragment of the DNA molecule on which the region of the central loop of tRNA is synthesized has the following nucleotide sequence: CTTACGGGGCATGGCT. Establish the nucleotide sequence of the tRNA region that is synthesized on this fragment if the third triplet corresponds to the tRNA anticodon. Explain your answer.
Explanation: Based on the given sequence of nucleotides in DNA, we will find the sequence of tRNA nucleotides. We will use the principle of complementarity: A=U, G=C.
tRNA: GAAOGCCCCGUACCCGA
The third triplet - CCG corresponds to the mRNA - GGC.
Task No. 28.
A man suffering from deafness and color blindness married a healthy woman. They had a son who was deaf and colorblind and a daughter who had good hearing but was colorblind. In humans, deafness is an autosomal, recessive trait, while color blindness is a recessive trait, linked to sex. Make a diagram for solving the problem. Indicate the possible phenotypes and genotypes of children in this family. Determine the probability of having children suffering from both anomalies.
Explanation:
aa - deaf
Aa, AA - not deaf (carries the deafness gene in the second case)
X D X d - healthy mother (carries the color blindness gene)
X d Y - sick father
АаХ D X d x ааX d Y
Gametes: AX D, aX D, AX d, aX d x aX d, aY
Possible gentypes of children:
Girls:
AaX D X d - normal hearing, normal vision (healthy child)
ааX D X d - deaf, normal vision
AaX d X d - normal hearing, colorblind
aaX d X d - deaf, color blind
Boys:
AaX D Y - normal hearing, normal vision (healthy child)
АаX D Y - deaf, normal vision
AaX d Y - normal hearing, colorblind
AaX d Y - deaf, colorblind
Among boys, the probability of having both anomalies is 1/4, and among girls too, that is, 25%.
G.S. Kalinova, T. V. Mazyarkina Biology Typical test tasks. Unified State Exam 2017. 10 options.